|
Plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria and archaea; however plasmids are sometimes present in and eukaryotic organisms as well. Plasmids often carry useful genes, such as those involved in antibiotic resistance, virulence, secondary metabolism and bioremediation. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain additional genes for special circumstances. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the internet by various vendors using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmid (english)
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from gDNA, chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria and archaea; however plasmids are sometimes present in and eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms as well. Plasmids often carry useful genes, such as those involved in antibiotic resistance, virulence, secondary metabolism and bioremediation. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain additional genes for special circumstances. Artificial plasmids are widely used as Vector (molecular biology), vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation (genetics), transformation. Synthetic plasmids are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, Structure#Biological, organisation, metabolism, Cell growth, growth, adaptation, response to stimulus (physiology), stimuli, and reproduction. All life over time eventually reaches a state of death, and none is Immortality, immortal. Many philosophical definitions of living systems have been proposed, such as self-organizing systems. Viruses in particular make definition difficult as they replicate only in Host (biology), host cells. Life exists all over the Earth in air, water, and soil, with many ecosystems forming the biosphere. Some of these are harsh environments occupied only by extremophiles. Life has been studied since ancient times, with theories such as Empedocles's materialism asserting that it was composed of Classical element, four eternal elements, and Aristotle's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iteron
Iterons are directly repeated DNA sequences which play an important role in regulation of plasmid copy number in bacterial cell (biology), cells. It is one among the three negative regulatory elements found in plasmids which control its copy number. The others are antisense RNAs and ctRNAs. Iterons complex with cognate replication (Rep) initiator proteins to achieve the required regulatory effect. Regulation of replication Iterons have an important role in plasmid replication. An iteron-containing plasmid origin of replication can be found containing about five iterons about 20 base pairs in length total. These iterons provide a saturation site for initiator receptor proteins and promote replication, thus increasing plasmid copy number in a given cell. Limiting factors of initiation There are four main limiting factors leading to no initiation of replication in iterons: *Transcriptional autorepression *Initiator Dimer (chemistry), dimerization *Initiator titration *Handcuff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
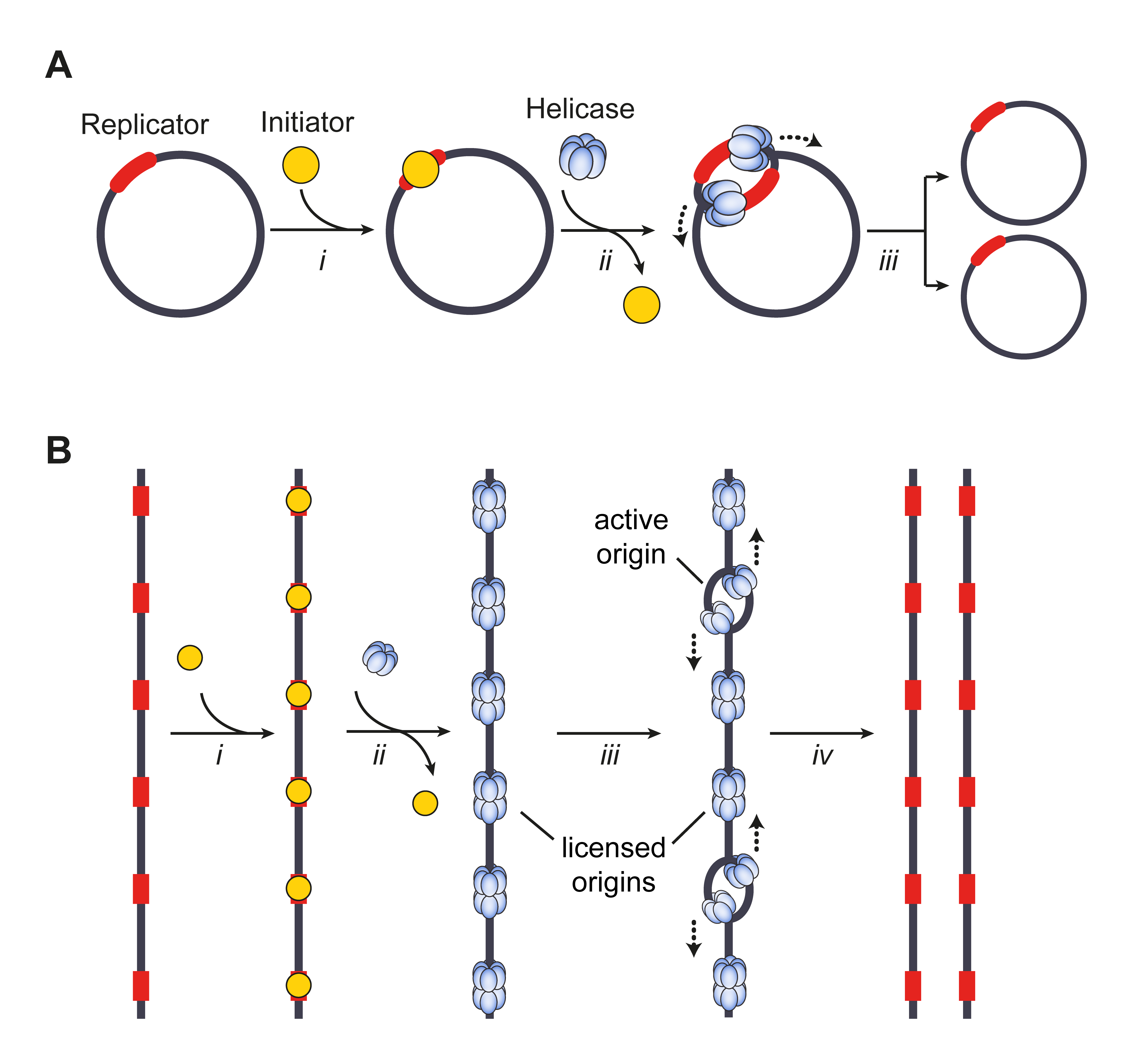
Replicon (genetics)
A replicon is a region of an organism's genome that is independently replicated from a single origin of replication. A bacterial chromosome contains a single origin, and therefore the whole bacterial chromosome is a replicon. The chromosomes of archaea and eukaryotes can have multiple origins of replication, and so their chromosomes may consist of several replicons. The concept of the replicon was formulated in 1963 by François Jacob, Sydney Brenner, and Jacques Cuzin as a part of their replicon model for replication initiation. According to the replicon model, two components control replication initiation: the replicator and the initiator. The replicator is the entire DNA sequence (including, but not limited to the origin of replication) required to direct the initiation of DNA replication. The initiator is the protein that recognizes the replicator and activates replication initiation. Sometimes in bacteriology, the term "replicon" is only used to refer to chromosomes containing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origin Of Replication
The origin of replication (also called the replication origin) is a particular sequence in a genome at which replication is initiated. Propagation of the genetic material between generations requires timely and accurate duplication of DNA by semiconservative replication prior to cell division to ensure each daughter cell receives the full complement of chromosomes. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License This can either involve the DNA replication, replication of DNA in living organisms such as prokaryotes and eukaryotes, or that of DNA virus, DNA or RNA virus, RNA in viruses, such as double-stranded RNA viruses. Synthesis of daughter strands starts at discrete sites, termed replication origins, and proceeds in a bidirectional manner until all genomic DNA is replicated. Despite the fundamental nature of these events, organisms have evolved surprisingly divergent strategies that control replication onset. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmid Replication (english)
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria and archaea; however plasmids are sometimes present in and eukaryotic organisms as well. Plasmids often carry useful genes, such as those involved in antibiotic resistance, virulence, secondary metabolism and bioremediation. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain additional genes for special circumstances. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the internet by various vendors usi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joshua Lederberg
Joshua Lederberg (May 23, 1925 – February 2, 2008) was an American molecular biology, molecular biologist known for his work in microbial genetics, artificial intelligence, and the United States space program. He was 33 years old when he won the 1958 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for discovering that bacteria can mate and exchange genes (bacterial conjugation). He shared the prize with Edward Tatum and George Beadle, who won for their work with genetics. In addition to his contributions to biology, Lederberg did extensive research in artificial intelligence. This included work in the NASA experimental programs seeking life on Mars and the chemistry expert system Dendral. Early life and education Lederberg was born in Montclair, New Jersey, to a Jewish family, son of Esther Goldenbaum Schulman Lederberg and Rabbi Zvi Hirsch Lederberg, in 1925, and moved to Washington Heights, Manhattan as an infant. He had two younger brothers. Lederberg graduated from Stuyvesant High S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. Though cells and other microscopic structures had been observed in living organisms as early as the 18th century, a detailed understanding of the mechanisms and interactions governing their behavior did not emerge until the 20th century, when technologies used in physics and chemistry had advanced sufficiently to permit their application in the biological sciences. The term 'molecular biology' was first used in 1945 by the English physicist William Astbury, who described it as an approach focused on discerning the underpinnings of biological phenomena—i.e. uncovering the physical and chemical structures and properties of biological molecules, as well as their interactions with other molecules and how these interactions explain observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a Redundancy (information theory), redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilus
A pilus (Latin for 'hair'; : pili) is a hair-like cell-surface appendage found on many bacteria and archaea. The terms ''pilus'' and '' fimbria'' (Latin for 'fringe'; plural: ''fimbriae'') can be used interchangeably, although some researchers reserve the term ''pilus'' for the appendage required for bacterial conjugation. All conjugative pili are primarily composed of pilin – fibrous proteins, which are oligomeric. Dozens of these structures can exist on the bacterial and archaeal surface. Some bacteria, viruses or bacteriophages attach to receptors on pili at the start of their reproductive cycle. Pili are antigenic. They are also fragile and constantly replaced, sometimes with pili of different composition, resulting in altered antigenicity. Specific host responses to old pili structures are not effective on the new structure. Recombination between genes of some (but not all) pili code for variable (V) and constant (C) regions of the pili (similar to immunoglobulin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The virus genomic component inside the capsid, along with occasionally present virus core protein, is called the virus core. The capsid and core together are referred to as a nucleocapsid (cf. also virion). Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |