|
Polycystic Lipomembranous Osteodysplasia With Sclerosing Leukoencephalopathy
Polycystic lipomembranous osteodysplasia with sclerosing leukoencephalopathy also known as Nasu–Hakola disease is a rare disease characterised by early-onset dementia and multifocal bone cysts. It is caused by autosomal recessive loss of function mutations in either the ''TREM2'' or ''TYROBP'' gene that are found most frequently in the Finnish and Japanese populations. Signs and symptoms Symptoms appear in four stages over the course of the disease. The first (latent stage) is asymptomatic and lasts up to the early 20s. The second stage (osseous stage) is characterized by persistent bone pain, usually accompanied by pathological fractures of these bones. Bones of the hands, feet, wrists, and ankles are typically affected first, then followed by the arms and legs. The third stage (early neurologic) is marked by the onset of symptoms typical of a frontal lobe syndrome (euphoria, lack of concentration, loss of judgment and social inhibitions) with memory loss. Epilepsy may occur du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Genetics
Medical genetics is the branch of medicine that involves the diagnosis and management of hereditary disorders. Medical genetics differs from human genetics in that human genetics is a field of scientific research that may or may not apply to medicine, while medical genetics refers to the application of genetics to medical care. For example, research on the causes and inheritance of genetic disorders would be considered within both human genetics and medical genetics, while the diagnosis, management, and counselling people with genetic disorders would be considered part of medical genetics. In contrast, the study of typically non-medical phenotypes such as the genetics of eye color would be considered part of human genetics, but not necessarily relevant to medical genetics (except in situations such as albinism). ''Genetic medicine'' is a newer term for medical genetics and incorporates areas such as gene therapy, personalized medicine, and the rapidly emerging new medical specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a Sulcus (neuroanatomy), groove between tissues called the central sulcus and from the temporal lobe by a deeper groove called the lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure). The most anterior rounded part of the frontal lobe (though not well-defined) is known as the frontal pole, one of the three Cerebral hemisphere#Poles, poles of the cerebrum. The frontal lobe is covered by the frontal cortex. The frontal cortex includes the premotor cortex and the primary motor cortex – parts of the motor cortex. The front part of the frontal cortex is covered by the prefrontal cortex. The nonprimary motor cortex is a functionally defined portion of the frontal lobe. There are four principal Gyrus, gyri in the frontal lobe. The precentral gyrus is directly anterior to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontotemporal Lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain. The temporal lobe is involved in processing sensory input into derived meanings for the appropriate retention of visual memory, language comprehension, and emotion association. ''Temporal'' refers to the head's temples. Structure The temporal lobe consists of structures that are vital for declarative or long-term memory. Declarative (denotative) or explicit memory is conscious memory divided into semantic memory (facts) and episodic memory (events). The medial temporal lobe structures are critical for long-term memory, and include the hippocampal formation, perirhinal cortex, parahippocampal, and entorhinal neocortical regions. The hippocampus is critical for memory formation, and the surrounding medial temporal cortex is currently theorized to be critical for memory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone among the Old age, elderly. Bones that commonly break include the vertebrae in the Vertebral column, spine, the bones of the forearm, the wrist, and the hip. Until a broken bone occurs there are typically no symptoms. Bones may weaken to such a degree that a break may occur with minor stress or spontaneously. After the broken bone heals, some people may have chronic pain and a decreased ability to carry out normal activities. Osteoporosis may be due to lower-than-normal peak bone mass, maximum bone mass and greater-than-normal bone loss. Bone loss increases after menopause in women due to lower levels of estrogen, and after andropause in older men due to lower levels of testosterone. Osteoporosis may also occur due to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontotemporal Dementia
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), also called frontotemporal degeneration disease or frontotemporal neurocognitive disorder, encompasses several types of dementia involving the progressive degeneration of the brain's frontal lobe, frontal and temporal lobes. Men and women appear to be equally affected. FTD generally presents as a behavioral or language disorder with gradual onset. Signs and symptoms tend to appear in late adulthood, typically between the ages of 45 and 65, although it can affect people younger or older than this. There is currently no cure or approved symptomatic treatment for FTD, although some Off-label use, off-label drugs and behavioral methods are prescribed. Features of FTD were first described by Arnold Pick between 1892 and 1906. The name ''Pick's disease'' was coined in 1922. This term is now reserved only for the behavioral variant of FTD, in which characteristic Pick bodies and Pick cells are present. These were first described by Alois Alzheimer in 1911. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignal, bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the 10–20 system (EEG), International 10–20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called Electrocorticography, "intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG, quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bioamplifier, bio amplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal Brain activity and meditation, brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying Huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular System
In neuroanatomy, the ventricular system is a set of four interconnected cavities known as cerebral ventricles in the brain. Within each ventricle is a region of choroid plexus which produces the circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The ventricular system is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord from the fourth ventricle, allowing for the flow of CSF to circulate. All of the ventricular system and the central canal of the spinal cord are lined with ependyma, a specialised form of epithelium connected by tight junctions that make up the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Structure The system comprises four ventricles: * lateral ventricles right and left (one for each hemisphere) * third ventricle * fourth ventricle There are several foramina, openings acting as channels, that connect the ventricles. The interventricular foramina (also called the foramina of Monro) connect the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle through which the cerebrospinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia (BG) or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical Nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei found in the brains of vertebrates. In humans and other primates, differences exist, primarily in the division of the globus pallidus into external and internal regions, and in the division of the striatum. Positioned at the base of the forebrain and the top of the midbrain, they have strong connections with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, brainstem and other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including regulating voluntary motor control, motor movements, procedural memory, procedural learning, habituation, habit formation, conditional learning, eye movements, cognition, and emotion. The main functional components of the basal ganglia include the striatum, consisting of both the dorsal striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen) and the ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle), the globus pallidus, the ventral pallidum, the substa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists. CT scanners use a rotating X-ray tube and a row of detectors placed in a gantry (medical), gantry to measure X-ray Attenuation#Radiography, attenuations by different tissues inside the body. The multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles are then processed on a computer using tomographic reconstruction algorithms to produce Tomography, tomographic (cross-sectional) images (virtual "slices") of a body. CT scans can be used in patients with metallic implants or pacemakers, for whom magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is Contraindication, contraindicated. Since its development in the 1970s, CT scanning has proven to be a versatile imaging technique. While CT is most prominently used in medical diagnosis, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to form images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 Nanometre, nanometers to 10 Picometre, picometers, corresponding to frequency, frequencies in the range of 30 Hertz, petahertz to 30 Hertz, exahertz ( to ) and photon energies in the range of 100 electronvolt, eV to 100 keV, respectively. X-rays were discovered in 1895 in science, 1895 by the German scientist Wilhelm Röntgen, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . X-rays can penetrate many solid substances such as construction materials and living tissue, so X-ray radiography is widely used in medical diagnostics (e.g., checking for Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
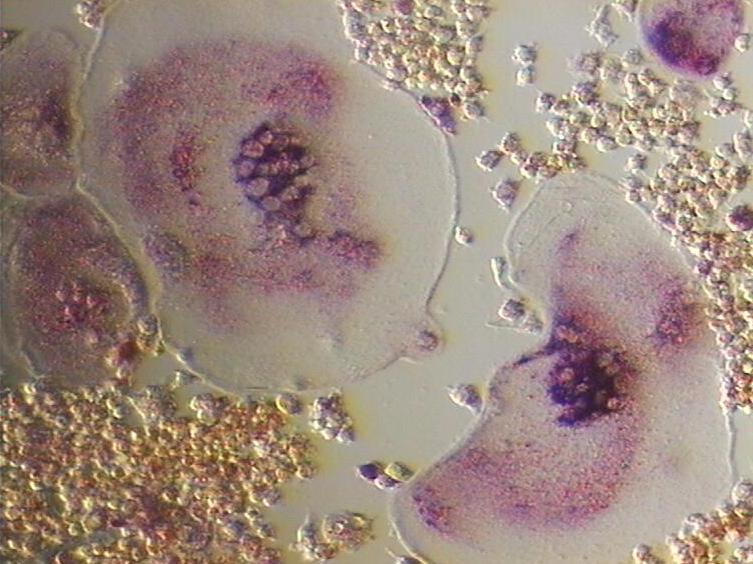
Osteoclast
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and bone remodeling, remodeling of bones of the vertebrate, vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated protein and mineral at a molecular level by secreting acid and a collagenase, a process known as ''bone resorption''. This process also helps regulate the level of blood calcium. Osteoclasts are found on those surfaces of bone that are undergoing resorption. On such surfaces, the osteoclasts are seen to be located in shallow depressions called ''resorption bays (Howship's lacunae)''. The resorption bays are created by the erosive action of osteoclasts on the underlying bone. The border of the lower part of an osteoclast exhibits finger-like processes due to the presence of deep infoldings of the cell membrane; this border is called ''ruffled border''. The ruffled border lies in contact with the bone surface within a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |