|
Praefectus
''Praefectus'', often with a further qualification, was the formal title of many, fairly low to high-ranking, military or civil officials in the Roman Empire, whose authority was not embodied in their person (as it was with elected Magistrates) but conferred by delegation from a higher authority. They did have some authority in their prefecture, such as controlling prisons and in civil administration. Praetorian prefects The Praetorian prefect (''Praefectus praetorio'') began as the military commander of a general's guard company in the field, then grew in importance as the Praetorian Guard became a potential kingmaker during the Empire. From the Emperor Diocletian's tetrarchy (c. 300) they became the administrators of the four Praetorian prefectures, the government level above the (newly created) dioceses and (multiplied) provinces. Police and civil prefects *'' Praefectus urbi'', or '' praefectus urbanus'': city prefect, in charge of the administration of Rome. *'' Praefec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praefectus Vigilum
The ''praefectus vigilum'' (, pl.: ''praefecti vigilum'') was, starting with the reign of the Emperor Augustus, the commander of the city guards in Rome (''cohortes vigilum'' or ''vigiles''), whom were responsible for maintaining peace and order at night--a kind of fire and security police. Although less important than the other prefects, the office was considered a first step in order to reach an important position in the imperial administration. Description Headquarters The offices of the ''praefectus vigilum'' were located in the ''Campus Martius'', perhaps in the quadriportico of the theatre of Balbus (along the '' via Lata''), inside the barracks of the First Cohort of ''Vigiles'' ().Lefebvre (2011), p. 185 The reason to think that is that all the dedications found in the remains of these barracks are inscribed in the name of the prefect.Homo (1971), p. 164 It was in this building that the ''praefectus vigilum'' had his offices and his courtroom and it was from there t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
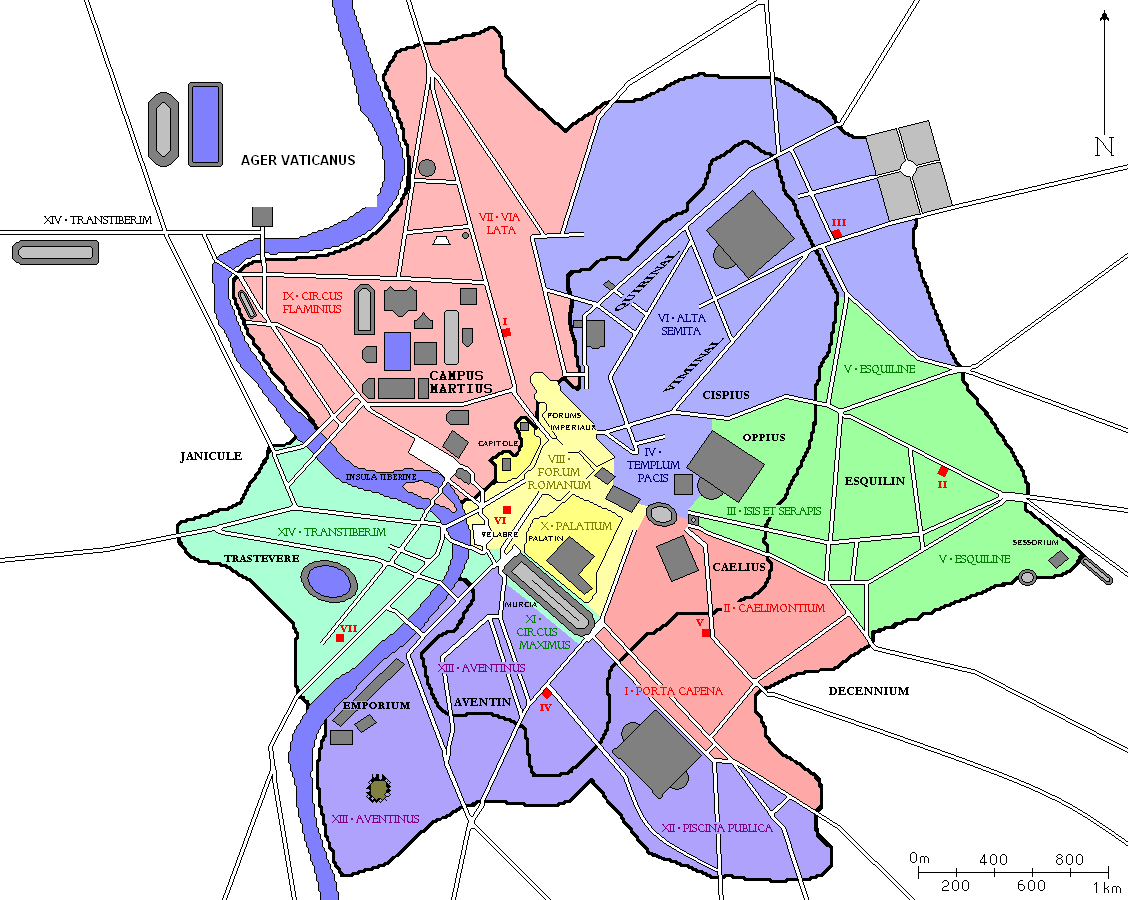
Praefectus Urbanus
The ''praefectus urbanus'', also called ''praefectus urbi'' or urban prefect in English, was prefect of the city of Rome, and later also of Constantinople. The office originated under the Roman kings, continued during the Republic and Empire, and held high importance in late Antiquity. The office survived the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, and the last urban prefect of Rome, named Iohannes, is attested in 599. Lançon (2000), p. 45 In the East, in Constantinople, the office survived until the 13th century. Regal period According to Roman tradition, in 753 BC when Romulus founded the city of Rome and instituted the monarchy, he also created the office of ''custos urbis'' (guardian of the city) to serve as the king's chief lieutenant. Appointed by the king to serve for life, the ''custos urbis'' served concurrently as the ''princeps Senatus''. As the second highest office of state, the ''custos urbis'' was the king's personal representative. In the absence of the king from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praefectus Urbi
The ''praefectus urbanus'', also called ''praefectus urbi'' or urban prefect in English, was prefect of the city of Rome, and later also of Constantinople. The office originated under the Roman kings, continued during the Republic and Empire, and held high importance in late Antiquity. The office survived the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, and the last urban prefect of Rome, named Iohannes, is attested in 599. Lançon (2000), p. 45 In the East, in Constantinople, the office survived until the 13th century. Regal period According to Roman tradition, in 753 BC when Romulus founded the city of Rome and instituted the monarchy, he also created the office of ''custos urbis'' (guardian of the city) to serve as the king's chief lieutenant. Appointed by the king to serve for life, the ''custos urbis'' served concurrently as the '' princeps Senatus''. As the second highest office of state, the ''custos urbis'' was the king's personal representative. In the absence of the king fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vigiles
''Vigiles'' or more properly the ''Vigiles Urbani'' ("watchmen of the Rome, City") or ''Cohortes Vigilum'' ("Cohort (military unit), cohorts of the watchmen") were the firefighters and police of ancient Rome. History The ''triumviri, triumviri nocturni'' (meaning ''three men of the night'') were the first men, being privately owned Slavery in ancient Rome, slaves, organized into a group that combatted the common problems of fire and conflagrations in Rome. Another organization dedicated to fighting fires in ancient Rome was a band of slaves led by the aedile Marcus Egnatius Rufus. The privately operated system became ineffective, so in the interest of keeping himself and Rome safe, Augustus instituted a new public firefighting force called the ''vigiles''. Augustus modelled the new firefighters after the fire brigade of Alexandria, Egypt. The ''vigiles'' were also known by their nickname ''Spartoli'' or "little bucket fellows", given to them because of the buckets they carried w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praefectus Laetorum
(), the plural form of (), was a term used in the late Roman Empire to denote communities of (" barbarians"), i.e. foreigners, or people from outside the Empire, permitted to settle on, and granted land in, imperial territory on condition that they provide recruits for the Roman military. The term is of uncertain origin. It means "lucky" or "happy" in Latin, but may derive from a non-Latin word. It may derive from a Germanic word meaning "serf" or "half-free colonist". Other authorities suggest the term was of Celtic or Iranian origin. Origin The ' may have been groups of migrants drawn from the tribes that lived beyond the Empire's borders. These had been in constant contact and intermittent warfare with the Empire since its northern borders were stabilized in the reign of Augustus in the early 1st century. In the West, these tribes were primarily Germans, living beyond the Rhine. There is no mention in the sources of ' in the Eastern section of the Empire.Jones (1964) 620 L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praefectus Annonae
The ("prefect of the provisions"), also called the ("prefect of the grain supply"), was a Roman official charged with the supervision of the grain supply to the city of Rome. Under the Republic, the job was usually done by an aedile. However, in emergencies, or in times of extraordinary scarcity, someone would be elected to the office, and would take charge of supplying the entire city with provisions. Lucius Minucius Augurinus, the accuser of Spurius Maelius, was the first individual appointed to this office, serving from 439 BC. During the early 60s BC, following the sacking of the port of Ostia by pirates, Pompey held the powers of the office. Around 7 BC, the first Roman Emperor, Augustus, followed this example, and after vesting himself with these powers, specified that two former praetors should be appointed each year to carry out the functions of this office. Augustus transferred powers from the aediles to this office, and specified that all holders of the office b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praefectus Augustalis
During the Roman Empire, the governor of Roman Egypt ''(praefectus Aegypti)'' was a prefect who administered the Roman province of Egypt with the delegated authority ''( imperium)'' of the emperor. Egypt was established as a Roman province in consequence of the Battle of Actium, where Cleopatra as the last independent ruler of Egypt and her Roman ally Mark Antony were defeated by Octavian, the adopted heir of the assassinated Roman dictator Julius Caesar. Octavian then rose to supreme power with the title Augustus, ending the era of the Roman Republic and installing himself as ''princeps'', the so-called "leading citizen" of Rome who in fact acted as an autocratic ruler. Although senators continued to serve as governors of most other provinces (the senatorial provinces), especially those annexed under the Republic, the role of Egypt during the civil war with Antony and its strategic and economic importance prompted Augustus to ensure that no rival could secure ''Aegyptus'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetorian Prefect
The praetorian prefect (; ) was a high office in the Roman Empire. Originating as the commander of the Praetorian Guard, the office gradually acquired extensive legal and administrative functions, with its holders becoming the Emperor's chief aides. Under Constantine I, the office was much reduced in power and transformed into a purely civilian administrative post, while under his successors, territorially-defined praetorian prefectures emerged as the highest-level administrative division of the Empire. The prefects again functioned as the chief ministers of the state, with many laws addressed to them by name. In this role, praetorian prefects continued to be appointed by the Eastern Roman Empire (and the Ostrogothic Kingdom) until the reign of Heraclius in the 7th century AD, when wide-ranging reforms reduced their power and converted them to mere overseers of provincial administration. The last traces of the prefecture disappeared in the Byzantine Empire by the 840s. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praefectus Castrorum
The ''praefectus castrorum'' ("camp prefect") was, in the Roman army of the early Empire, the third most senior staff officer of the Roman legion after the legate ('' legatus'') and the senior military tribune (''tribunus laticlavius''), both of whom were from the senatorial class. The ''praefectus castrorum'' was a quartermaster responsible for military logistics and requisition (training, equipment procurement and maintenance, and construction of the camp, etc.) but could command the legion whenever the senior commanders were absent. The post was usually held by a soldier promoted from the centurionate, having already served as a chief centurion (''primus pilus'') of a legion, and was therefore open to ordinary, plebeian citizens. Prefects of this rank, for example Sextus Vibius Gallus,'' SEG'' 57 1293 were awarded prizes (''dona'') to mark their achievements. See also * Military logistics * Praefectus ''Praefectus'', often with a further qualification, was the formal ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praefectus Cohortus
''Praefectus'', often with a further qualification, was the formal title of many, fairly low to high-ranking, military or civil officials in the Roman Empire, whose authority was not embodied in their person (as it was with elected Magistrates) but conferred by delegation from a higher authority. They did have some authority in their prefecture, such as controlling prisons and in civil administration. Praetorian prefects The Praetorian prefect (''Praefectus praetorio'') began as the military commander of a general's guard company in the field, then grew in importance as the Praetorian Guard became a potential kingmaker during the Empire. From the Emperor Diocletian's tetrarchy (c. 300) they became the administrators of the four Praetorian prefectures, the government level above the (newly created) dioceses and (multiplied) provinces. Police and civil prefects *''Praefectus urbi'', or '' praefectus urbanus'': city prefect, in charge of the administration of Rome. *'' Praefectus vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praefectus Classis
The naval forces of the ancient Roman state () were instrumental in the Roman conquest of the Mediterranean Basin, but it never enjoyed the prestige of the Roman legions. Throughout their history, the Romans remained a primarily land-based people and relied partially on their more nautically inclined subjects, such as the Greeks and the Egyptians, to build their ships. Because of that, the navy was never completely embraced by the Roman state, and deemed somewhat "un-Roman". In antiquity, navies and trading fleets did not have the logistical autonomy that modern ships and fleets possess, and unlike modern naval forces, the Roman navy even at its height never existed as an autonomous service but operated as an adjunct to the Roman army. During the course of the First Punic War, the Roman navy was massively expanded and played a vital role in the Roman victory and the Roman Republic's eventual ascension to hegemony in the Mediterranean Sea. In the course of the first half of the 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerarium Militare
The ''aerarium militare'' was the military treasury of Imperial Rome. It was instituted by Augustus, the first Roman emperor, as a "permanent revenue source" for pensions ''(praemia)'' for veterans of the Imperial Roman army. The treasury derived its funding from new taxes, an inheritance tax and a sales tax, and regularized the ad hoc provisions for veterans that under the Republic often had involved socially disruptive confiscation of property. The ''praefecti aerarii militaris'' (singular ''praefectus'') were the three prefects who oversaw the treasury. Benefits The Imperial biographer and historian Suetonius saw the ''aerarium militare'' as a response to the uncertainty of retired military men in need who might be inclined to support a coup or foment unrest. The professionalizing of the army during the Republic created the new problem of veterans, since earlier in Rome's history male citizens served short-term to confront specific threats or carry out seasonal camp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |