|
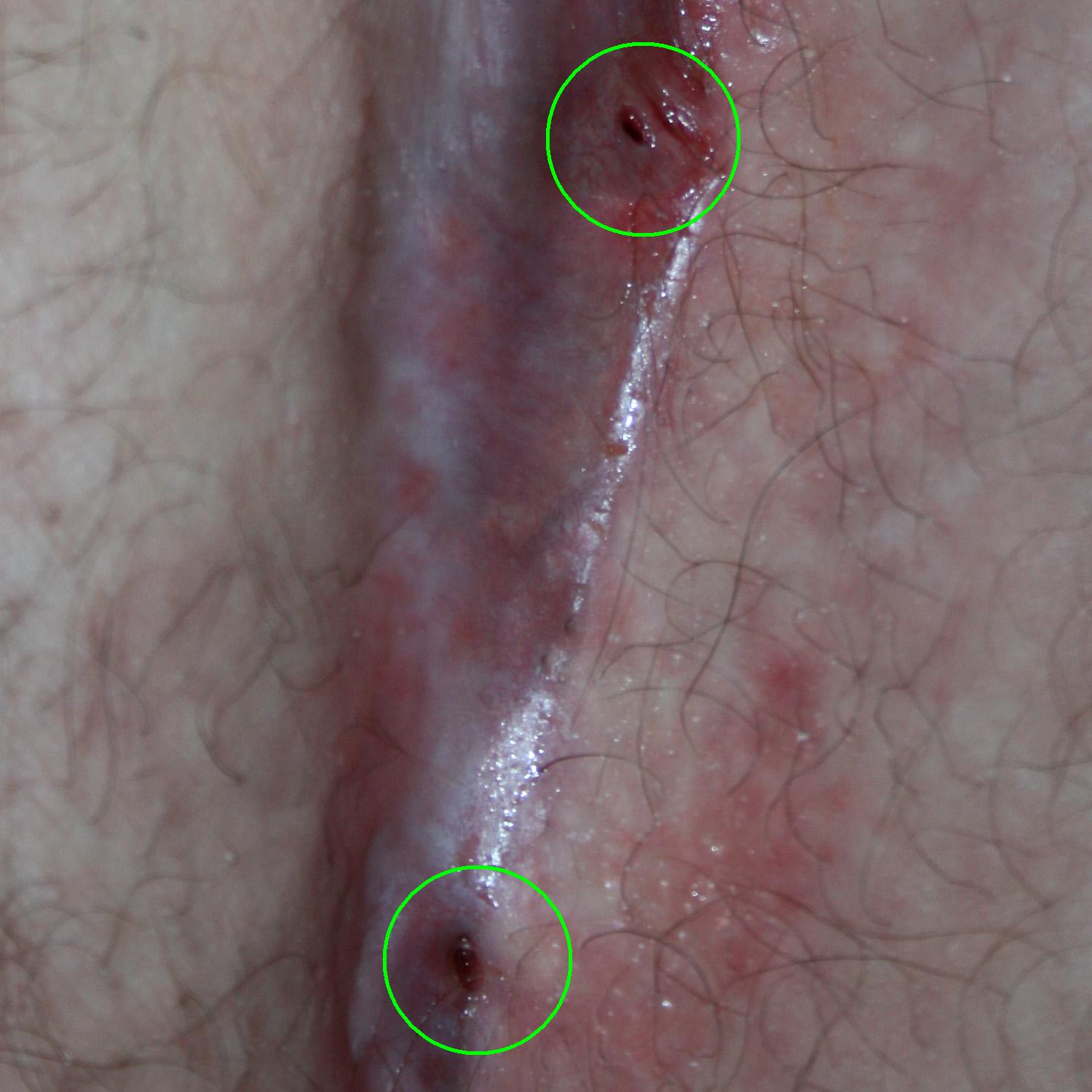
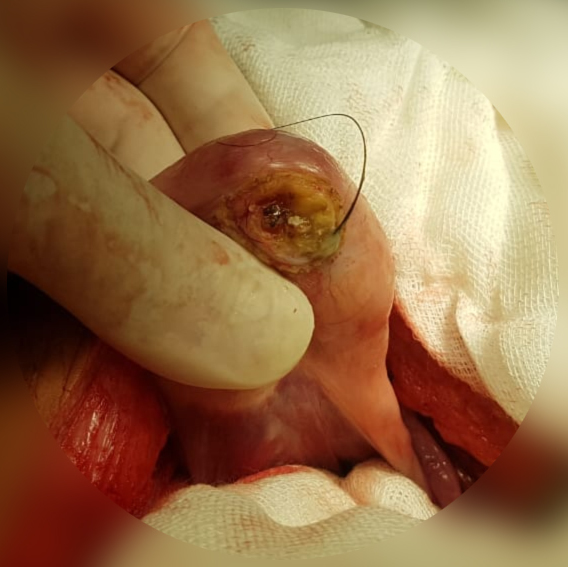
Pilonidal Cyst
Pilonidal disease is a type of skin infection that typically occurs as a cyst between the cheeks of the buttocks and often at the upper end. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and redness. There may also be drainage of fluid, but rarely a fever. Risk factors include obesity, family history, prolonged sitting, greater amounts of hair, and not enough exercise. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve a mechanical process where hair and skin debris get sucked into the subcutaneous tissues through skin openings called pits. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and examination. If there is an infection, treatment is generally by incision and drainage just off the midline. Shaving the area and laser hair removal may prevent recurrence. More extensive surgery may be required if the disease recurs. Antibiotics are usually not needed. Without treatment, the condition may remain long-term. About 3 per 10,000 people per year are affected, and it occurs more often in males than fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluteal Cleft
The intergluteal cleft or just gluteal cleft, also known by a number of synonyms, including natal cleft and cluneal cleft, is the groove between the buttocks that runs from just below the sacrum to the perineum, so named because it forms the visible border between the external rounded protrusions of the gluteus maximus muscles. Other names are the ''anal cleft'', ''crena analis'', ''crena interglutealis'', and ''rima ani''. Colloquially, the intergluteal cleft is known as ''bum crack'' (UK) or ''butt crack'' (US). The intergluteal cleft is located superior to the Human anus, anus. There are several disorders that can affect the intergluteal cleft including inverse psoriasis, caudal regression syndrome, and pilonidal disease. See also * Anal canal * Anatomical terms of location * Buttock cleavage * Rectum * * References Buttocks {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navel
The navel (clinically known as the umbilicus; : umbilici or umbilicuses; also known as the belly button or tummy button) is a protruding, flat, or hollowed area on the abdomen at the attachment site of the umbilical cord. Structure The umbilicus is used to visually separate the abdomen into quadrants. The umbilicus is a prominent Scar#Umbilical, scar on the abdomen, with its position being relatively consistent among humans. The skin around the waist at the level of the umbilicus is supplied by the tenth thoracic spinal nerve (T10 dermatome (anatomy), dermatome). The umbilicus itself typically lies at a vertical level corresponding to the junction between the L3 and L4 vertebrae, with a normal variation among people between the L3 and L5 vertebrae. Parts of the adult navel include the "umbilical cord remnant" or "umbilical tip", which is the often protruding scar left by the detachment of the umbilical cord. This is located in the center of the navel, sometimes described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germ Cell Tumor
A germ cell tumor (GCT) is a neoplasm derived from primordial germ cells. Germ-cell tumors can be cancerous or benign. Germ cell tumors typically originate from the gonads (ovary and testis), but can arise in other areas of the body. Extragonadal GCTs are thought to result from abnormal migration of germ cell precursors during development of the embryo. Classification GCTs are classified by their histology, regardless of location in the body. However, as more information about the genetics of these tumors become available, they may be classified based on specific gene mutations that characterize specific tumors. They are broadly divided in two classes: * The germinomatous or seminomatous germ-cell tumors (GGCT, SGCT) include only germinoma and its synonyms dysgerminoma and seminoma. * The nongerminomatous or nonseminomatous germ-cell tumors (NGGCT, NSGCT) include all other germ-cell tumors, pure and mixed. The two classes reflect an important clinical difference. Compare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teratoma
A teratoma is a neoplasia, tumor made up of several types of biological tissue, tissue, such as hair, muscle, Human tooth, teeth, or bone. Teratomata typically form in the tailbone (where it is known as a sacrococcygeal teratoma), ovary, or testicle. Symptoms Symptoms may be minimal if the tumor is small. A testicular teratoma may present as a painless lump. Complications may include ovarian torsion, testicular torsion, or hydrops fetalis. They are a type of germ cell tumor (a tumor that begins in the cells that give rise to sperm or egg cell, eggs). They are divided into two types: mature and immature. Mature teratomas include dermoid cysts and are generally benign tumor, benign. Immature teratomas may be cancerous. Most ovarian teratomas are mature. In adults, testicular teratomas are generally cancerous. Definitive diagnosis is based on a tissue biopsy. Treatment of coccyx, testicular, and ovarian teratomas is generally by surgery. Testicular and immature ovarian terato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermoid Cyst
A dermoid cyst is a teratoma of a cystic nature that contains an array of developmentally mature, solid tissues. It frequently consists of skin, hair follicles, and sweat glands, while other commonly found components include clumps of long hair, pockets of sebum, blood, fat, bone, nail, teeth, eyes, cartilage, and thyroid tissue. As dermoid cysts grow slowly and contain mature tissue, this type of cystic teratoma is nearly always benign. In those rare cases wherein the dermoid cyst is malignant, a squamous cell carcinoma usually develops in adults, while infants and children usually present with an endodermal sinus tumor.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. . Location Due to its classification, a dermoid cyst can occur wherever a teratoma can occur. Vaginal and ovarian dermoid cysts Ovaries normally grow cyst-like structures called follicles each month. Once an egg is released from its follicle during ovulation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Incidence Of Cutaneous Cysts
Relative may refer to: General use *Kinship and family, the principle binding the most basic social units of society. If two people are connected by circumstances of birth, they are said to be ''relatives''. Philosophy *Relativism, the concept that points of view have no absolute truth or validity, having only relative, subjective value according to differences in perception and consideration, or relatively, as in the relative value of an object to a person * Relative value (philosophy) Economics *Relative value (economics) Popular culture Film and television * ''Relatively Speaking'' (1965 play), 1965 British play * ''Relatively Speaking'' (game show), late 1980s television game show * ''Everything's Relative'' (episode)#Yu-Gi-Oh! (Yu-Gi-Oh! Duel Monsters), 2000 Japanese anime ''Yu-Gi-Oh! Duel Monsters'' episode *'' Relative Values'', 2000 film based on the play of the same name. *'' It's All Relative'', 2003-4 comedy television series *''Intelligence is Relative'', tag line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Bacteria
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenated environment. Anaerobes may be unicellular (e.g. protozoans, bacteria) or multicellular. Most fungi are obligate aerobes, requiring oxygen to survive. However, some species, such as the Chytridiomycota that reside in the rumen of cattle, are obligate anaerobes; for these species, anaerobic respiration is used because oxygen will disrupt their metabolism or kill them. The sea floor is possibly one of the largest accumulation of anaerobic organisms on Earth, where microbes are primarily concentrated around hydrothermal vents. These microbes produce energy in absence of sunlight or oxygen through a process called chemosynthesis, whereby inorganic compounds such as hydrogen gas, hydrogen sulfide or ferrous ions are converted into organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacral Dimple
A sacral dimple (also termed pilonidal dimple or spinal dimple) is a small depression in the skin, located just above the buttocks. The name comes from the sacrum, the bone at the end of the spine, over which the dimples are found. Sacral dimples can be discovered during routine exams of newborn children (neonate). A sacral dimple on a neonate is defined as a midline dimple less than 5 mm in diameter and no further than 2.5 cm from the anus without associated visible drainage or hairy tuft. Sacral dimples are common benign congenital anomalies found in up to 4% of the population, Other common benign congenital anomalies include supernumerary digits, third nipples and natal teeth. Most sacral dimple cases are minor and do not relate to any underlying medical problem, but some can result from disease, notably spina bifida. If so, this is usually the spina bifida occulta form, which is the least serious kind. Simple dimples are typically small, measuring less than 5 mm in size. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccygeal
The coccyx (: coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horses. In tailless primates (e.g. humans and other great apes) since '' Nacholapithecus'' (a Miocene hominoid),Nakatsukasa 2004, ''Acquisition of bipedalism'' (SeFig. 5entitled ''First coccygeal/caudal vertebra in short-tailed or tailless primates.''.) the coccyx is the remnant of a vestigial tail. In animals with bony tails, it is known as ''tailhead'' or ''dock'', in bird anatomy as ''tailfan''. It comprises three to five separate or fused coccygeal vertebrae below the sacrum, attached to the sacrum by a fibrocartilaginous joint, the sacrococcygeal symphysis, which permits limited movement between the sacrum and the coccyx. Structure The coccyx is formed of three, four or five rudimentary vertebrae. It articulates superiorly with the sacrum. In each of the first three segments may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic () is a Nonprofit organization, private American Academic health science centre, academic Medical centers in the United States, medical center focused on integrated health care, healthcare, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science, education, and research. It maintains three major campuses in Rochester, Minnesota; Jacksonville, Florida; and Phoenix, Arizona, Phoenix/Scottsdale, Arizona. Mayo Clinic employs over 7,300 physicians and scientists, along with another 66,000 administrative and allied health staff. The practice specializes in treating difficult cases through Health care#Tertiary care, tertiary care and Medical tourism#United States, destination medicine. It is home to the top-15 ranked Mayo Clinic Alix School of Medicine in addition to many of the highest regarded residency education programs in the United States. It spends over $660 million a year on research and has more than 3,000 full-time research personnel. William Worrall Mayo settled his family i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingrown Hair
Ingrown hair is a condition where a hair curls back or grows sideways into the skin. The condition is most prevalent among people who have coarse or curly hair. It may or may not be accompanied by an infection of the hair follicle (folliculitis) or "razor bumps" ( pseudofolliculitis barbae), which vary in size. While ingrown hair most commonly appears in areas where the skin is shaved or waxed (beard, legs, pubic region), it can appear anywhere. Anything that causes the hair to be broken off unevenly with a sharp tip can cause ingrown hairs. Ingrown hairs are also caused because of lack of natural exfoliation in the skin. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of ingrown hair include rash, itching skin, and hair that remains despite shaving. The site of the ingrown hair forms a reddish, raised bump, similar in appearance to a pimple. Prevention When shaving, a few precautions can be taken to prevent ingrown hairs. When shaving, applying the proper amount of lubrication (in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinus (anatomy)
A sinus is a sac or cavity in any organ or tissue, or an abnormal cavity or passage. In common usage, "sinus" usually refers to the paranasal sinuses, which are air cavities in the cranial bones, especially those near the nose and connecting to it. Most individuals have four paired cavities located in the cranial bone or skull. Etymology ''Sinus'' is Latin for "bay", "pocket", "curve", or "bosom". In anatomy, the term is used in various contexts. The word "sinusitis" is used to indicate that one or more of the membrane linings found in the sinus cavities has become inflamed or infected. It is however distinct from a fistula, which is a tract connecting two epithelial surfaces. If left untreated, infections occurring in the sinus cavities can affect the chest and lungs. Sinuses in the body * Paranasal sinuses ** Maxillary ** Ethmoid ** Sphenoid ** Frontal * Dural venous sinuses ** Anterior midline *** Cavernous *** Superior petrosal *** Inferior petrosal ** Central sul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |