|
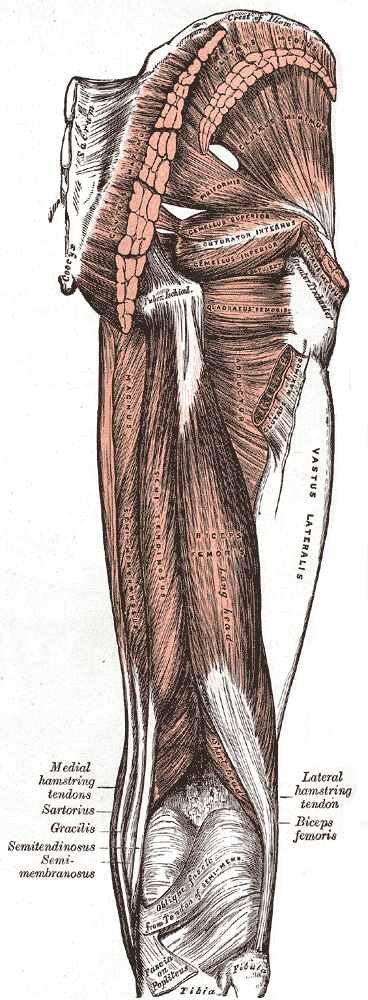
Posterior Femoral Cutaneous Nerve
The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh (also called the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve) is a sensory nerve of the thigh. It is a branch of the sacral plexus. It supplies the skin of the posterior surface of the thigh, leg, buttock, and also the perineum. Unlike most nerves termed "cutaneous" which are subcutaneous, only the terminal branches of this nerve pass into subcutaneous tissue before being distributed to the skin, with most of the nerve itself situated deep to the deep fascia. Structure Origin The posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a branch of the sacral plexus. It arises from the posterior divisions of the S1- S2, and the anterior divisions of S2- S3 sacral spinal nerves. Course It leaves the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen inferior to the piriformis muscle. It then descends deep to the gluteus maximus muscle, medial or posterior to the sciatic nerve, and alongside the inferior gluteal artery. It descends within the posterior thigh deep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thigh
In anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb. The single bone in the thigh is called the femur. This bone is very thick and strong (due to the high proportion of bone tissue), and forms a ball and socket joint at the hip, and a modified hinge joint at the knee. Structure Bones The femur is the only bone in the thigh and serves as an attachment site for all thigh muscles. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with the tibia and patella forming the knee. By most measures, the femur is the strongest and longest bone in the body. The femur is categorised as a long bone and comprises a diaphysis, the shaft (or body) and two epiphyses, the lower extremity and the upper extremity of femur, that articulate with adjacent bones in the hip and knee. Muscular compartments In cross-section, the thigh is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Piriformis Muscle
The piriformis muscle () is a flat, pyramidally-shaped muscle in the buttock, gluteal region of the lower limbs. It is one of the six muscles in the lateral rotator group. The piriformis muscle has its origin upon the front surface of the sacrum, and inserts onto the greater trochanter of the femur. Depending upon the given position of the leg, it acts either as external (lateral) rotator of the thigh or as abductor of the thigh. It is innervated by the piriformis nerve. Structure The piriformis is a flat muscle, and is pyramidal in shape. Origin The piriformis muscle originates from the Pelvic surface of sacrum, anterior (front) surface of the sacrum by three fleshy digitations attached to the Sacrum, second, third, and fourth sacral vertebra. It also arises from the superior margin of the greater sciatic notch, the gluteal surface of the Ilium (bone), ilium (near the posterior inferior iliac spine), the sacroiliac joint capsule, and (sometimes) the sacrotuberous ligament (m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inferior Cluneal Nerves
The inferior clunial nerves (also gluteal branches of posterior femoral cutaneous nerve) are branches of the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh that innervate the skin of the lower part of the buttocks The buttocks (: buttock) are two rounded portions of the exterior anatomy of most mammals, located on the posterior of the pelvic region. In humans, the buttocks are located between the lower back and the perineum. They are composed of a lay .... They pass inferior to the inferior border of the gluteus maximus muscle. References External links * * - "Superficial Anatomy of the Lower Extremity: Cutaneous Nerves of the Posterior Aspect of the Lower Extremity" Nerves of the lower limb and lower torso Buttocks {{Neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Popliteal Fossa
The popliteal fossa (also referred to as hough or kneepit in analogy to the cubital fossa) is a shallow depression located at the back of the knee joint. The bones of the popliteal fossa are the femur and the tibia. Like other flexion surfaces of large joints (groin, armpit, cubital fossa and essentially the anterior part of the neck), it is an area where blood vessels and nerves pass relatively superficially, and with an increased number of lymph nodes. Structure Boundaries The boundaries of the fossa are: Roof Moving from superficial to deep structures, the roof is formed by: # the skin. # the superficial fascia. This contains the small saphenous vein, the terminal branch of the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh, posterior division of the medial cutaneous nerve, lateral sural cutaneous nerve, and medial sural cutaneous nerve. # the popliteal fascia. Floor The floor is formed by: # the popliteal surface of the femur. # the capsule of the knee joint and the obli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inferior Clunial Nerves
The inferior clunial nerves (also gluteal branches of posterior femoral cutaneous nerve) are branches of the posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh that innervate the skin of the lower part of the buttocks The buttocks (: buttock) are two rounded portions of the exterior anatomy of most mammals, located on the posterior of the pelvic region. In humans, the buttocks are located between the lower back and the perineum. They are composed of a lay .... They pass inferior to the inferior border of the gluteus maximus muscle. References External links * * - "Superficial Anatomy of the Lower Extremity: Cutaneous Nerves of the Posterior Aspect of the Lower Extremity" Nerves of the lower limb and lower torso Buttocks {{Neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sural Nerve
The sural nerve ''(L4-S1)'' is generally considered a pure cutaneous nerve of the posterolateral leg to the lateral ankle. The sural nerve originates from a combination of either the sural communicating branch and medial sural cutaneous nerve, or the lateral sural cutaneous nerve. This group of nerves is termed the sural nerve complex. There are eight documented variations of the sural nerve complex. Once formed the sural nerve takes its course midline posterior to posterolateral around the lateral malleolus. The sural nerve terminates as the lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve. Anatomy The sural nerve ''(L4-S1)'' is a cutaneous sensory nerve of the posterolateral calf with cutaneous innervation to the distal one-third of the lower leg. Formation of the ''sural nerve'' is the result of either anastomosis of the medial sural cutaneous nerve and the sural communicating nerve, or it may be found as a continuation of the lateral sural cutaneous nerve traveling parallel to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Small Saphenous Vein
The small saphenous vein (also short saphenous vein or lesser saphenous vein) is a relatively large superficial vein of the posterior leg. Structure The origin of the small saphenous vein (SSV) is where the dorsal vein from the fifth digit (smallest toe) merges with the dorsal venous arch of the foot, which attaches to the great saphenous vein (GSV). It is a superficial vein, being subcutaneous (just under the skin). From its origin, it courses around the lateral aspect of the foot (inferior and posterior to the lateral malleolus) and runs along the posterior aspect of the leg (with the sural nerve), where it passes between the heads of the gastrocnemius muscle. This vein presents a number of different draining points. Usually, it drains into the popliteal vein, at or above the level of the knee joint. Variation Sometimes, the SSV joins the common gastrocnemius vein before draining in the popliteal vein. Sometimes, it does not make contact with the popliteal vein, but goes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Biceps Femoris
The biceps femoris () is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it consists of two heads; the long head is considered part of the hamstring muscle group, while the short head is sometimes excluded from this characterization, as it only causes knee flexion (but not hip extension) and is activated by a separate nerve (the peroneal, as opposed to the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve). Structure It has two heads of origin: *the ''long head'' arises from the lower and inner impression on the posterior part of the tuberosity of the ischium. This is a common tendon origin with the semitendinosus muscle, and from the lower part of the sacrotuberous ligament. *the ''short head'', arises from the lateral lip of the linea aspera, between the adductor magnus and vastus lateralis extending up almost as high as the insertion of the gluteus maximus, from the lateral prolongation of the linea aspera to within 5 cm. of the lateral condyle; and from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hamstring Muscles
A hamstring () is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in human anatomy between the hip and the knee: from medial to lateral, the semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps femoris. Etymology The word "ham" is derived from the Old English “ham” or “hom” meaning the hollow or bend of the knee, from a Germanic base where it meant "crooked". It gained the meaning of the leg of an animal around the 15th century. ''String'' refers to tendons, and thus the hamstrings' string-like tendons felt on either side of the back of the knee. Criteria The common criteria of any hamstring muscles are: # Muscles should originate from ischial tuberosity. # Muscles should be inserted over the knee joint, in the tibia or in the fibula. # Muscles will be innervated by the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve. # Muscle will participate in flexion of the knee joint and extension of the hip joint. Those muscles which fulfill all of the four criteria are called true hamstrings. The adduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fascia Lata
The fascia lata is the deep fascia of the thigh. It encloses the thigh muscles and forms the outer limit of the fascial compartments of thigh, which are internally separated by the medial intermuscular septum and the lateral intermuscular septum. The fascia lata is thickened at its lateral side where it forms the iliotibial tract, a structure that runs to the tibia and serves as a site of muscle attachment. Structure The fascia lata is an investment for the whole of the thigh, but varies in thickness in different parts. It is thicker in the upper and lateral part of the thigh, where it receives a fibrous expansion from the gluteus maximus, and where the tensor fasciae latae is inserted between its layers; it is very thin behind and at the upper and medial part, where it covers the adductor muscles, and again becomes stronger around the knee, receiving fibrous expansions from the tendon of the biceps femoris laterally, from the sartorius medially, and from the quadriceps fem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inferior Gluteal Artery
The inferior gluteal artery (sciatic artery) is a terminal branch of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen. It is distributed chiefly to the buttock and the back of the thigh. Anatomy Origin It is the smaller of the two terminal branches of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. Course It passes posterior-ward within parietal pelvic fascia. It travels in between the S1 nerve and S2 (or S2-S3) nerve(s). It descends upon the nerves of the sacral plexus and the piriformis muscle, posterior to the internal pudendal artery. It passes through the inferior part of the greater sciatic foramen. It exits the pelvis inferior to the piriformis muscle, between piriformis muscle and coccygeus muscle. It then descends in the interval between the greater trochanter of the femur and tuberosity of the ischium. It is accompanied by the sciatic nerve and the posterior femoral cutaneous nerves, and covered by the glu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sciatic Nerve
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals. It is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the right lower limb. It is the longest and widest single nerve in the human body, going from the top of the leg to the foot on the posterior aspect. The sciatic nerve has no cutaneous branches for the thigh. This nerve provides the connection to the nervous system for the skin of the lateral leg and the whole foot, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot. It is derived from Spinal nerve, spinal nerves Lumbar spinal nerve 4, L4 to Sacral spinal nerve 3, S3. It contains Axon, fibres from both the anterior and posterior divisions of the lumbosacral plexus. Structure In humans, the sciatic nerve is formed from the L4 to S3 segments of the sacral plexus, a collection of nerve fibres that emerge from the Sacrum, sacral part of the spinal cord. The lumbosacral trunk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |