|
Postsynaptic Density-95
PSD-95 (postsynaptic density protein 95) also known as SAP-90 (synapse-associated protein 90) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DLG4'' (discs large homolog 4) gene. PSD-95 is a member of the membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) family. With PSD-93 it is recruited into the same NMDA receptor and potassium channel clusters. These two MAGUK proteins may interact at postsynaptic sites to form a multimeric scaffold for the clustering of receptors, ion channels, and associated signaling proteins. PSD-95 is the best studied member of the MAGUK-family of PDZ domain-containing proteins. Like all MAGUK-family proteins, its basic structure includes three PDZ domains, an SH3 domain, and a guanylate kinase-like domain (GK) connected by disordered linker regions. It is almost exclusively located in the post synaptic density of neurons, and is involved in anchoring synaptic proteins. Its direct and indirect binding partners include neuroligin, NMDA receptors, AMPA rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent Protein Kinase
CAMK, also written as CaMK or CCaMK, is an abbreviation for the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase class of enzymes. CAMKs are activated by increases in the concentration of intracellular calcium ions (Ca2+) and calmodulin. When activated, the enzymes transfer phosphates from ATP to defined serine or threonine residues in other proteins, so they are serine/threonine-specific protein kinases. Activated CAMK is involved in the phosphorylation of transcription factors and therefore, in the regulation of expression of responding genes. CAMK also works to regulate the cell life cycle (i.e. programmed cell death), rearrangement of the cell's cytoskeletal network, and mechanisms involved in the learning and memory of an organism. Types There are 2 common types of CAM Kinase proteins: specialized and multi-functional CAM kinases. ;Substrate-specific CAM Kinases: only have one target that they can phosphorylate, such as myosin light chain kinases. This group of proteins includes CA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose Tolerance Test
The glucose tolerance test (GTT, not to be confused with GGT test) is a medical test in which glucose is given and blood samples taken afterward to determine how quickly it is cleared from the blood. The test is usually used to test for diabetes, insulin resistance, impaired beta cell function, and sometimes reactive hypoglycemia and acromegaly, or rarer disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. In the most commonly performed version of the test, an ''oral glucose tolerance test'' (OGTT), a standard dose of glucose is ingested by mouth and blood levels are checked two hours later. Many variations of the GTT have been devised over the years for various purposes, with different standard doses of glucose, different routes of administration, different intervals and durations of sampling, and various substances measured in addition to blood glucose. History The glucose tolerance test was first described in 1923 by Jerome W. Conn. The test was based on the previous work in 1913 by A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indirect Calorimetry
Indirect calorimetry calculates heat that living organisms produce by measuring either their production of carbon dioxide and nitrogen waste (frequently ammonia in aquatic organisms, or urea in terrestrial ones), or from their consumption of oxygen. Indirect calorimetry estimates the type and rate of substrate utilization and energy metabolism in vivo starting from gas exchange measurements (oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production during rest and steady-state exercise). This technique provides unique information, is noninvasive, and can be advantageously combined with other experimental methods to investigate numerous aspects of nutrient assimilation, thermogenesis, the energetics of physical exercise, and the pathogenesis of metabolic diseases.Ferrannini "The theoretical bases of indirect calorimetry: a review."Metabolism. 1988 Mar;37(3):287-301. Scientific background Indirect calorimetry measures O2 consumption and CO2 production. On the assumption that all the oxyge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
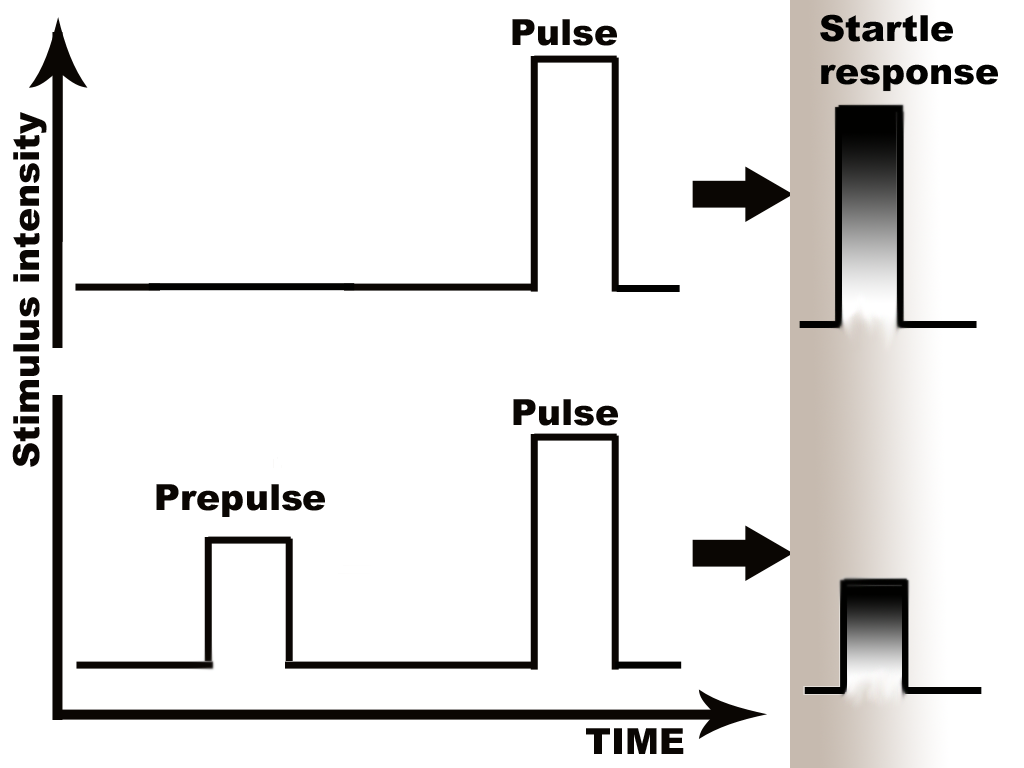
Prepulse Inhibition
Prepulse inhibition (PPI) is a neurological phenomenon in which a weaker prestimulus (prepulse) inhibits the reaction of an organism to a subsequent strong reflex-eliciting stimulus (pulse), often using the startle reflex. The stimuli are usually acoustic, but tactile stimuli (e.g. via air puffs onto the skin) and light stimuli are also used. When prepulse inhibition is high, the corresponding one-time startle response is reduced. The reduction of the amplitude of startle reflects the ability of the nervous system to temporarily adapt to a strong sensory stimulus when a preceding weaker signal is given to warn the organism. PPI is detected in numerous species including mice and humans. Although the extent of the adaptation affects numerous systems, the most comfortable to measure are the muscular reactions, which are normally diminished as a result of the nervous inhibition. Deficits of prepulse inhibition manifest in the inability to filter out the unnecessary information; they h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysmorphology
Teratology is the study of abnormalities of physiological development in organisms during their life span. It is a sub-discipline in medical genetics which focuses on the classification of congenital abnormalities in dysmorphology. The related term developmental toxicity includes all manifestations of abnormal development that are caused by environmental insult. These may include growth retardation, delayed mental development or other congenital disorders without any structural malformations. Teratogens are substances that may cause birth defects via a toxic effect on an embryo or fetus. Known teratogens include: retinol, thalidomide, mercury, alcohol, lead, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin. Etymology The term was borrowed in 1842 from the French , where it was formed in 1830 from the Greek (word stem ), meaning "sign sent by the gods, portent, marvel, monster", and (''-ology''), used to designate a discourse, treaty, science, theory, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Plate Test
The hot plate test is a test of the pain response in animals, similar to the tail flick test. Both hot plate and tail-flick methods are used generally for centrally acting analgesic, while peripherally acting drugs are ineffective in these tests but sensitive to acetic acid-induced writhing test. The hot plate test is used in basic pain research and in testing the effectiveness of analgesics by observing the reaction to pain caused by heat. It was proposed by Eddy and Leimbach in 1953. They used a behavioral model of nociception where behaviors such as jumping and hind paw-licking are elicited following a noxious thermal stimulus. Licking is a rapid response to painful thermal stimuli that is a direct indicator of nociceptive threshold. Jumping represents a more elaborated response, with a latency, and encompasses an emotional component of escaping. Procedure * A transparent glass cylinder is used to keep the animal on the heated surface of the plate. * The temperature of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Field (animal Test)
Developed by Calvin S. Hall, the open field test is an experimental test used to assay general locomotor activity levels, anxiety, and willingness to explore in animals (usually rodents) in scientific research. However, the extent to which behavior in the open field measures anxiety is controversial. The open field test can be used to assess memory by evaluating the ability of the animal to recognize a stimuli or object. Another animal test that is used to assess memory using that same concept is the novel object recognition test. Concept Animals such as rats and mice display a natural aversion to brightly lit open areas. However, they also have a drive to explore a perceived threatening stimulus. Decreased levels of anxiety lead to increased exploratory behavior. Increased anxiety will result in less locomotion and a preference to stay close to the walls of the field ( thigmotaxis). Experimental design The open field is an arena with walls to prevent escape. Commonly, the fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homozygote
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid. Diploid organisms have the same loci on each of their two sets of homologous chromosomes except that the sequences at these loci may differ between the two chromosomes in a matching pair and that a few chromosomes may be mismatched as part of a chromosomal sex-determination system. If both alleles of a diploid organism are the same, the organism is homozygous at that locus. If they are different, the organism is heterozygous at that locus. If one allele is missing, it is hemizygous, and, if both alleles are missing, it is nullizygous. The DNA sequence of a gene often varies from one individual to another. These gene variants are called alleles. While some g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calmodulin
Calmodulin (CaM) (an abbreviation for calcium-modulated protein) is a multifunctional intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells. It is an intracellular target of the secondary messenger Ca2+, and the binding of Ca2+ is required for the activation of calmodulin. Once bound to Ca2+, calmodulin acts as part of a calcium signal transduction pathway by modifying its interactions with various target proteins such as kinases or phosphatases. Structure Calmodulin is a small, highly conserved protein that is 148 amino acids long (16.7 kDa). The protein has two approximately symmetrical globular domains (the N- and C- domains) each containing a pair of EF hand motifs separated by a flexible linker region for a total of four Ca2+ binding sites, two in each globular domain. In the Ca2+-free state, the helices that form the four EF-hands are collapsed in a compact orientation, and the central linker is disordered; in the Ca2+-saturated state, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base ( adenine), the sugar ribose, and the triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar ( ribose), which in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |