|
Portolans
Portolan charts are nautical charts, first made in the 13th century in the Mediterranean basin and later expanded to include other regions. The word ''portolan'' comes from the Italian ''portolano'', meaning "related to ports or harbors", and which since at least the 17th century designates "a collection of sailing directions". Definition The term "portolan chart" was coined in the 1890s because at the time it was assumed that these maps were related to portolani, medieval or early modern books of sailing directions. Other names that have been proposed include rhumb line charts, compass charts or loxodromic charts whereas modern French scholars prefer to call them nautical charts to avoid any relationship with portolani. Several definitions of portolan chart coexist in the literature. A narrow definition includes only medieval or, at the latest, early modern sea charts (i.e. maps that primarily cover maritime rather than inland regions) that include a network of rhumb lines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhumbline Network
A rhumbline network (or windrose network) is a navigational aid consisting in lines drawn from multiple vertices in different directions forming a web-like mesh. They were featured on portolan charts and other early nautical charts used in the medieval age and age of exploration in marine navigation. Since the invention of the Mercator projection , the term ''rhumb line'' (or ''loxodrome'') has been redefined to mean a mathematically precise curve of constant bearing on the Earth's surface. To avoid confusion, the lines on earlier sailing charts can be unambiguously called ''windrose lines'' (after wind roses), since they are not true rhumb lines by the modern definition. A rhumb line in the modern sense is only straight on a chart drawn with the Mercator projection, but not on charts from the 13th–16th centuries. Older windrose lines were a close approximation on charts of the Mediterranean Sea and surrounding areas, but the rhumb lines on small-scale maps such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
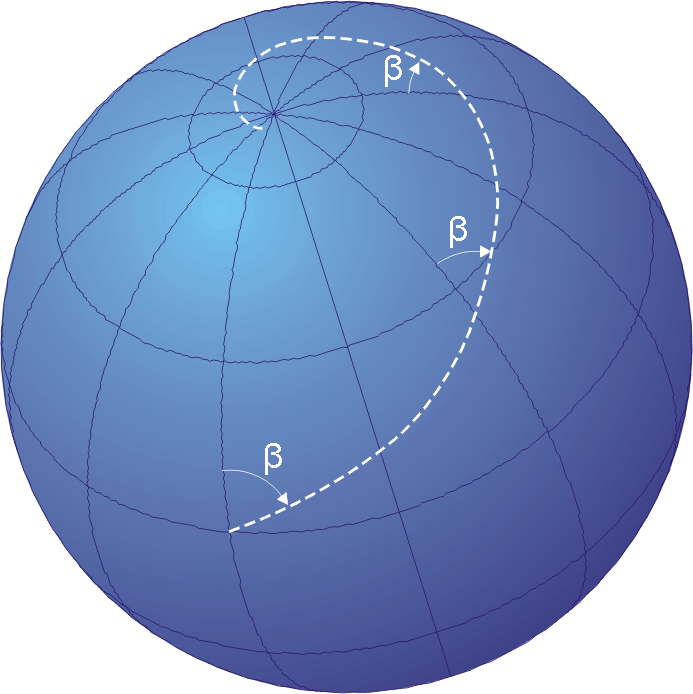
Rhumb Line
In navigation, a rhumb line, rhumb (), or loxodrome is an arc crossing all meridians of longitude at the same angle, that is, a path with constant azimuth ( bearing as measured relative to true north). Navigation on a fixed course (i.e., steering the vessel to follow a constant cardinal direction) would result in a rhumb-line track. Introduction The effect of following a rhumb line course on the surface of a globe was first discussed by the Portuguese mathematician Pedro Nunes in 1537, in his ''Treatise in Defense of the Marine Chart'', with further mathematical development by Thomas Harriot in the 1590s. A rhumb line can be contrasted with a great circle, which is the path of shortest distance between two points on the surface of a sphere. On a great circle, the bearing to the destination point does not remain constant. If one were to drive a car along a great circle one would hold the steering wheel fixed, but to follow a rhumb line one would have to turn the wheel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Chart Fourteenth Century2
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccation, desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The sea was an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bearing (navigation)
In navigation, bearing or azimuth is the horizontal angle between the direction of an object and north or another object. The angle value can be specified in various angular units, such as degrees, mils, or grad. More specifically: * Absolute bearing refers to the clockwise angle between the magnetic north (''magnetic bearing'') or true north (''true bearing'') and an object. For example, an object to due east would have an absolute bearing of 90 degrees. Thus, it is the same as azimuth.U.S. Army, ''Advanced Map and Aerial Photograph Reading'', Headquarters, War Department, Washington, D.C. (17 September 1941), pp. 24-2/ref> * #Relative, Relative bearing refers to the angle between the craft's forward direction ( heading) and the location of another object. For example, an object relative bearing of 0 degrees would be immediately in front; an object relative bearing 180 degrees would be behind. Bearings can be measured in mils, points, or degrees. Thus, it is the same as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic North Pole
The north magnetic pole, also known as the magnetic north pole, is a point on the surface of Earth's Northern Hemisphere at which the planet's magnetic field points vertically downward (in other words, if a magnetic compass needle is allowed to rotate in three dimensions, it will point straight down). There is only one location where this occurs, near (but distinct from) the geographic north pole. The Earth's Magnetic North Pole is actually considered the "south pole" in terms of a typical magnet, meaning that the north pole of a magnet would be attracted to the Earth's magnetic north pole. The north magnetic pole moves over time according to magnetic changes and flux lobe elongation in the Earth's outer core. In 2001, it was determined by the Geological Survey of Canada to lie west of Ellesmere Island in northern Canada at . It was situated at in 2005. In 2009, while still situated within the Canadian Arctic at , it was moving toward Russia at between per year. In 2013, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discover (magazine)
''Discover'' is an American general audience science magazine launched in October 1980 by Time Inc. It is currently owned by LabX Media Group. History Founding ''Discover'' was created primarily through the efforts of ''Time'' magazine editor Leon Jaroff. He noticed that magazine sales jumped every time the cover featured a science topic. Jaroff interpreted this as a considerable public interest in science, and in 1971, he began agitating for the creation of a science-oriented magazine. This was difficult, as a former colleague noted, because "Selling science to people who graduated to be managers was very difficult".Hevesi, Dennis"Leon Jaroff, Editor at Time and Discover Magazines, Dies at 85" ''The New York Times'', 21 October 2012 Jaroff's persistence finally paid off, and ''Discover'' magazine published its first edition in 1980. ''Discover'' was originally launched into a burgeoning market for science magazines aimed at educated non-professionals, intended to be eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Declination
Magnetic declination (also called magnetic variation) is the angle between magnetic north and true north at a particular location on the Earth's surface. The angle can change over time due to polar wandering. Magnetic north is the direction that the north end of a magnetized compass needle points, which corresponds to the direction of the Earth's magnetic field lines. True north is the direction along a meridian towards the geographic North Pole. Somewhat more formally, Bowditch defines variation as "the angle between the magnetic and geographic meridians at any place, expressed in degrees and minutes east or west to indicate the direction of magnetic north from true north. The angle between magnetic and grid meridians is called grid magnetic angle, grid variation, or grivation." By convention, declination is positive when magnetic north is east of true north, and negative when it is to the west. '' Isogonic lines'' are lines on the Earth's surface along which the declination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T And O Map
A T and O map or O–T or T–O map (''orbis terrarum'', orb or circle of the lands; with the letter T inside an O), also known as an Isidoran map, is a type of early world map that represents the Afro-Eurasian landmass as a circle (= O) divided into three parts by a T-shaped combination of the Mediterranean sea, the river Tanais (Don) and the Nile. The origins of this diagram are contested, with some scholars hypothesizing an origin in Roman or late antiquity, while others consider it to have originated in 7th or early-8th century Spain. The earliest surviving example of a T-O map is found in a late-7th or early-8th century copy of Isidore of Seville's (c. 560–636) ''De natura rerum'', which alongside his ''Etymologiae'' (c. 625) are two of the most common texts to be accompanied by such a diagram in the Middle Ages. A later manuscript added the names of Noah's sons ( Sem, Iafeth and Cham) for each of the three continents (see Biblical terminology for race).: "...the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periplus
A periplus (), or periplous, is a manuscript document that lists the ports and coastal landmarks, in order and with approximate intervening distances, that the captain of a vessel could expect to find along a shore. In that sense, the periplus was a type of log and served the same purpose as the later Roman itinerarium of road stops. However, the Greek navigators added various notes, which, if they were professional geographers, as many were, became part of their own additions to Greek geography. The form of the ''periplus'' is at least as old as the earliest Greek historian, the Ionian Hecataeus of Miletus. The works of Herodotus and Thucydides contain passages that appear to have been based on ''peripli''. Etymology ''Periplus'' is the Latinization of the Greek word περίπλους (''periplous'', contracted from περίπλοος ''periploos''), which is "a sailing-around." Both segments, ''peri-'' and ''-plous'', were independently productive: the ancient Greek speaker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curvature Of The Earth
Spherical Earth or Earth's curvature refers to the approximation of the figure of the Earth as a sphere. The earliest documented mention of the concept dates from around the 5th century BC, when it appears in the writings of Greek philosophers. In the 3rd century BC, Hellenistic astronomy established the roughly spherical shape of Earth as a physical fact and calculated the Earth's circumference. This knowledge was gradually adopted throughout the Old World during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, displacing earlier beliefs in a flat earth.Adoption by China via European science: and A practical demonstration of Earth's sphericity was achieved by Ferdinand Magellan and Juan Sebastián Elcano's circumnavigation (1519–1522). The realization that the figure of the Earth is more accurately described as an ellipsoid dates to the 17th century, as described by Isaac Newton in '' Principia''. In the early 19th century, the flattening of the earth ellipsoid was determined to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |