|
Poppyseed Oil
Poppyseed oil (also poppy seed oil and poppy oil) is an edible oil obtained from poppy seeds (specifically seeds of ''Papaver somniferum'', the opium poppy). Poppy seeds yield 45–50% oil. Like poppy seeds, poppyseed oil is highly palatable, high in vitamin E, and has no narcotic properties. Poppy seeds are especially high in tocopherols other than vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol). Compared to other vegetable oils, poppyseed oil has a moderate amount of phytosterols: higher than soybean oil and peanut oil, lower than safflower oil, sesame oil, wheat germ oil, corn oil, and rice bran oil. It has little or no odor and a pleasant taste, and it is less likely than some other oils to become rancid. Uses The oil is sometimes used as a cooking oil; it is also used for moisturizing skin. Its primary use, however, is in the manufacture of paints, varnishes, and soaps. Poppyseed oil is a drying oil. In oil painting, the most popular oil for binding pigment, thinning paint, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytosterol
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanol ester, stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified. Free phytosterols extracted from oils are insoluble in water, relatively insoluble in oil, and soluble in alcohols. Phytosterol-enriched foods and dietary supplements have been marketed for decades. Despite well-documented LDL cholesterol-lowering effects from long-term consumption of phytosterols, there is insufficient evidence for an effect on cardiovascular diseases, fasting blood sugar, glycated hemoglobin, or overall mortality rate. Structure They have a fused polycyclic structure and vary in carbon side chains and / or presence or absence of a double bond (saturation). They are divided into 4,4-dimethyl phytosterols, 4-monomethyl phytosterols, and 4-desmethyl phytosterols based on the location of methyl groups at the carbon-4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice Bran Oil
Rice bran oil is the oil extracted from the hard outer brown layer of rice called bran. It is known for its high smoke point of and mild flavor, making it suitable for high-temperature cooking methods such as stir frying and deep frying. It is popular as a cooking oil in East Asia, the Indian subcontinent, and Southeast Asia including India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Japan, Southern China and Malaysia. Composition and properties Rice bran oil has a composition similar to that of peanut oil, with 38% monounsaturated, 37% polyunsaturated, and 25% saturated fatty acids. A component of rice bran oil is the γ-oryzanol, at around 2% of crude oil content. Thought to be a single compound when initially isolated, γ-oryzanol is now known to be a mixture of steryl and other triterpenyl esters of ferulic acids. Also present are tocopherols and tocotrienols (two types of vitamin E) and phytosterols. ;Fatty acid composition ;Physical properties of crude and refined r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poppy Seeds
Poppy seed is an oilseed obtained from the poppy plant (''Papaver somniferum''). The tiny, kidney-shaped seeds have been harvested from dried seed pods by various civilizations for thousands of years. It is still widely used in many countries, especially in Central Europe and South Asia, where it is legally grown, used in food products and sold in shops. The seeds are used whole or ground into meal as an ingredient in many foods – especially in pastry and bread – and they are pressed to yield poppyseed oil. History The poppy seed is mentioned in ancient medical texts from many civilizations. For instance, the Egyptian Ebers Papyrus, written c. 1550 BCE, lists the poppy seed as a sedative. The Minoan civilization (approximately 2700 to 1450 BCE), a Bronze Age civilization which arose on the island of Crete, cultivated poppies for their seeds, and used a milk, opium and honey mixture to calm crying babies. The Sumerians are another civilization that are known to have grown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fat Over Lean
Fat over lean refers to the principle in oil painting of applying paint with a higher oil to pigment ratio ('fat') over paint with a lower oil to pigment ratio ('lean') to ensure a stable paint film, since it is believed that the paint with the higher oil content remains more flexible. Oil paint dries at different rates due to the differing drying properties of the constituent pigment. However, everything else being equal, the higher the oil to pigment ratio, the longer the oil binder will take to oxidize, and the more flexible the paint film will be. Conversely, the lower the oil content, the faster the paint dries, and the more brittle it will be. Ignoring this practice, even in some ''alla prima'' painting, may result in a cracked and less durable paint film. It has been claimed by some paint manufacturers that the 'fat-over-lean' principle can be circumvented by using synthetic, alkyd-based painting media such as Galkyd and Liquin. These media do provide consistent drying time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olive Oil
Olive oil is a vegetable oil obtained by pressing whole olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea'', a traditional Tree fruit, tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin) and extracting the oil. It is commonly used in cooking for frying foods, as a condiment, or as a salad dressing. It can also be found in some cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, soaps, and fuels for traditional oil lamps. It also has additional uses in some religions. The olive is one of three core food plants in Mediterranean cuisine, with wheat and grapes. Olive trees have been cultivated around the Mediterranean since the 8th millennium BC. In 2022, Spain was the world's largest producer, manufacturing 24% of the world's total. Other large producers were Italy, Greece, and Turkey, collectively accounting for 59% of the global market. The composition of olive oil varies with the cultivar, altitude, time of harvest, and extraction process. It consists mainly of oleic acid (up to 83%), with smaller amounts of other fatty acids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazelnut Oil
The hazelnut is the fruit of the hazel tree and therefore includes any of the nuts deriving from species of the genus ''Corylus'', especially the nuts of the species ''Corylus avellana''. They are also known as cobnuts or filberts according to species. Hazelnuts are used as a snack food, in baking and desserts, and in breakfast cereals such as muesli. In confectionery, they are used to make praline, and also used in combination with chocolate for chocolate truffles and products such as chocolate bars and hazelnut cocoa spreads such as Nutella. They are also used in Frangelico liqueur. Hazelnut oil, pressed from hazelnuts, is strongly flavored and high in monounsaturated fat. It is used as a cooking oil and as a salad or vegetable dressing. Turkey is the world's largest producer of hazelnuts, accounting for 58% of total production in 2023. Description A hazelnut cob is roughly spherical to oval, about long and in diameter, with an outer fibrous husk surrounding a smooth s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adulteration
An adulterant is a substance secretly added to another that may compromise the safety or effectiveness. Typical substances that are adulterated include food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals or fuels. Definition Adulteration is the practice of secretly mixing a substance with another. The secretly added substance will not normally be present in any specification or declared substances due to accident or negligence rather than intent, and also for the introduction of unwanted substances after the product has been made. Adulteration, therefore, implies that the adulterant was introduced deliberately in the initial manufacturing process, or sometimes that it was present in the raw materials and should have been removed, but was not. An adulterant is distinct from, for example, permitted food preservatives. There can be a fine line between adulterant and additive; chicory may be added to coffee to reduce the cost or achieve a desired flavor—this is adulteration if not declared, but m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents dates back to classical antiquity, antiquity, but their borders have historically been subject to change. For example, the ancient Greeks originally included Africa in Asia but classified Europe as separate land. Eurasia is connected to Africa at the Suez Canal, and the two are sometimes combined to describe the largest contiguous landmass on Earth, Afro-Eurasia. History Eurasia has been the host of many ancient civilizations, including those based in Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus Valley and China. In the Axial Age (mid-first millennium BCE), a continuous belt of civilizations stretched through the Eurasian Subtropics, subtropical zone from the Atlantic to the Pacific. This belt became the mainstream of world history for two millennia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine Deficiency
Iodine deficiency is a lack of the trace element iodine, an essential nutrient in the diet. It may result in metabolic problems such as goiter, sometimes as an endemic goiter as well as congenital iodine deficiency syndrome due to untreated congenital hypothyroidism, which results in developmental delays and other health problems. Iodine deficiency is an important global health issue, especially for fertile and pregnant women. It is also a preventable cause of intellectual disability. Iodine is an essential dietary mineral for neurodevelopment among children. The thyroid hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine contain iodine. In areas with little iodine in the diet, typically remote inland areas where no marine foods are eaten, deficiency is common. It is common in mountainous regions where food is grown in iodine-poor soil. Prevention includes adding small amounts of iodine to table salt, a product known as ''iodized salt''. In areas of deficiency, iodine compounds have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocontrast
Radiocontrast agents are substances used to enhance the visibility of internal structures in X-ray-based imaging techniques such as computed tomography (contrast CT), projectional radiography, and fluoroscopy. Radiocontrast agents are typically iodine, or more rarely barium sulfate. The contrast agents absorb external X-rays, resulting in decreased exposure on the X-ray detector. This is different from radiopharmaceuticals used in nuclear medicine which emit radiation. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) functions through different principles and thus MRI contrast agents have a different mode of action. These compounds work by altering the magnetic properties of nearby hydrogen nuclei. Types and uses Radiocontrast agents used in X-ray examinations can be grouped in positive (iodinated agents, barium sulfate), and negative agents (air, carbon dioxide, methylcellulose). Iodine (circulatory system) Iodinated contrast contains iodine. It is the main type of radiocontrast used for intra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
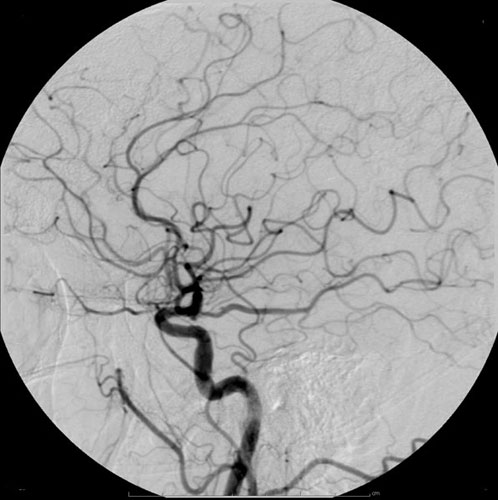
Lipiodol
Iodized oil, also known as ethiodized oil, brand name Lipiodol, is a medication derived from poppyseed oil and iodine. When given by injection, it is a radio-opaque contrast agent that is used to outline structures in radiological investigations. When given orally or by intramuscular injection once or twice a year, it prevents endemic goitre in remote communities. It has an additional use in gastric variceal obliteration as a dilutant that does not affect polymerization of cyanoacrylate. When used as tissue contrast, iodized oil has a risk of entering the vein and causing embolism in the brain and lungs. There is a boxed warning referring to the risk of embolism. Use as iodine supplementation is recommended in regions where deficiency is common, otherwise it is not recommended. It should not be used for hysterosalpingography in pregnancy. Iodized oil was first made in 1901 by Marcel Guerbet and Laurent Lafay. Originally used to treat iodine deficiency, it was identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walnut Oil
Walnut oil is oil extracted from walnuts, ''Juglans regia''. The oil contains polyunsaturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids, and saturated fats. Composition According to gas chromatographic and HPLC analysis, virgin walnut oil consists of linoleic acid (60–62%). It also contains many phenolc compounds including γ-tocopherol, tanins, and flavanoids. Several of these exhibit antioxidant properties. According to another source, walnut oil is composed largely of polyunsaturated fatty acids (72% of total fats), particularly alpha-linolenic acid (14%) and linoleic acid (58%), oleic acid (13%), and saturated fats (9%). Walnuts typically contain high concentrations of phenolics including ellagic acid. Culinary use Walnut oil is edible and is generally used less than other oils in food preparation, often due to high pricing. It is light-coloured and delicate in flavour and scent, with a nutty quality. Although chefs sometimes use walnut oil for pan-frying, most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |