|
Physoclisti
Physoclisti are, collectively, fishes that lack a connection between the gas bladder and the alimentary canal, with the bladder serving only as a buoyancy Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the p ... organ. Addition and removal of the gases from the gas bladder in such physoclistous fishes occurs through specialised structures called the gas gland and ovale respectively. The pneumatic duct that connects the gut and gas bladder is present in the embryos of these fish but it is lost during development. This anatomical state (the physoclistous condition) is believed to be evolutionarily derived from the ancestral physostomous state. Some fishes, such as eels, are anatomically physostomous, but their gas bladders function similar to those of physoclists. See also * Physosto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
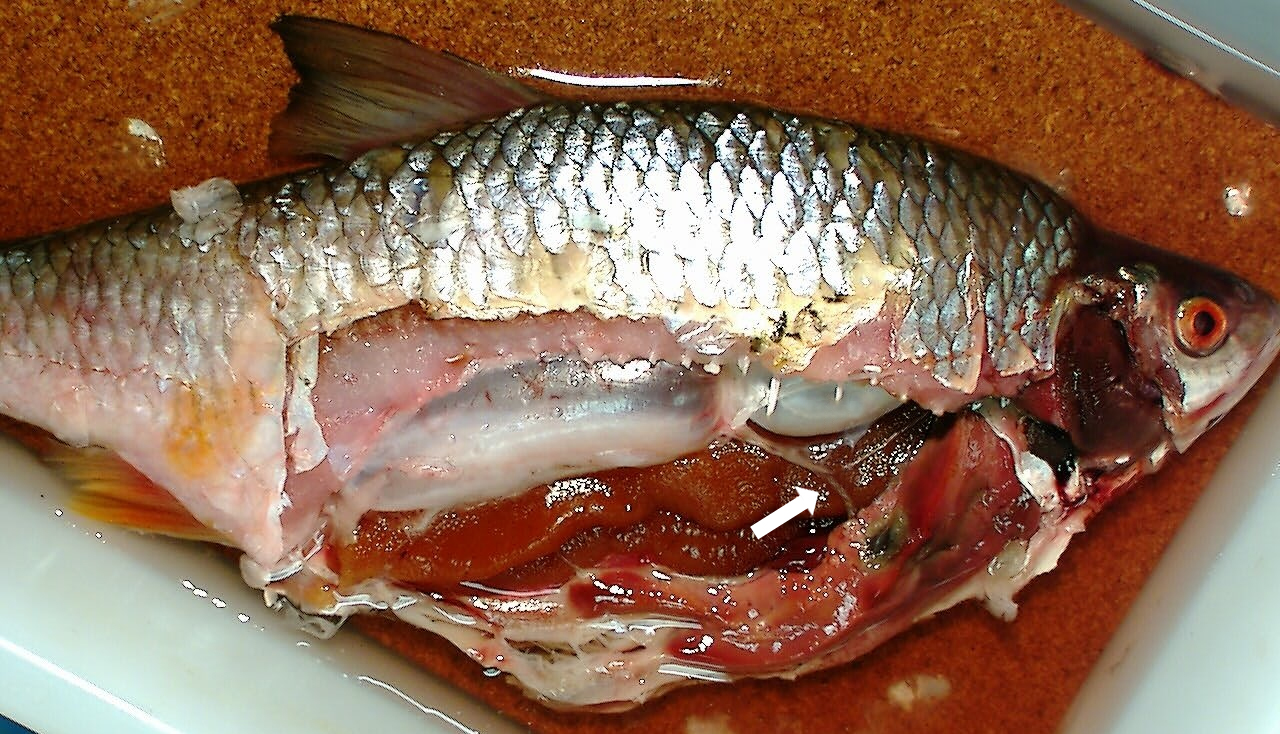
Gas Bladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their current water depth without having to expend energy in swimming. Also, the dorsal position of the swim bladder means the center of mass is below the center of volume, allowing it to act as a stabilizing agent. Additionally, the swim bladder functions as a resonating chamber, to produce or receive sound. The swim bladder is evolutionarily homologous to the lungs. Charles Darwin remarked upon this in ''On the Origin of Species''.Darwin, Charles (1859''Origin of Species''Page 190, reprinted 1872 by D. Appleton. Darwin reasoned that the lung in air-breathing vertebrates had derived from a more primitive swim bladder. In the embryonic stages, some species, such as redlip blenny, have lost the swim bladder again, mostly bottom dwellers like the weather fish. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alimentary Canal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores (ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore ( osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
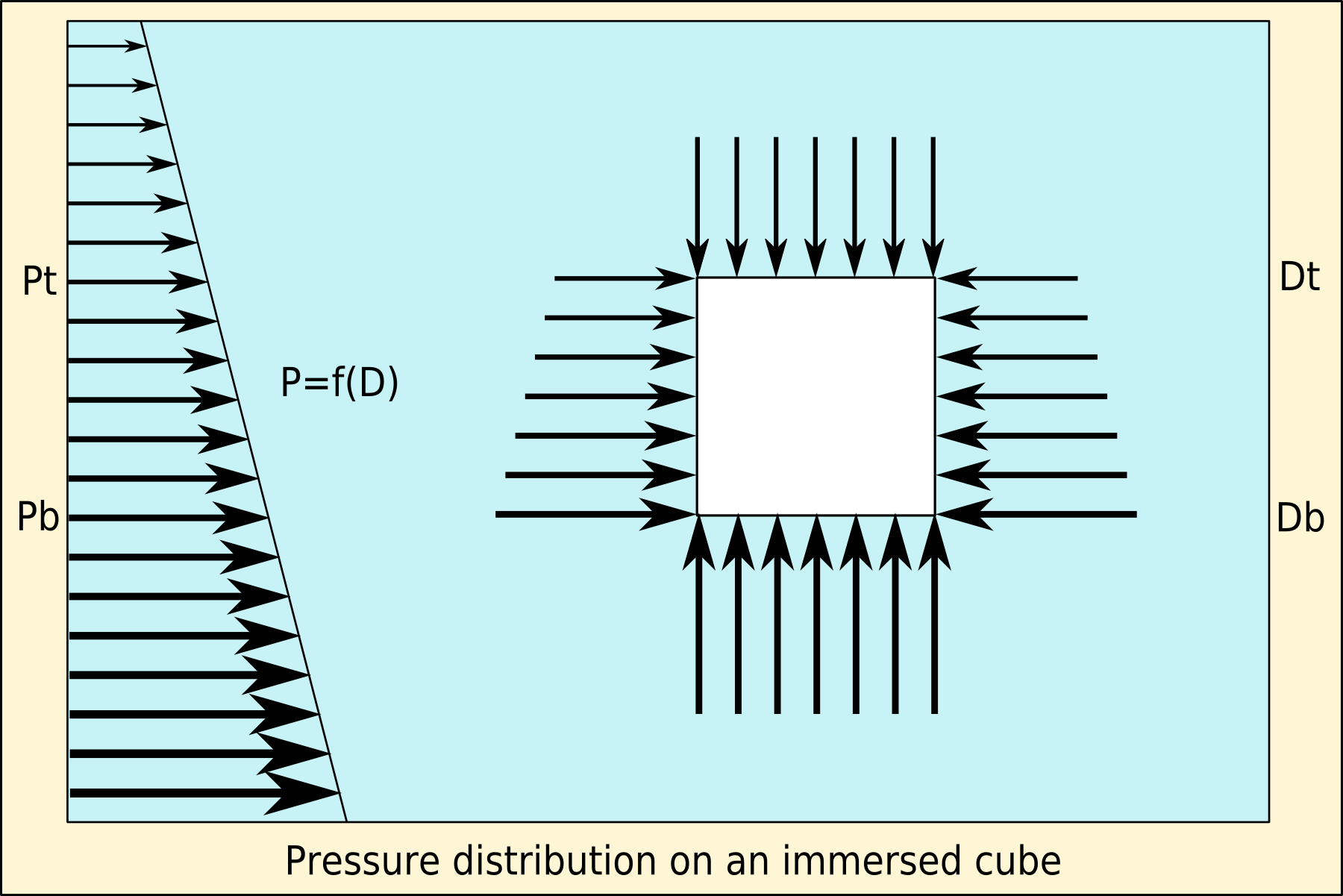
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swim Bladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of many bony fish (but not cartilaginous fish) to control their buoyancy, and thus to stay at their current water depth without having to expend energy in swimming. Also, the dorsal position of the swim bladder means the center of mass is below the center of volume, allowing it to act as a stabilizing agent. Additionally, the swim bladder functions as a resonating chamber, to produce or receive sound. The swim bladder is evolutionarily homologous to the lungs. Charles Darwin remarked upon this in ''On the Origin of Species''.Darwin, Charles (1859''Origin of Species''Page 190, reprinted 1872 by D. Appleton. Darwin reasoned that the lung in air-breathing vertebrates had derived from a more primitive swim bladder. In the embryonic stages, some species, such as redlip blenny, have lost the swim bladder again, mostly bottom dwellers like the weather fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physostome
Physostomes are fishes that have a pneumatic duct connecting the gas bladder to the alimentary canal. This allows the gas bladder to be filled or emptied via the mouth. This not only allows the fish to fill their bladder by gulping air, but also to rapidly ascend in the water without the bladder expanding to bursting point. In contrast, fish without any connection to their gas bladder are called physoclisti. The physostome fish encompass the bichirs, gars, a number of carps, trouts, herrings, catfish, eels and the lungfish. While the gas bladder in fish mainly serves as a buoyancy Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the p ... organ, some physostomes (though not all) can use their gas bladder as a lung, allowing them to live from atmospheric oxygen in conditions where aquatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |