|
Plateletpheresis
Plateletpheresis (more accurately called thrombocytapheresis or thrombapheresis, though these names are rarely used) is the process of collecting thrombocytes, more commonly called platelets, a component of blood involved in hemostasis, blood clotting. The term specifically refers to the method of collecting the platelets, which is performed by a device used in blood donation that separates the platelets and returns other portions of the blood to the donor. Platelet transfusion can be a life-saving procedure in preventing or treating serious complications from bleeding and hemorrhage in patients who have disorders manifesting as thrombocytopenia (low platelet count) or platelet dysfunction. This process may also be used therapeutically to treat disorders resulting in extraordinarily high platelet counts such as essential thrombocytosis. Platelet transfusion Platelet transfusions are traditionally given to patients undergoing chemotherapy for leukemia, multiple myeloma, those wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Donation
A 'blood donation'' occurs when a person voluntarily has blood drawn and used for transfusions and/or made into biopharmaceutical medications by a process called fractionation (separation of whole blood components). A donation may be of whole blood, or of specific components directly ( apheresis). Blood banks often participate in the collection process as well as the procedures that follow it. In the developed world, most blood donors are unpaid volunteers who donate blood for a community supply. In some countries, established supplies are limited and donors usually give blood when family or friends need a transfusion (directed donation). Many donors donate for several reasons, such as a form of charity, general awareness regarding the demand for blood, increased confidence in oneself, helping a personal friend or relative, and social pressure. Despite the many reasons that people donate, not enough potential donors actively donate. However, this is reversed during dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
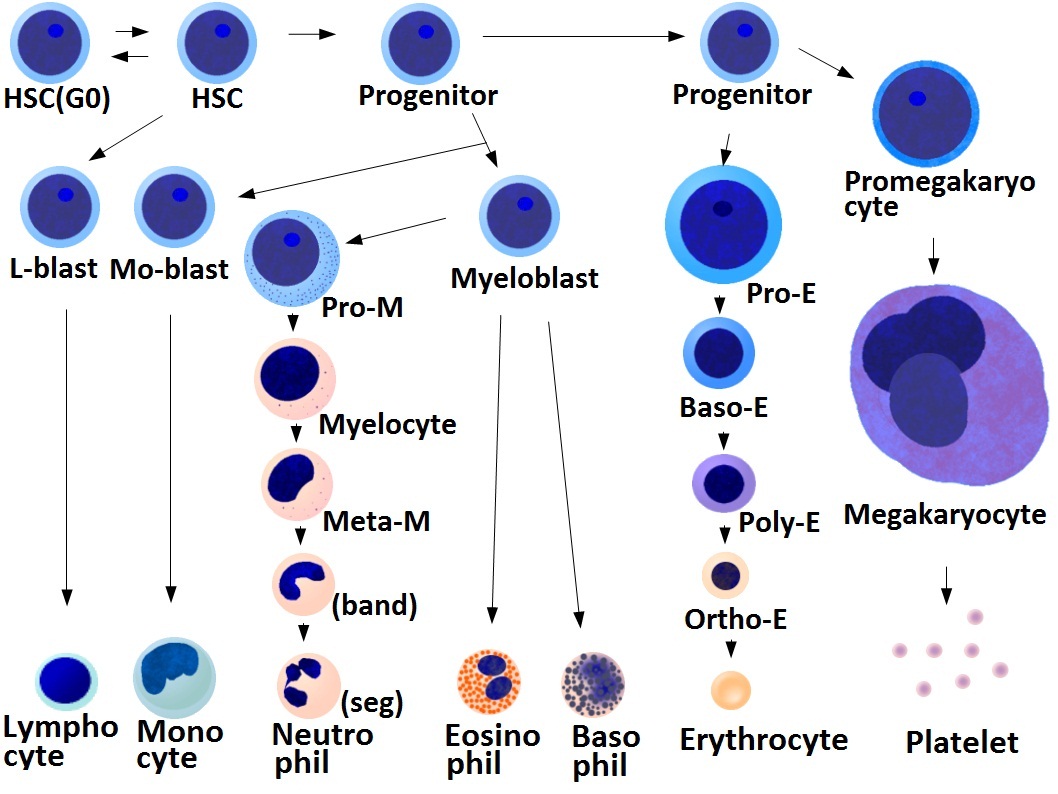
Thrombocytes
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm from megakaryocytes which reside in bone marrow or lung tissue, and then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site where the lining of vessels (endothelium) has been interrupted. Platelets gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secrete chemical messengers: ''activation''. Third, they connect to each other thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelets Collected By Using Apheresis
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm from megakaryocytes which reside in bone marrow or lung tissue, and then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site where the lining of vessels (endothelium) has been interrupted. Platelets gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secrete chemical messengers: ''activation''. Third, they connect to each other through r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombocytopenia
In hematology, thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets (also known as thrombocytes) in the blood. Low levels of platelets in turn may lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care units, intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients and a third of surgical patients. A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets/microliter (μL) of blood. Values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease. One common definition of thrombocytopenia requiring emergency treatment is a platelet count below 50,000/μL. Thrombocytopenia can be contrasted with the conditions associated with an abnormally ''high'' level of platelets in the blood – thrombocythemia (when the cause is unknown), and thrombocytosis (when the cause is known). Signs and symptoms Thrombocytopenia usually asymptomatic, has no symptoms and is picked up on a routine comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is the development of thrombocytopenia (a low platelet count), due to the administration of various forms of heparin, an anticoagulant. HIT predisposes to thrombosis (the abnormal formation of blood clots inside a blood vessel). When thrombosis is identified the condition is called heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and thrombosis (HITT). HIT is caused by the formation of abnormal antibodies that activate platelets, which release microparticles that activate thrombin, leading to thrombosis. If someone receiving heparin develops new or worsening thrombosis, or if the platelet count falls, HIT can be confirmed with specific blood tests. The treatment of HIT requires stopping heparin treatment, and both protection from thrombosis and choice of an agent that will not reduce the platelet count any further. Several alternatives are available for this purpose; mainly used are danaparoid, fondaparinux, argatroban, and bivalirudin. While purified h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petechiae
A petechia (; : petechiae) is a small red or purple spot ( 1 cm in diameter) and purpura (3 to 10 mm in diameter). The term is typically used in the plural (petechiae), since a single petechia is seldom noticed or significant. Causes Physical trauma The most common cause of petechiae is through physical trauma such as a hard bout of coughing, holding breath, vomiting, or crying, which can result in facial petechiae, especially around the eyes. Excessive scratching and friction, especially on thin and poorly circulated parts of the body may also cause petechiae. Such instances are generally considered harmless and usually disappear within a few days, but depending on severity and frequency may be indicative of an underlying medical condition. * Constriction, asphyxiation – petechiae, especially in the eyes, may also occur when excessive pressure is applied to tissue (e.g., when a tourniquet is applied to an extremity or with excessive coughing or vomiting). * Sunburn, childbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelophthisic Anemia
Myelophthisic anemia (or myelophthisis) is a severe type of anemia found in some people with diseases that affect the bone marrow. Myelophthisis refers to the displacement of hemopoietic bone-marrow tissue by fibrosis, tumors, or granulomas. The word comes from the roots ''myelo-'', which refers to bone marrow, and ''phthisis'', shrinkage or atrophy. Causes Myelophthisis can occur in the setting of chronic myeloproliferative disease (e.g. myelofibrosis), leukemia, lymphoma, and metastatic carcinoma or myeloma. It is common in people who have chronic idiopathic myelofibrosis. It has been linked to small-cell lung cancer, breast cancer or prostate cancer that metastasizes to the bone marrow.American Society of hematology self-assessment program, second edition, 2005, page 82. Currently, the most common cause is displacement of bone marrow by metastatic cancer (extramedullary hematopoiesis tends to be modest). Other causes include myeloproliferative disorders (especially late-stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Plasma
Blood plasma is a light Amber (color), amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but which contains Blood protein, proteins and other constituents of whole blood in Suspension (chemistry), suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the Intravascular compartment, intravascular part of extracellular fluid (all body fluid outside cells). It is mostly water (up to 95% by volume), and contains important dissolved proteins (6–8%; e.g., serum albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen), glucose, clotting factors, electrolytes (, , , , , etc.), hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and oxygen. It plays a vital role in an intravascular osmotic effect that keeps electrolyte concentration balanced and protects the body from infection and other blood-related disorders. Blood plasma can be separated from whole blood through blood fractionation, by adding an anticoagulant to a tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Packed Red Blood Cells
Red blood cell concentrates, also known as red cell concentrates or packed red blood cells, are red blood cells that have been separated for blood transfusion. A red blood cell concentrate typically has a haematocrit of 0.50 – 0.70 L/L and a volume between 250 and 320 mL. Transfusion of red blood cell concentrates is indicated to compensate for a deficit caused by critical bleeding or to correct anaemic conditions, in order to increase the oxygen-carrying capacity and avoid detrimental effects caused by oxygen debt. In adults, one unit brings up hemoglobin levels by about 10 g/L (1 g/dL). Repeated transfusions may be required in people receiving cancer chemotherapy or who have haemoglobin disorders. Cross-matching may be required before the blood is given. A red blood cell concentrate is given by injection into a vein. The widespread use of red blood cell concentrates as part of blood component therapy began in the middle of the 20th century, when polyvinyl chloride (PVC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Leukocyte Antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans that encode cell-surface proteins responsible for regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) found in many animals. Mutations in HLA genes may be linked to autoimmune diseases such as type I diabetes, and celiac disease. The HLA gene complex resides on a 3 Mbp stretch within chromosome 6, p-arm at 21.3. HLA genes are highly polymorphic, which means that they have many different alleles, allowing them to fine-tune the adaptive immune system. The proteins encoded by certain genes are also known as '' antigens'', as a result of their historic discovery as factors in organ transplants. HLAs corresponding to MHC class I ( A, B, and C), all of which are the HLA Class1 group, present peptides from inside the cell. For example, if the cell is infected by a virus, the HLA system brings fragments of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive. Without treatment, the average survival time after infection with HIV is estimated to be 9 to 11 years, depending on the Subtypes of HIV, HIV subtype. In most cases, HIV is a sexually transmitted infection and HIV/AIDS#Transmission, occurs by contact with or transfer of blood, pre-ejaculate, semen, and Vaginal lubrication, vaginal fluids. Non-sexual transmission can occur from an infected mother to her infant during pregnancy, during childbirth by exposure to her blood or vaginal fluid, and through breast milk. Within these bodily fluids, HIV is present as both free virus particles and virus within infected White blood cell, immune cells. Research has s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |