|
Precedence Graph
A precedence graph, also named conflict graph and serializability graph, is used in the context of concurrency control in databases. It is the directed graph representing precedence of transactions in the schedule, as reflected by precedence of conflicting operations in the transactions. A schedule is ''conflict-serializable'' if and only if its precedence graph of ''committed transactions'' is '' acyclic''. The precedence graph for a schedule S contains: * A node for each committed transaction in S * An arc from Ti to Tj if an action of Ti precedes and conflicts with one of Tj's actions. That is the actions belong to different transactions, at least one of the actions is a write operation, and the actions access the same object (read or write). Cycles of committed transactions can be prevented by aborting an ''undecided'' (neither committed, nor aborted) transaction on each cycle in the precedence graph of all the transactions, which can otherwise turn into a cycle of committed tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
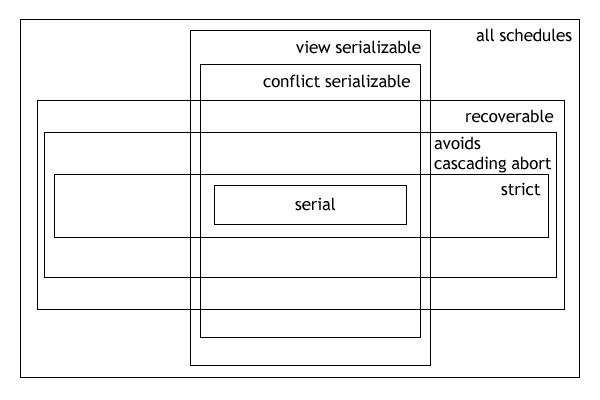 |
Serializability
In the fields of databases and transaction processing (transaction management), a schedule (or history) of a system is an abstract model to describe the order of executions in a set of transactions running in the system. Often it is a ''list'' of operations (actions) ordered by time, performed by a set of transactions that are executed together in the system. If the order in time between certain operations is not determined by the system, then a ''partial order'' is used. Examples of such operations are requesting a read operation, reading, writing, aborting, committing, requesting a lock, locking, etc. Often, only a subset of the transaction operation types are included in a schedule. Schedules are fundamental concepts in database concurrency control theory. In practice, most general purpose database systems employ conflict-serializable and strict recoverable schedules. Notation Grid notation: * Columns: The different transactions in the schedule. * Rows: The time order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Concurrency Control
In information technology and computer science, especially in the fields of computer programming, operating systems, multiprocessors, and databases, concurrency control ensures that correct results for concurrent operations are generated, while getting those results as quickly as possible. Computer systems, both software and hardware, consist of modules, or components. Each component is designed to operate correctly, i.e., to obey or to meet certain consistency rules. When components that operate concurrently interact by messaging or by sharing accessed data (in memory or storage), a certain component's consistency may be violated by another component. The general area of concurrency control provides rules, methods, design methodologies, and theories to maintain the consistency of components operating concurrently while interacting, and thus the consistency and correctness of the whole system. Introducing concurrency control into a system means applying operation constraints ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an application associated with the database. Before digital storage and retrieval of data have become widespread, index cards were used for data storage in a wide range of applications and environments: in the home to record and store recipes, shopping lists, contact information and other organizational data; in business to record presentation notes, project research and notes, and contact information; in schools as flash c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
If And Only If
In logic and related fields such as mathematics and philosophy, "if and only if" (often shortened as "iff") is paraphrased by the biconditional, a logical connective between statements. The biconditional is true in two cases, where either both statements are true or both are false. The connective is biconditional (a statement of material equivalence), and can be likened to the standard material conditional ("only if", equal to "if ... then") combined with its reverse ("if"); hence the name. The result is that the truth of either one of the connected statements requires the truth of the other (i.e. either both statements are true, or both are false), though it is controversial whether the connective thus defined is properly rendered by the English "if and only if"—with its pre-existing meaning. For example, ''P if and only if Q'' means that ''P'' is true whenever ''Q'' is true, and the only case in which ''P'' is true is if ''Q'' is also true, whereas in the case of ''P if Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Directed Acyclic Graph
In mathematics, particularly graph theory, and computer science, a directed acyclic graph (DAG) is a directed graph with no directed cycles. That is, it consists of vertices and edges (also called ''arcs''), with each edge directed from one vertex to another, such that following those directions will never form a closed loop. A directed graph is a DAG if and only if it can be topologically ordered, by arranging the vertices as a linear ordering that is consistent with all edge directions. DAGs have numerous scientific and computational applications, ranging from biology (evolution, family trees, epidemiology) to information science (citation networks) to computation (scheduling). Directed acyclic graphs are also called acyclic directed graphs or acyclic digraphs. Definitions A graph is formed by vertices and by edges connecting pairs of vertices, where the vertices can be any kind of object that is connected in pairs by edges. In the case of a directed graph, each edg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Database Transaction Schedule
In the fields of databases and transaction processing (transaction management), a schedule (or history) of a system is an abstract model to describe the order of Execution (computing), executions in a set of transactions running in the system. Often it is a ''list'' of operations (actions) ordered by time, performed by a set of Database transaction, transactions that are executed together in the system. If the order in time between certain operations is not determined by the system, then a ''partial order'' is used. Examples of such operations are requesting a read operation, reading, writing, aborting, Commit (data management), committing, requesting a Lock (computer science), lock, locking, etc. Often, only a subset of the transaction operation types are included in a schedule. Schedules are fundamental concepts in database concurrency control theory. In practice, most general purpose database systems employ conflict-serializable and strict recoverable schedules. Notation Gri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Serializability
In the fields of databases and transaction processing (transaction management), a schedule (or history) of a system is an abstract model to describe the order of executions in a set of transactions running in the system. Often it is a ''list'' of operations (actions) ordered by time, performed by a set of transactions that are executed together in the system. If the order in time between certain operations is not determined by the system, then a ''partial order'' is used. Examples of such operations are requesting a read operation, reading, writing, aborting, committing, requesting a lock, locking, etc. Often, only a subset of the transaction operation types are included in a schedule. Schedules are fundamental concepts in database concurrency control theory. In practice, most general purpose database systems employ conflict-serializable and strict recoverable schedules. Notation Grid notation: * Columns: The different transactions in the schedule. * Rows: The time order of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Precedence Graph
A precedence graph, also named conflict graph and serializability graph, is used in the context of concurrency control in databases. It is the directed graph representing precedence of transactions in the schedule, as reflected by precedence of conflicting operations in the transactions. A schedule is ''conflict-serializable'' if and only if its precedence graph of ''committed transactions'' is '' acyclic''. The precedence graph for a schedule S contains: * A node for each committed transaction in S * An arc from Ti to Tj if an action of Ti precedes and conflicts with one of Tj's actions. That is the actions belong to different transactions, at least one of the actions is a write operation, and the actions access the same object (read or write). Cycles of committed transactions can be prevented by aborting an ''undecided'' (neither committed, nor aborted) transaction on each cycle in the precedence graph of all the transactions, which can otherwise turn into a cycle of committed tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Abraham Silberschatz
Avi Silberschatz (; born in Haifa, Israel) is an Israeli computer scientist and researcher. He is known for having authored many influential texts in computer science. He finished high school at the Hebrew Reali School in Haifa and graduated in 1976 with a Ph.D. in computer science from the State University of New York (SUNY) at Stony Brook. His research interests include database systems, operating systems, storage systems, and network management. He held a professorship at the University of Texas at Austin, where he taught until 1993. He became a professor at Yale University in 2005, where he was the chair of the Computer Science department from 2005 to 2011. Prior to coming to Yale in 2003, Silberschatz worked at the Bell Labs. Awards and recognition Silberschatz was elected an ACM Fellow in 1996 and received the Karl V. Karlstrom Outstanding Educator Award in 1998. He was elected an IEEE The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Henry Korth
Henry may refer to: People and fictional characters * Henry (given name), including lists of people and fictional characters * Henry (surname) * Henry, a stage name of François-Louis Henry (1786–1855), French baritone Arts and entertainment * ''Henry'' (2011 film), a Canadian short film * ''Henry'' (2015 film), a virtual reality film * '' Henry: Portrait of a Serial Killer'', a 1986 American crime film * ''Henry'' (comics), an American comic strip created in 1932 by Carl Anderson * "Henry", a song by New Riders of the Purple Sage Places Antarctica * Henry Bay, Wilkes Land Australia *Henry River (New South Wales) *Henry River (Western Australia) Canada * Henry Lake (Vancouver Island), British Columbia * Henry Lake (Halifax County), Nova Scotia * Henry Lake (District of Chester), Nova Scotia New Zealand * Lake Henry (New Zealand) * Henry River (New Zealand) United States * Henry, Illinois * Henry, Indiana * Henry, Nebraska * Henry, South Dakota * Henry County (disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Database Management Systems
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an application associated with the database. Before digital storage and retrieval of data have become widespread, index cards were used for data storage in a wide range of applications and environments: in the home to record and store recipes, shopping lists, contact information and other organizational data; in business to record presentation notes, project research and notes, and contact information; in schools as flash card ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |