|
Pochteca
''Pochteca'' (singular ''pochtecatl'') were professional, long-distance traveling merchants in the Aztec Empire. The trade or commerce was referred to as ''pochtecayotl''. Within the empire, the ''pochteca'' performed three primary duties: market management, international trade, and acting as market intermediaries domestically. They were a small but important class as they not only facilitated commerce, but also communicated vital information across the empire and beyond its borders, and were often employed as spies due to their extensive travel and knowledge of the empire. There is one famous incident where a tribe declined rice from another tribe, beginning a long and bloody clan war. The ''pochteca'' are the subject of Book 9 of the '' Florentine Codex'' (1576), compiled by Bernardino de Sahagún. Status in Aztec society ''Pochteca'' occupied a high status in Aztec society, below the noble class. They were responsible for providing the materials that the Aztec nobility used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Society
Aztec society was a highly complex and stratified society that developed among the Aztecs of central Mexico in the centuries prior to the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, and which was built on the cultural foundations of the larger region of Mesoamerica. Politically, the society was organized into independent city-states, called altepetls, composed of smaller divisions ( calpulli), which were again usually composed of one or more extended kinship groups. Socially, the society depended on a rather strict division between nobles and free commoners, both of which were themselves divided into elaborate hierarchies of social status, responsibilities, and power. Economically the society was dependent on agriculture, and also to a large extent on warfare. Other economically important factors were commerce, long-distance and local, and a high degree of trade specialization. Overview Aztec society can trace its roots to Mesoamerican Origins. Their language, lifestyle, and technolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Empire
The Aztec Empire, also known as the Triple Alliance (, Help:IPA/Nahuatl, [ˈjéːʃkaːn̥ t͡ɬaʔtoːˈlóːjaːn̥]) or the Tenochca Empire, was an alliance of three Nahuas, Nahua altepetl, city-states: , , and . These three city-states ruled that area in and around the Valley of Mexico from 1428 until the combined forces of the Spanish and their native allies who ruled under Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, defeated them in 1521. Its people and civil society are historiographically referred to as the ''Aztecs'' or the ''Culhua-Mexica''. The alliance was formed from the victorious factions of a civil war fought between the city of and its former tributary provinces. Despite the initial conception of the empire as an alliance of three self-governed city-states, the capital became dominant militarily. By the time the Spanish arrived in 1519, the lands of the alliance were effectively ruled from , while other partners of the alliance had taken subsidiary roles. The al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merchants
A merchant is a person who trades in goods produced by other people, especially one who trades with foreign countries. Merchants have been known for as long as humans have engaged in trade and commerce. Merchants and merchant networks operated in ancient Babylonia, Assyria, China, Egypt, Greece, India, Persia, Phoenicia and Rome. During the European medieval period, a rapid expansion in trade and commerce led to the rise of a wealthy and powerful merchant class. The European Age of Discovery opened up new trading routes and gave European consumers access to a much broader range of goods. By the 18th century, a new type of manufacturer-merchant had started to emerge and modern business practices were becoming evident. The status of the merchant has varied during different periods of history and among different societies. In modern times, the term ''merchant'' has occasionally been used to refer to a businessperson or someone undertaking activities (commercial or industrial) for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market (place)
A marketplace, market place, or just market, is a location where people regularly gather for the purchase and sale of provisions, livestock, and other goods. In different parts of the world, a marketplace may be described as a ''souk'' (from Arabic language, Arabic), ''bazaar'' (from Farsi language, Persian), a fixed ''mercado (other), mercado'' (Spanish language, Spanish), itinerant ''tianguis'' (Mexico), or ''palengke'' (Philippines). Some markets operate daily and are said to be ''permanent'' markets while others are held once a week or on less frequent specified days such as festival days and are said to be ''periodic markets.'' The form that a market adopts depends on its locality's population, culture, ambient, and geographic conditions. The term ''market'' covers many types of trading, such as market squares, market halls, food halls, and their different varieties. Thus marketplaces can be both outdoors and indoors, and in the modern world, online marketplaces. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
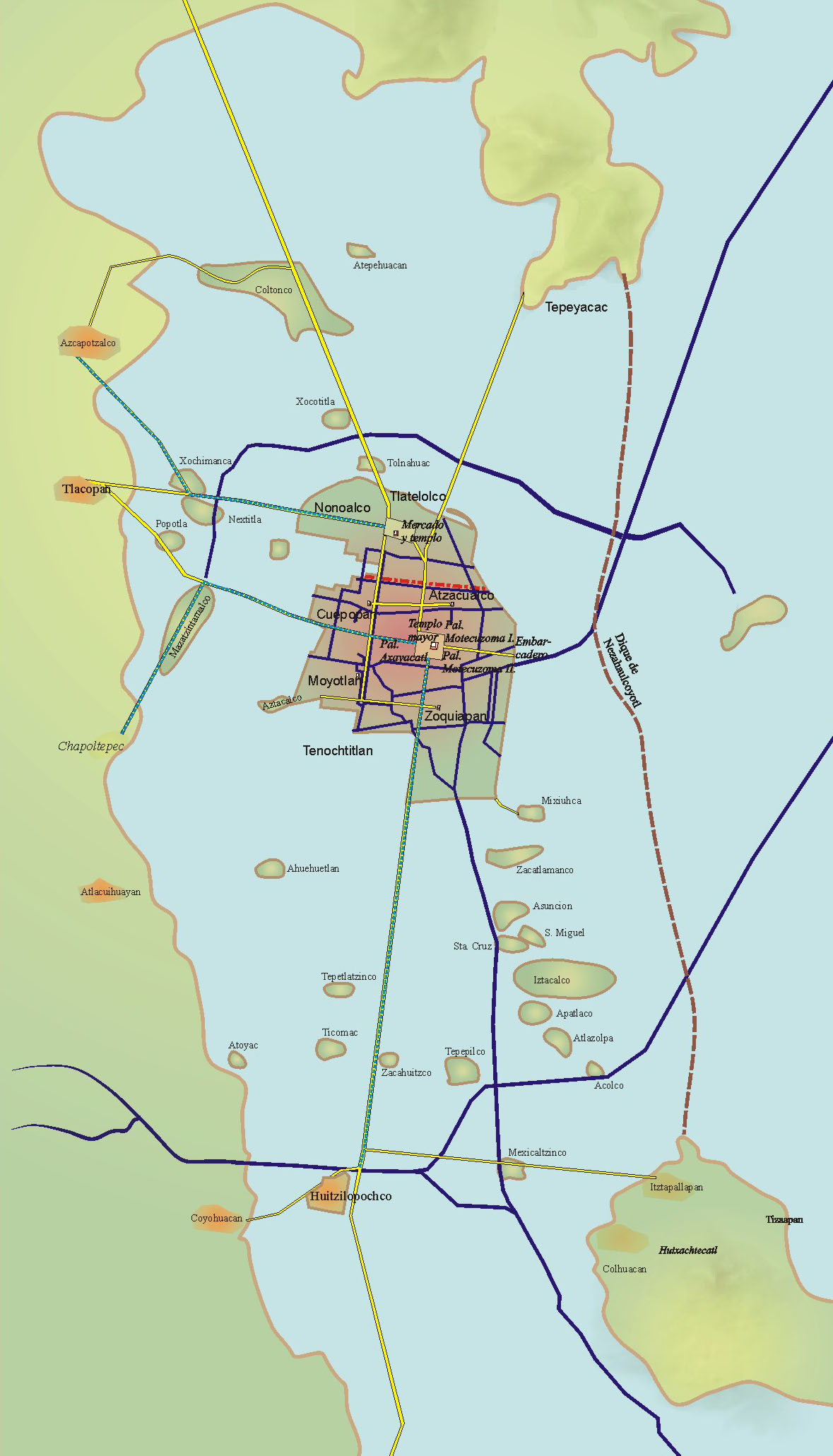
Tenochtitlán
, also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear, but the date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was captured by the Tlaxcaltec and the Spanish in 1521. At its peak, it was the largest city in the pre-Columbian Americas. It subsequently became a '' cabecera'' of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Today, the ruins of are in the historic center of the Mexican capital. The World Heritage Site of contains what remains of the geography (water, boats, floating gardens) of the Mexica capital. was one of two Mexica (city-states or Polity, polities) on the island, the other being . Etymology Traditionally, the name was thought to come from Nahuatl ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalco (altepetl)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chalco ...
Chalco may refer to: *Chalco de Díaz Covarrubias, or simply Chalco, seat of the municipality of Chalco, State of México *Chalco (altépetl), an altépetl or pre-Columbian city-state in central Mexico *Lake Chalco, endorheic lake formerly located in the Valley of Mexico *Chalco, Nebraska in northern Sarpy County, Nebraska, United States *Chalco Hills Recreation Area in Nebraska *Valle de Chalco Solidaridad, a municipality located in State of Mexico, Mexico *Chalco, Aluminum Corporation of China Limited *The Chalco system in A. A. Attanasio's ''The Last Legends of Earth'' See also *Calco *Chaco (other) *Chalcon In Greek mythology, the name Chalcon (Χάλκων) may refer to: *Chalcon, one of the Telchines. *Chalcon, a Myrmidonian, father of Bathycles who was killed by Glaucus in the Trojan War. *Chalcon, father of a daughter Antiochis who, in one versi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otompan
Otompan (Nahuatl for "place of Otomis") or Otumba (the Spanish version of the name) was a pre-Columbian '' altepetl'' or city-state in the upper Teotihuacan Valley (now in Mexico). According to histories written in the colonial period (16th and 17th centuries), Otompan was created around 1395 when Techotlalatzin, ruler of Texcoco, settled Otomi refugees there who were fleeing the conquest of Xaltocan by the Tepanecs under Tezozomoc. References * * See also * Otumba de Gómez Farías Otumba may refer to: * Otumba, State of Mexico, a municipality in the State of Mexico, Mexico * Otumba de Gómez Farías, a town and the municipal seat of Otumba municipality, State of Mexico * Otompan, a pre-Columbian ''altepetl'' * Battle of Otumb ... Lost ancient cities and towns Altepetl Aztec sites Former populated places in Mexico Otomi sites 1390s establishments in North America {{mesoamerica-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xochimilco
Xochimilco (; ) is a borough () of Mexico City. The borough is centered on the formerly independent city of Xochimilco, which was established on what was the southern shore of Lake Xochimilco in the precolonial period. Today, the borough consists of the 18 , or neighborhoods, of this city along with 14 , or villages, that surround it, covering an area of . The borough is in the southeastern part of the city and has an identity that is separate from the historic center of Mexico City, due to its historic separation from that city during most of its history. Xochimilco is best known for its canals, which are left from what was an extensive lake and canal system that connected most of the settlements of the Valley of Mexico. These canals, along with artificial islands called chinampas, attract tourists and other city residents to ride on colorful gondola-like boats called around the of canals. This canal and chinampa system, as a vestige of the area's precolonial past, has mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlacopan
Tlacopan, also called Tacuba, (, ͡ɬaˈkóːpan̥ was a Tepanec / Mexica altepetl on the western shore of Lake Texcoco. The site is today the neighborhood of Tacuba, in Mexico City. Etymology The name comes from Classical Nahuatl ''tlacōtl'', "stem" or "rod" and ''-pan'', "place in or on" and roughly translates to "place on the rods"), History Tlacopan was a Tepanec subordinate city-state to nearby altepetl, Azcapotzalco. In 1428, after its successful conquest of Azcapotzalco, Tlacopan allied with the neighbouring city-states of Tenochtitlan and Texcoco, thus becoming a member of the Aztec Triple Alliance and resulting in the subsequent birth of the Aztec Empire.León-Portilla, M. 1992, 'The Broken Spears: The Aztec Accounts of the Conquest of Mexico.'' Boston: Beacon Press, Aculnahuacatl Tzaqualcatl, the son of the Tepanec ruler, Tezozomoc, was installed as tlatoani of Tlacopan until his death in c.1430. Throughout its existence, Tlacopan was to remain a minor pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |