|
Physionotrace
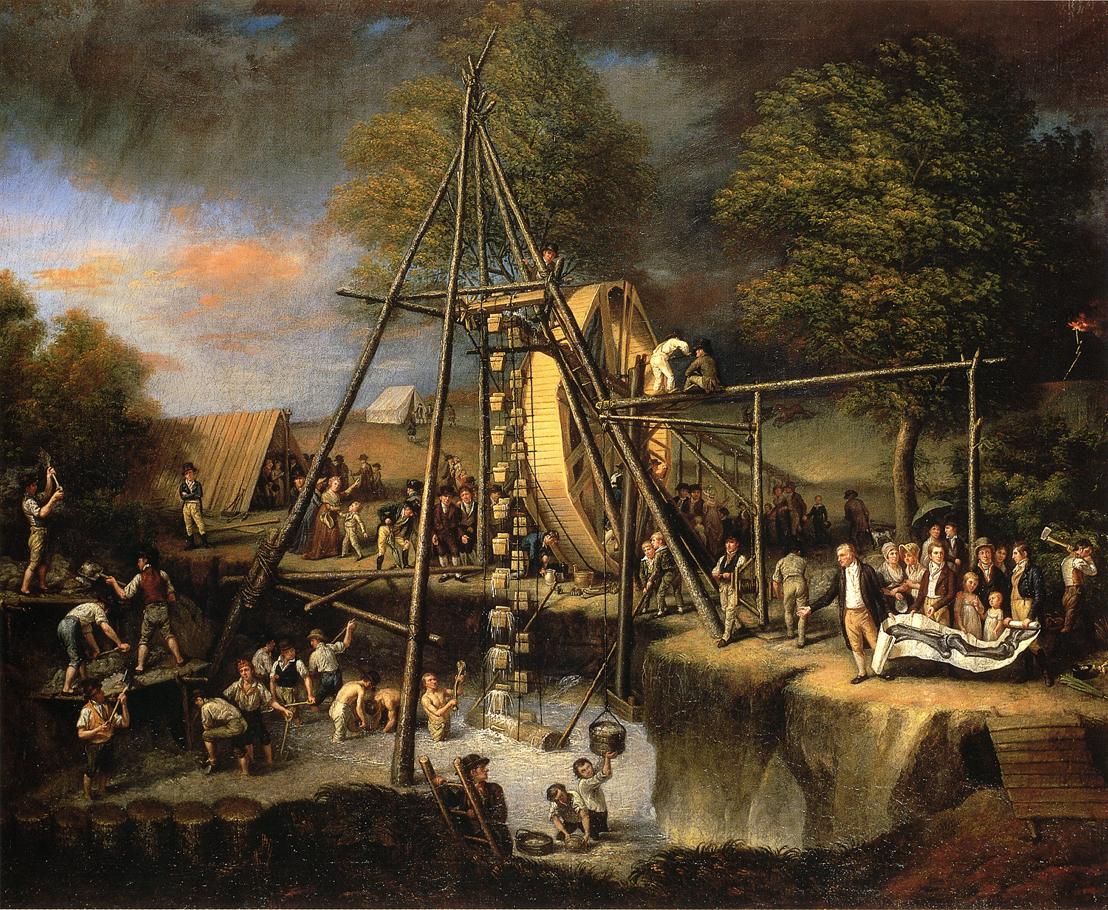
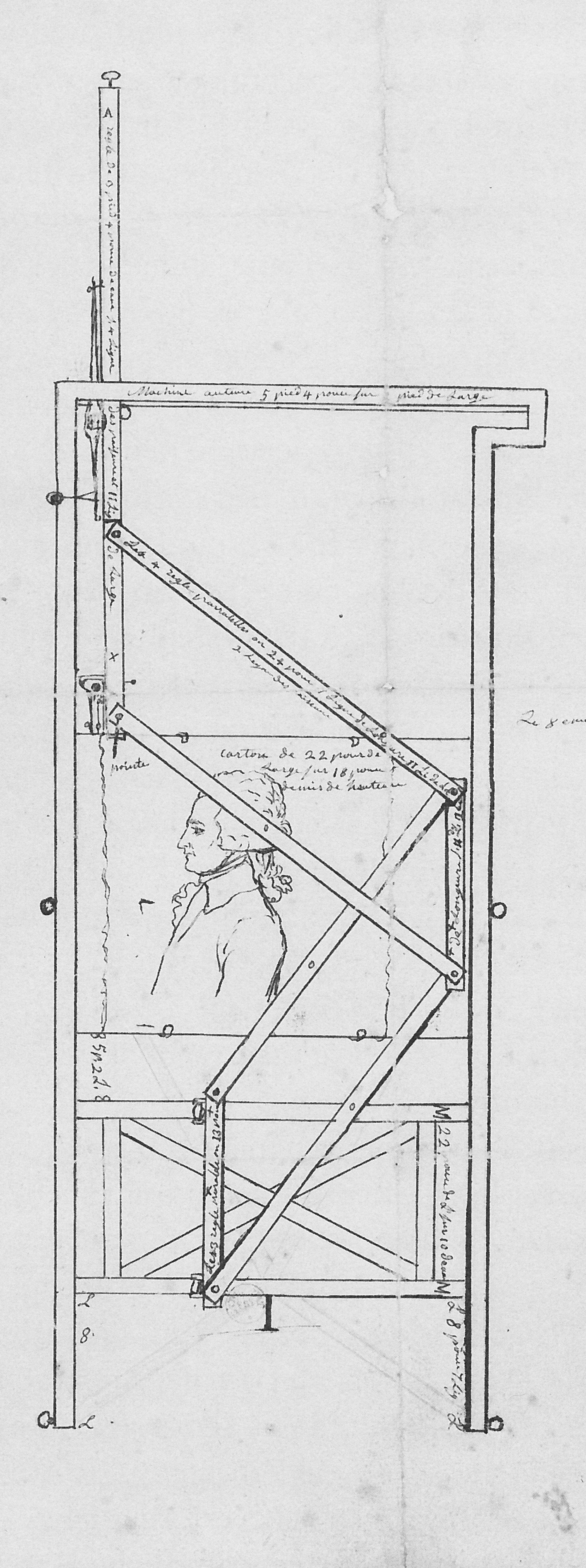
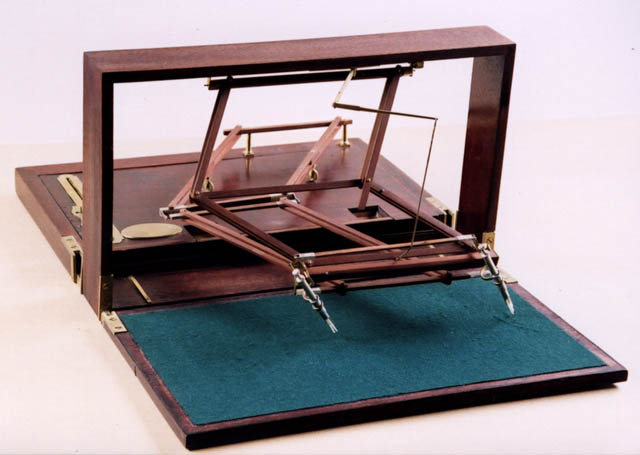
A physiognotrace is an instrument, designed to trace a person's physiognomy to make semi-automated portrait aquatints. Invented in France in 1783–1784, it was popular for some decades. The sitter climbed into a wooden frame (1.75m high x 0.65m wide), sat and turned to the side to pose. A pantograph connected to a pencil produced within a few minutes a "grand trait", a contour line on a piece of paper. With the help of a second scaling-down pantograph, the basic features of the portrait were transferred from the sheet in the form of dotted lines to a copper plate, which had previously been prepared with a ground for etching. One week later, the sitter received an etched plate and twelve little prints. The device but also the aquatint prints are called physiognotraces. History In 1783–1784, the Frenchman Gilles-Louis Chrétien invented the "physionotrace" to aid in the production of silhouette portraits, which became popular during the reign of Louis XVI of France, Louis XVI. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gilles-Louis Chrétien
Gilles-Louis Chrétien (5 February 1754 – 4 March 1811) was a French cellist and engraver. Chrétien was born at Versailles. In 1787 he invented a machine called a "physionotrace", with which he took portraits in profile from life. He worked initially with Edmé Quenedey, but then went into partnership with the miniaturist Jean-Baptiste Fouquet, until the latter's death in or about 1799. Fouquet produced the ''grand trait'' drawing, sometimes highlighted or coloured in pastel, which Chrétien then engraved in aquatint. Many of these portraits are of great interest on account of the celebrity of the persons represented, for example "L'Incorruptible" Maximilien Robespierre, Robespierre, Honoré Gabriel Riqueti, comte de Mirabeau, Mirabeau, and Jean-Paul Marat, Marat, who were among the hundreds which he produced. Also, Dutch patriottentijd, patriots, such as Johan Valckenaer, Samuel Iperusz Wiselius and Quint Ondaatje, who fled to France or visited Paris, ordered sets of physiono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Silhouettes
A silhouette (, ) is the image of a person, animal, object or scene represented as a solid shape of a single colour, usually black, with its edges matching the outline of the subject. The interior of a silhouette is featureless, and the silhouette is usually presented on a light background, usually white, or none at all. The silhouette differs from an outline, which depicts the edge of an object in a linear form, while a silhouette appears as a solid shape. Silhouette images may be created in any visual artistic medium, but were first used to describe pieces of cut paper, which were then stuck to a backing in a contrasting colour, and often framed. Cutting portraits, generally in profile, from black card became popular in the mid-18th century, though the term ''silhouette'' was seldom used until the early decades of the 19th century, and the tradition has continued under this name into the 21st century. They represented a cheap but effective alternative to the portrait miniature, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Portable Physiognotrace Used By Raphaelle Peale, Early 1800s, Mahogany, Glass, Ivory, Steel, Brass, Etc
Portable may refer to: General * Portable building, a manufactured structure that is built off site and moved in upon completion of site and utility work * Portable classroom, a temporary building installed on the grounds of a school to provide additional classroom space where there is a shortage of capacity * Portable toilet, a modern, portable, self-contained outhouse manufactured of molded plastic Computing * Portable object (computing), a distributed computing term for an object which can be accessed through a normal method call while possibly residing in memory on another computer * Software portability, software that can easily be ported to multiple platforms * Portable applications, applications that do not require any kind of installation onto a computer, and can store data in the program's directory Electronics * Portable electronics * Portable device, a wearable or handheld device * Portable audio player, a personal electronic device that allows the user to listen to re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Technical Drawing Tools
Drafting tools may be used for measurement and layout of drawings, or to improve the consistency and speed of creation of standard drawing elements. Tools such as pens and pencils mark the drawing medium. Other tools such as straight edges, assist the operator in drawing straight lines, or assist the operator in drawing complicated shapes repeatedly. Various scales and the protractor are used to measure the lengths of lines and angles, allowing accurate scale drawing to be carried out. The compass is used to draw arcs and circles. A drawing board was used to hold the drawing media in place; later boards included drafting machines that sped the layout of straight lines and angles. Tools such as templates and lettering guides assisted in the drawing of repetitive elements such as circles, ellipses, schematic symbols and text. Other auxiliary tools were used for special drawing purposes or for functions related to the preparation and revision of drawings. The tools used for manual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles Balthazar Julien Févret De Saint-Mémin
Charles Balthazar Julien Févret de Saint-Mémin (; 1770–1852) was a French portrait painter and museum director. He left France during the French Revolution, Revolution, and worked as a portrait engraver in the United States in the early 19th century. He created portraits from life of George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, and others. He later served as museum director in Dijon. Brief history Born in France in 1770 to Benigne Charles Fevret and Victoire Marie de Motmans, Saint-Memin was educated at École Militaire, Paris, graduating in 1785. In 1788 he served in the French Guards. During the French Revolution, Saint-Memin and his family travelled to Old Swiss Confederacy, Switzerland, and then in 1793 to New York City. They intended to go to Saint-Domingue, ”to prevent the sequestration of the lands of his creole mother [However] in New York news of the sad Haitian Revolution, fate of that colony made them decide to remain where they were. Faced with earning a living, they f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
James Madison
James Madison (June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison was popularly acclaimed as the "James Madison as Father of the Constitution, Father of the Constitution" for his pivotal role in drafting and promoting the Constitution of the United States and the United States Bill of Rights, Bill of Rights. Madison was born into a prominent slave-owning Planter class, planter family in Virginia. In 1774, strongly opposed to British taxation, Madison joined with the Patriot (American Revolution), Patriots. He was a member of the Virginia House of Delegates and the Continental Congress during and after the American Revolutionary War. Dissatisfied with the weak national government established by the Articles of Confederation, he helped organize the Constitutional Convention (United States), Constitutional Convention, which produced a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dolley Madison
Dolley Todd Madison (née Payne; May 20, 1768 – July 12, 1849) was the wife of James Madison, the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. She was noted for holding Washington social functions in which she invited members of both political parties, essentially spearheading the concept of bipartisan cooperation. Previously, founders such as Thomas Jefferson would only meet with members of one party at a time, and politics could often be a violent affair resulting in physical altercations and even duels. Madison helped to create the idea that members of each party could amicably socialize, network, and negotiate with each other without violence. By innovating political institutions as the wife of James Madison, Dolley Madison did much to define the role of the President's spouse, known only much later by the title First Lady—a function she had sometimes performed earlier for the widowed Thomas Jefferson. Madison also helped to furnish the newly constructed W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
George Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revolution), Patriot forces to victory in the American Revolutionary War against the British Empire. He is commonly known as the Father of the Nation for his role in bringing about American independence. Born in the Colony of Virginia, Washington became the commander of the Virginia Regiment during the French and Indian War (1754–1763). He was later elected to the Virginia House of Burgesses, and opposed the perceived oppression of the American colonists by the British Crown. When the American Revolutionary War against the British began in 1775, Washington was appointed Commanding General of the United States Army, commander-in-chief of the Continental Army. He directed a poorly organized and equipped force against disciplined British troops. Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
James Sharples (portrait Painter)
James Sharples (1751 or 1752, in Lancashire – 26 February 1811, in New York City) was an English portrait painter and pastelist, who moved to the United States in 1794. He first exhibited at the Royal Academy in 1779. Biography Sharples first intended to enter the Catholic Church, Catholic priesthood, but became an artist instead. Sharples headed a family of successful portrait artists, including his third wife Ellen Sharples. He had four children: George by his first wife; Felix Thomas Sharples from his second marriage (c. 1786- after 1823); and James Sharples Jr.(c. 1788–1839) and daughter Rolinda Sharples (1793–1838) with this third wife, Ellen. Felix, James Jr. and Rolinda joined the family enterprise at ages 17, 15, and 13 respectively. Before marrying Ellen Wallace, James had been active in Bristol, Liverpool, and Bath, Somerset, Bath, where he taught drawing. The family left for the United States in 1796, but, according to Ellen's diaries, their ship fell into t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polygraph (duplicating Device)
A polygraph is a duplicating device that produces a copy of a piece of writing simultaneously with the creation of the original, using pens and ink. Patented by John Isaac Hawkins on May 17, 1803, it was most famously used by the third U.S. president, Thomas Jefferson, who acquired his first polygraph in 1804 and later suggested improvements to Charles Willson Peale, owner of the American rights. . Because Jefferson was a prolific letter writer, the preservation of his copies have offered historians extensive insights into Jefferson's viewpoints and actions. Jefferson called the polygraph "the finest invention of the present age". Another American, Benjamin Henry Latrobe, was the first customer of Peale's and not only introduced the device to Jefferson but was also instrumental in its improvement.Bedini, Silvio A. (1984). ''Thomas Jefferson and His Copying Machines''. Charlottesville: University Press of Virginia. . pp. 53 ff. Mechanisms of this type are more generally kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Peale's Philadelphia Museum
The Philadelphia Museum was an early museum in Philadelphia Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ... started by the painter Charles Willson Peale and continued by his family. It was opened in 1784 as an art museum and added a natural history collection in 1786. The exhibits included the first nearly complete skeleton of the mastodon, a relative of the mammoth. Peale died in 1827 and the collection was sold in 1849 and 1854. History Early years Peale opened the Philadelphia Museum in his home at Third and Lombard Streets in 1784. The first exhibition was a collection of forty-four portraits of "worthy personages" from the American Revolutionary War. Two years later, in 1786, he advertised his museum as a repository for natural curiosities. In addition to portraits the mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |