|
Praetorian Prefecture Of Italy
The praetorian prefecture of Italy (, in its full form (until 356) ) was one of four praetorian prefectures into which the Late Roman Empire was divided since the first half of the 4th century. It comprised the Italian peninsula, the western Balkans, the upper Danube, Danubian provinces and parts of North Africa. The Prefecture's seat moved from Rome to Mediolanum, Milan and finally, Ravenna. It existed during the Later Roman Empire, and was part of the Western Roman Empire. The prefecture continued to function within Odoacer's and Ostrogothic Kingdom, Ostrogothic kingdoms, and later within the Byzantine Empire, up to 584, when it was reorganized into the Exarchate of Ravenna. Structure and history The prefecture was established in the division of the Empire after the death of Constantine the Great in 337, and was made up of Roman diocese, dioceses. Initially these were the Diocese of Africa, the Roman Italy#Diocletian re-organization, Diocese of Italy, the Diocese of Pannonia, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetorian Prefecture
The praetorian prefecture (; in Ancient Greek, Greek variously named ) was the largest administrative division of the Late Antiquity, late Roman Empire, above the mid-level Roman diocese, dioceses and the low-level Roman province, provinces. Praetorian prefectures originated in the reign of Constantine I (r. 306–337), reaching their more or less final form in the last third of the 4th century and surviving until the 7th century, when the reforms of Heraclius diminished the prefecture's power, and the Early Muslim conquests, Muslim conquests forced the East Roman Empire, Eastern Roman Empire to adopt the new theme system. Elements of the prefecture's administrative apparatus, however, are documented to have survived in the Byzantine Empire until the first half of the 9th century. History The office of the praetorian prefect had a long history dating back to the origins of the Roman Empire: initially, its two holders were the commanders of the Praetorian Guard, but gradually, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odoacer
Odoacer ( – 15 March 493 AD), also spelled Odovacer or Odovacar, was a barbarian soldier and statesman from the Middle Danube who deposed the Western Roman child emperor Romulus Augustulus and became the ruler of Italy (476–493). Odoacer's overthrow of Romulus Augustulus is traditionally understood as marking the end of the Western Roman Empire. Although he held power over Italy, he also represented himself as the client of the Eastern Roman Emperor in Constantinople, Zeno. He was referred to not only as a king (), but also as commander (), or using the Roman honorific patrician, granted by Zeno. Odoacer himself used the title of king in the only surviving official document that emanated from his chancery, and it was also used by the consul Basilius. He had the support of the Roman Senate and was able to distribute land to his followers without much opposition. Unrest among his soldiers led to violence in 477–478, but no such disturbances occurred during the later p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
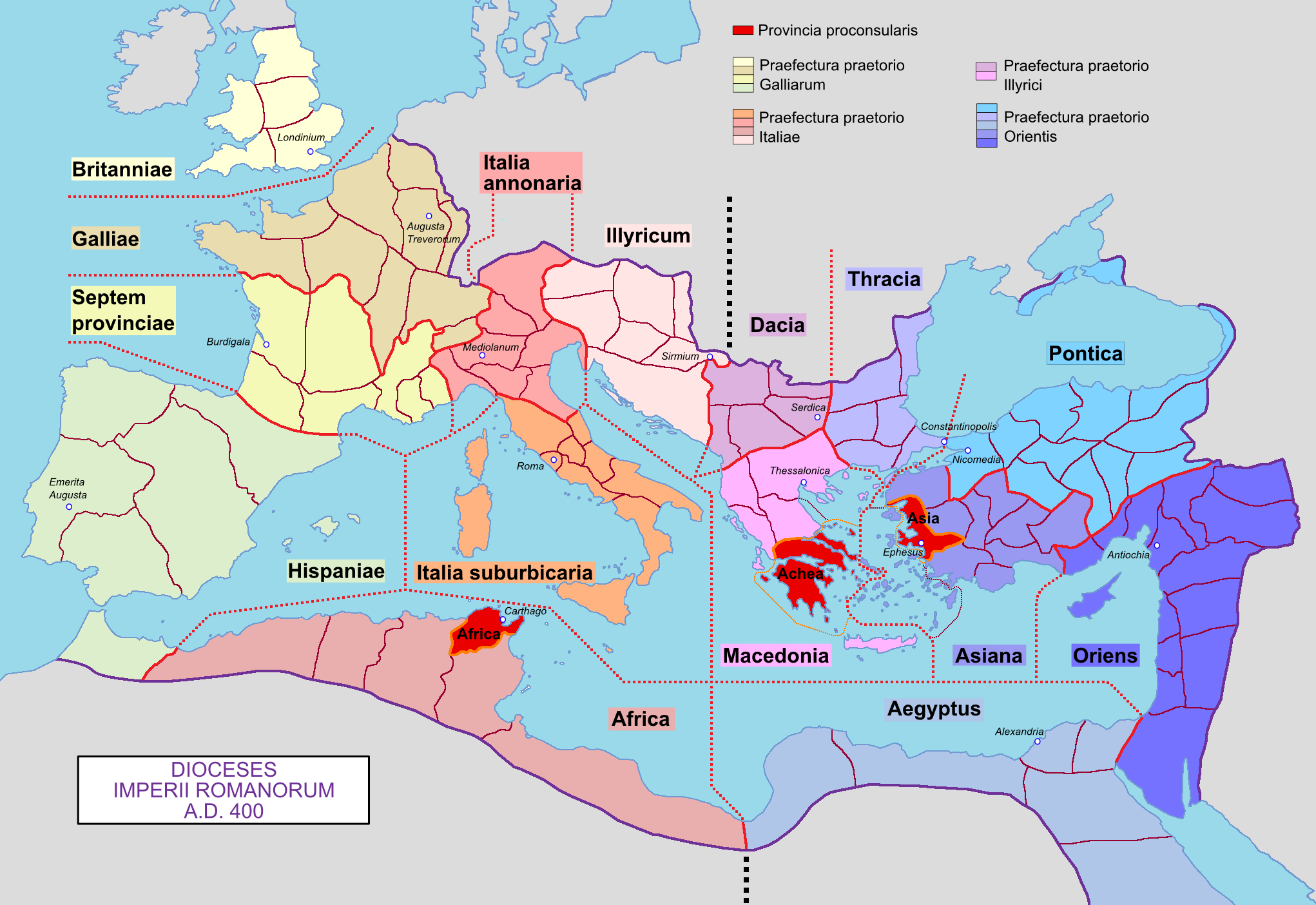
Roman Italy - AD 400
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of Roman civilization *Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter written by Paul, found in the New Testament of the Christian Bible * Ar-Rum (), the 30th sura of the Quran. Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music *Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *"Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television *Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People *Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters *Roman (surname), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Annonarian Italy
Roman Italy is the period of ancient Italian history going from the founding and rise of Rome to the decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire; the Latin name of the Italian peninsula in this period was ''Italia'' (continued to be used in the Italian language)."Roman Italy" ''.'' May 2025 According to , Italy was the ancestral home of , being the homeland of the |
Diocese Of Suburbicarian Italy
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into dioceses based on the civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situation must have hardly survived Julian, 361–363. Episcopal courts are not heard of again in the East until 398 and in the West in 408. The quality of these courts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Moesia
The Diocese of Moesia (, ) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, in the area of modern western Bulgaria, central Serbia, Montenegro, Albania, North Macedonia, and Greece. History The Diocese of Moesia was one of the twelve dioceses in which Diocletian (284–305) divided the Roman Empire during his administrative reforms. It encompassed most of the ancient Greek and Illyrian lands, stretching from the Crete to Danube. During the time of Tetrarchy, the diocese was under the jurisdiction of ''Caesar'' Galerius who kept it under his own control during much of his reign as ''Augustus'' (305-311). He died and was buried in the city of Felix Romuliana, on the territory of the Diocese of Moesia. The diocese was later split in two, forming the Diocese of Macedonia in the south and the Diocese of Dacia in the north, probably under Constantine I (r. 306–337), although the division is not attested until ca. 370. The two new dioceses were grouped into the new praetorian prefectur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Macedonia
The Diocese of Macedonia (; ) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, forming part of the praetorian prefecture of Illyricum. Its administrative centre was Thessalonica. History The diocese was formed, probably under Constantine I (r. 306–337), from the division of the Diocletianic Diocese of Moesia. It included the provinces of Macedonia Prima, Macedonia Salutaris, Thessalia, Epirus vetus, Epirus nova, Achaea, and Crete. Alongside Dacia and, until 379, Pannonia, it made up the Prefecture of Illyricum. In 379, Pannonia was detached and merged into the Praetorian prefecture of Italy and Thessaloniki became the Prefecture's new capital city instead of Sirmium. See also *Macedonia (terminology) * Macedonia (Roman province) * Macedonia (theme) Sources * ''Notitia dignitatum The (Latin for 'List of all dignities and administrations both civil and military') is a document of the Late Roman Empire that details the administrative organization of the Western and the Eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Dacia
The Diocese of Dacia () was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, in the area of modern western Bulgaria, central Serbia, Montenegro, Kosovo, northern Albania and northern North Macedonia. It was subordinate to the Praetorian prefecture of Illyricum. Its capital was at Serdica (modern Sofia). History Origin of the name Emperor Aurelian (270-275), confronted with the secession of Gallia and Hispania from the empire since 260, with the advance of the Sassanids in Asia, and the devastations that the Carpians and the Goths had created in Moesia and Illyria, abandoned the province of Dacia created by Trajan and withdrew his troops altogether, fixing the Roman frontier at the Danube. A new '' Dacia Aureliana'' was organised south of the Danube out of central Moesia, with its capital at Serdica. The abandonment of ''Dacia Traiana'' by the Romans is mentioned by Eutropius in his ''Breviarium historiae Romanae'', book IX : Creation During the administrative reforms of Diocl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Pannonia
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into dioceses based on the civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situation must have hardly survived Julian, 361–363. Episcopal courts are not heard of again in the East until 398 and in the West in 408. The quality of these courts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Italy
Roman Italy is the period of ancient Italian history going from the founding of Rome, founding and Roman expansion in Italy, rise of ancient Rome, Rome to the decline and fall of the Western Roman Empire; the Latin name of the Italian peninsula in this period was ''Italia'' (continued to be used in the Italian language)."Roman Italy" ''Encyclopædia Britannica.'' May 2025 According to Roman mythology, Italy was the ancestral home of Aeneas, being the homeland of the Troy, Trojans progenitor, Dardanus (son of Zeus), Dardanus; Aeneas, instructed by Jupiter (god), Jupiter, moved to Italy after the fall of Troy, and his descendants, Romulus and Remus, were the founding of Rome, founders of Rome. Aside from the legendary accounts, Rome was an Italic city-state that changed its form of government from Roman Kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Africa
The Diocese of Africa () was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of North Africa, except Mauretania Tingitana. Its seat was at Carthage, and it was subordinate to the Praetorian prefecture of Italy. The diocese included the provinces of Africa proconsularis (also known as Zeugitana), Byzacena, Mauretania Sitifensis, Mauretania Caesariensis, Numidia Cirtensis, Numidia Militiana and Tripolitania. In current geo-political terms, the Diocese of Africa included the entire coastline of Tunisia, Algeria with some mountainous hinterlands, plus the western half of Libya's coastline. The diocese existed from the time of the Diocletianian and Constantinian reforms in the last years of the 3rd century until it was overrun by the Vandals in the 430s. The provincial organization were retained under the Vandals, and after their defeat and the reconquest of Africa by the Eastern Roman Empire in the Vandalic War, they were grouped anew, but this time in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Diocese
In the Late Roman Empire, usually dated 284 AD to 641 AD, the regional governance district known as the Roman or civil diocese was made up of a grouping of provinces each headed by a '' Vicarius'', who were the representatives of praetorian prefects (who governed directly the dioceses they were resident in). There were initially twelve dioceses, rising to fourteen by the end of the 4th century. The term ''diocese'' comes from the , which derives from the ('' διοίκησις'') meaning "administration", "management", "assize district", or "group of provinces". Historical development Tetrarchy (286–305) Two major reforms to the administrative divisions of the empire were undertaken during the Tetrarchy. The first of these was the multiplication of the number of provinces, which had remained largely unchanged since the time of Augustus, from 48 at the beginning of Diocletian's reign to around a hundred by the time of his abdication. The multiplication of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |