|
Pre-Islamic Arabian Christianity
Christianity was one of the major religions of pre-Islamic Arabia. It was likely introduced in the fourth century, during the period of Late Antiquity, and had achieved a large presence by the fifth century. Bishoprics were established in multiple areas in Eastern Arabia, as well as in Arabia Petraea, Najran, and Zafar. Churches, martyria and monasteries were constructed across the peninsula, allowing local leaders to display their benefaction in the region, communicate with locals and with local officials, and to establish points of contact with Byzantine representatives. Christian proselytism also happened throughout the peninsula, especially in its northwest and southwest. Northern proselytization was driven by Syrian Christian missionaries, and the south, by Ethiopian Christians in the aftermath of the Ethiopian conquest of the South Arabian Kingdom of Himyar. Many conversion stories of Arabs are found in Byzantine Christian literature, especially those with a Syrian and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose coming as the Messiah#Christianity, messiah (Christ (title), Christ) was Old Testament messianic prophecies quoted in the New Testament, prophesied in the Old Testament and chronicled in the New Testament. It is the Major religious groups, world's largest and most widespread religion with over 2.3 billion followers, comprising around 28.8% of the world population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in Christianity by country, 157 countries and territories. Christianity remains Christian culture, culturally diverse in its Western Christianity, Western and Eastern Christianity, Eastern branches, and doctrinally diverse concerning Justification (theology), justification and the natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polytheism
Polytheism is the belief in or worship of more than one god. According to Oxford Reference, it is not easy to count gods, and so not always obvious whether an apparently polytheistic religion, such as Chinese folk religions, is really so, or whether the apparent different objects of worship are to be thought of as manifestations of a singular divinity. Polytheistic belief is usually assembled into a pantheon of gods and goddesses, along with their own religious sects and rituals. Polytheism is a type of theism. Within theism, it contrasts with monotheism, the belief in a singular god who is, in most cases, transcendent. In religions that accept polytheism, the different gods and goddesses may be representations of forces of nature or ancestral principles; they can be viewed either as autonomous or as aspects or emanations of a creator deity or transcendental absolute principle ( monistic theologies), which manifests immanently in nature (panentheistic and pantheistic theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyril Of Scythopolis
Cyril of Scythopolis (; – ), also known as Cyrillus Scythopolitanus, was a Christian monk, priest and Greek-language hagiographer or historian of monastic life in Palestine in the 6th century AD. Life Cyril was born in Scythopolis, in the province of Palaestina Secunda, sometime around 525. His father John, a lawyer, supervised his early religious education. Shortly after 532 he became an '' anagnostes'' (lector), and became a monk in 543. Very soon thereafter he went to Jerusalem and spent some months at a hermit community ('' lavra'') near the Jordan River, before entering the monastery of Euthymius the Great at Jericho in 544. He remained there until 555, when he was one of the orthodox monks sent to replace those expelled for Origenism at the New Lavra of Saint Sabas (today in ruins at Bir el-Wa'ar near Teqoa). Two years later he moved to the Great Lavra of Saint Sabas (today known as Mar Saba), where he died sometime in 557/558 or soon after. Cyril was influenced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus (mythology)
Venus (; ) is a Roman goddess whose functions encompass love, beauty, desire, sex, fertility, prosperity, and victory. In Roman mythology, she was the ancestor of the Roman people through her son, Aeneas, who survived the fall of Troy and fled to Italy. Julius Caesar claimed her as his ancestor. Venus was central to many religious festivals, and was revered in Roman religion under numerous cult titles. The Romans adapted the myths and iconography of her Greek counterpart Aphrodite for Roman art and Latin literature. In the later classical tradition of the West, Venus became one of the most widely referenced deities of Greco-Roman mythology as the embodiment of love and sexuality. As such, she is usually depicted nude. Etymology The Latin theonym and the common noun ('love, charm') stem from a Proto-Italic form reconstructed as ''*wenos-'' ('desire'), itself from Proto-Indo-European (PIE) ' ('desire'; cf. Messapic , Old Indic 'desire'). Derivatives include ''venust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dead Sea
The Dead Sea (; or ; ), also known by #Names, other names, is a landlocked salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east, the Israeli-occupied West Bank to the west and Israel to the southwest. It lies in the endorheic basin of the Jordan Rift Valley, and its main tributary is the Jordan River. As of 2025, the lake's surface is below sea level, making its shores the Lowest elevations, lowest land-based elevation on Earth. It is deep, the deepest hypersaline lake in the world. With a salinity of 342 g/kg, or 34.2% (in 2011), it is one of the List of bodies of water by salinity, world's saltiest bodies of water, 9.6 times as Seawater#Salinity, salty as the ocean—and has a density of 1.24 kg/litre, which makes swimming similar to Buoyancy, floating. This salinity makes for a harsh environment in which plants and animals cannot flourish, hence its name. The Dead Sea's main, northern basin is long and wide at its widest point. The Dead Sea has attracted visitors from around th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
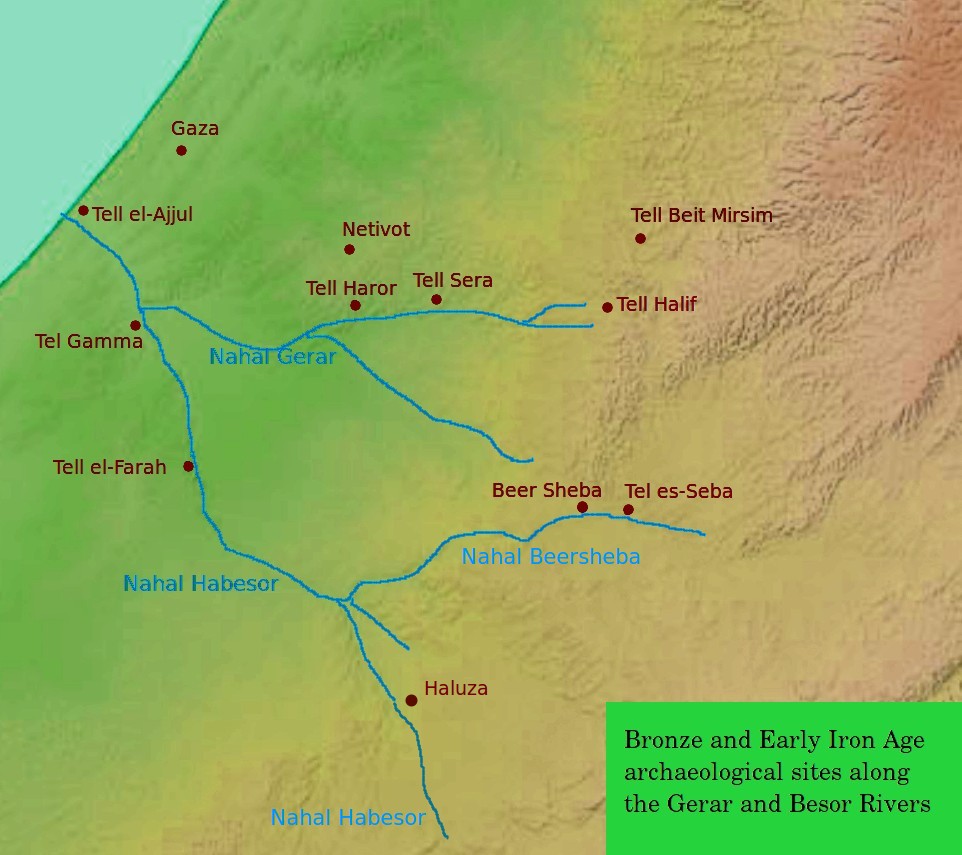
Elusa (Haluza)
The ancient city of Halasa or Chellous (), Elusa () in the Byzantine period, was a city in the Negev near present-day Kibbutz Mash'abei Sadeh that was once part of the Nabataean Incense Route. It lay on the route from Petra to Gaza.Carta's Official Guide to Israel, 1983. Today it is known as Haluza (), and during periods of Arab habitation it was known as al-Khalūṣ (; Early Muslim period) and Al-Khalasa (; 20th century). In the 5th century it was surrounded by vineyards and was famous for its wines. Due to its historic importance, UNESCO declared Haluza a World Heritage Site along with Mamshit, Avdat and Shivta. Name in ancient sources The city is called 'Chellous' (Χελλοὺς) in the Greek text of Judith, i, 9 (seJdt 1:9in NABRE), a work probably dating to the 1st century BCE. It is also mentioned in the 2nd century CE by Ptolemy, Peutinger's Table, Stephanus Byzantius (fl. 6th century; as being formerly in the province of Arabia Petraea, but "now" in Palaestin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilarion
Hilarion (291–371), also known by the bynames of Thavata, of Gaza, and in the Orthodox Church as the Great was a Christian anchorite who spent most of his life in the desert according to the example of Anthony the Great (c. 251–356). While Anthony is considered to have established Christian monasticism in the Western Desert (Egypt), Egyptian Desert, Hilarion, who lived in the Israeli Coastal Plain, coastal area near Gaza City, Gaza, is considered by his biographer Jerome (c. 342/347 – 420), to be the founder of Palaestina Prima, Palestinian monasticism - regarding this claim see also Hilarion's contemporary, Chariton the Confessor , Chariton (mid-3rd century – c. 350), founder of monasticism in the Judaean Desert. Hilarion is venerated as a saint exemplifying monastic virtues by the Eastern Orthodox Church, Oriental Orthodox Church and the Roman Catholic Church. Biography Origin and life as a hermit Hilarion was born around 291 to pagan parents in Tabatha, a village ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerome
Jerome (; ; ; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was an early Christian presbyter, priest, Confessor of the Faith, confessor, theologian, translator, and historian; he is commonly known as Saint Jerome. He is best known for his translation of the Bible into Latin (the translation that became known as the Vulgate) and his commentaries on the whole Bible. Jerome attempted to create a translation of the Old Testament based on a Hebrew version, rather than the Septuagint, as Vetus Latina, prior Latin Bible translations had done. His list of writings is extensive. In addition to his biblical works, he wrote polemical and historical essays, always from a theologian's perspective. Jerome was known for his teachings on Christian moral life, especially those in cosmopolitan centers such as Rome. He often focused on women's lives and identified how a woman devoted to Jesus should live her life. This focus stemmed from his close patron relationships with several pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghassanids
The Ghassanids, also known as the Jafnids, were an Tribes of Arabia, Arab tribe. Originally from South Arabia, they migrated to the Levant in the 3rd century and established what would eventually become a Christian state, Christian kingdom under the aegis of the Byzantine Empire. However, some of the Ghassanids may have already adhered to Christianity before they emigrated from South Arabia to escape religious persecution. As a Byzantine vassal, the Ghassanids participated in the Roman–Persian Wars, Byzantine–Sasanian Wars, fighting against the Sasanian Empire, Sasanian-allied Lakhmid kingdom, Lakhmids, who were also an Arabian tribe, but adhered to the non-Chalcedonian Church of the East. The lands of the Ghassanids also acted as a buffer zone protecting lands that had been annexed by the Romans against raids by Bedouins. After just over 400 years of existence, the Ghassanid kingdom fell to the Rashidun Caliphate during the Muslim conquest of the Levant. A few of the tribe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Mundhir III Ibn Al-Harith
Al-Mundhir ibn al-Ḥārith (), known in Byzantine sources as Flavios Alamoundaros (), was the king of the Ghassanid Arabs from 569 to circa 581. A son of al-Harith ibn Jabalah, he succeeded his father both in the kingship over his tribe and as the chief of the Byzantine Empire's Arab clients and allies in the East, with the rank of '' patricius''. Despite his victories over the rival Persian-backed Lakhmids, throughout Mundhir's reign his relations with Byzantium were lukewarm due to his staunch Miaphysitism. This led to a complete breakdown of the alliance in 572, after Mundhir discovered Byzantine plans to assassinate him. Relations were restored in 575 and Mundhir secured from the Byzantine emperor both recognition of his royal status and a pledge of tolerance towards the Miaphysite Church. In 580 or 581, Mundhir participated in an unsuccessful campaign against the Persian capital, Ctesiphon, alongside the Byzantine general (and future emperor) Maurice. The failure of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resafa
Resafa (), sometimes spelled Rusafa, and known in the Byzantine era as Sergiopolis ( or , ) and briefly as Anastasiopolis (, ), was a city located in the Roman province of Euphratensis, in modern-day Syria. It is an archaeological site situated southwest of the city of Raqqa and the Euphrates. Procopius describes at length the ramparts and buildings erected there by Justinian. The walls of Resafa, which are still well preserved, are over 1600 feet in length and about 1000 feet in width; round or square towers were erected about every hundred feet; there are also ruins of a church with three apses. Names Resafa corresponds to the Akkadian ''Raṣappa'' and the Biblical ''Rezeph'' (Septuagint; ), where it is mentioned in ; cuneiform sources give Rasaappa, Rasappa, and Rasapi. Ptolemy calls it ''Rhesapha'' (). In the late Roman '' Tabula Peutingeriana'', it is called ''Risapa''. Catholic Encyclopedia (1907), ''loc.cit.'' In the '' Notitia dignitatum'', it is ''Rosafa''. Proco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
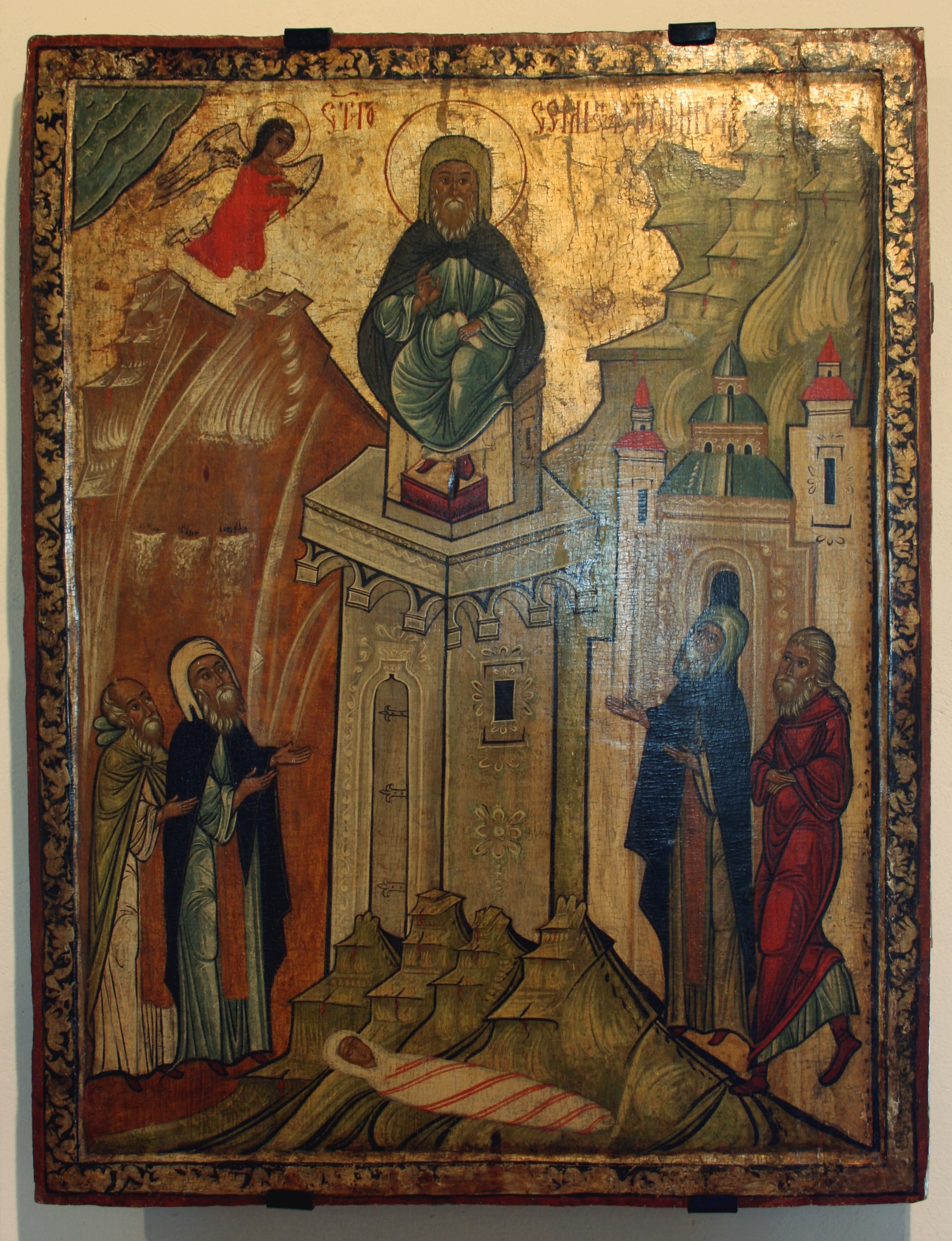
Simeon Stylites
Simeon Stylites or Symeon the Stylite ', Koine Greek ', ' (Greek language, Greek: Συμεών ό Στυλίτης; ; 2 September 459) was a Syrian Asceticism#Christianity, Christian ascetic, who achieved notability by living 36 years on a small platform on top of a pillar near Aleppo (in modern Syria). Several other stylites later followed his model (the Greek language, Greek word ''style'' means "pillar"). Simeon is venerated as a saint by the Eastern Catholic Churches, Oriental Orthodox Churches, Eastern Orthodox Church, and Roman Catholic Church. He is known formally as Simeon Stylites the Elder to distinguish him from Simeon Stylites the Younger, Simeon Stylites III and Symeon Stylites of Lesbos. Sources There exist three major early biographies of Simeon. The first of these is by Theodoret, bishop of Cyrrhus, and is found within his work ''Religious History''. This biography was written during Simeon's lifetime, and Theodoret relates several events of which he claims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |