|
Phthalates
Phthalates ( ), or phthalate esters, are esters of phthalic acid. They are mainly used as plasticizers, i.e., substances added to plastics to increase their flexibility, transparency, durability, and longevity. They are used primarily to soften polyvinyl chloride (PVC). While phthalates are commonly used as plasticizers, not all plasticizers are phthalates. The two terms are specific, unique, and not used interchangeably. Lower-molecular-weight phthalates are typically replaced in many products in the United States, Canada, and European Union over health concerns. They are being replaced by higher molecular-weight phthalates as well as non-phthalic plasticizers. Phthalates are commonly ingested in small quantities via the diet. One of the most commonly known phthalates is bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP). In many countries, DEHP is regulated as a toxin, and is banned from use in broad categories of consumer goods, such as cosmetics, children's toys, medical devices, and fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Di(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate, diethylhexyl phthalate, diisooctyl phthalate, DEHP; incorrectly — dioctyl phthalate, DIOP) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO2C8H17)2. DEHP is the most common member of the class of phthalates, which are used as plasticizers. It is the diester of phthalic acid and the branched-chain 2-ethylhexanol. This colorless viscous liquid is soluble in oil, but not in water. Production Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate is produced commercially by the reaction of excess 2-ethylhexanol with phthalic anhydride in the presence of an acid catalyst such as sulfuric acid or ''para''-toluenesulfonic acid. It was first produced in commercial quantities in Japan circa 1933 and in the United States in 1939. : DEHP has two stereocenters,Sheikh, I. A. (2016) Stereoselectivity and the potential endocrine disrupting activity of di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP) against human progesterone receptor: a computational perspective. Journal of app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyvinyl Chloride
Polyvinyl chloride (alternatively: poly(vinyl chloride), colloquial: vinyl or polyvinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic polymer of plastic (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year. PVC comes in rigid (sometimes abbreviated as RPVC) and flexible forms. Rigid PVC is used in construction for pipes, doors and windows. It is also used in making plastic bottles, packaging, and bank or membership cards. Adding plasticizers makes PVC softer and more flexible. It is used in plumbing, electrical cable insulation, flooring, signage, phonograph records, inflatable products, and in rubber substitutes. With cotton or linen, it is used in the production of canvas. Polyvinyl chloride is a white, brittle solid. It is soluble in ketones, chlorinated solvents, dimethylformamide, THF and DMAc. Discovery PVC was synthesized in 1872 by German chemist Eugen Baumann after extended investigation and experimenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasticizer
A plasticizer ( UK: plasticiser) is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its viscosity, and/or to decrease friction during its handling in manufacture. Plasticizers are commonly added to polymers and plastics such as PVC, either to facilitate the handling of the raw material during fabrication, or to meet the demands of the end product's application. Plasticizers are especially key to the usability of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), the third most widely used plastic. In the absence of plasticizers, PVC is hard and brittle; with plasticizers, it is suitable for products such as vinyl siding, roofing, vinyl flooring, rain gutters, plumbing, and electric wire insulation/coating. Plasticizers are also often added to concrete formulations to make them more workable and fluid for pouring, thus allowing the water contents to be reduced. Similarly, they are often added to clays, stucco, solid rocket fuel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butyl Benzyl Phthalate
Benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) is an organic compound historically used as a plasticizer, which has now been largely phased out due to health concerns. It is a phthalate ester of containing benzyl alcohol, and ''n''-butanol tail groups. Like most phthalates, BBP is non-volatile and remains liquid over a wide range of temperatures. It was mostly used as a plasticizer for PVC, but was also a common plasticizer for PVCA and PVB. BBP was commonly used as a plasticizer for vinyl foams, which are often used as sheet vinyl flooring and tiles. Compared to other phthalates it was less volatile than dibutyl phthalate and imparted better low temperature flexibility than di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate. BBP is classified as toxic by the European Chemical Bureau (ECB) and hence its use in Europe has declined rapidly. Structure and reactivity BBP is a diester. Since BBP contains two ester bonds it can react in a variety of chemical pathways. Both the carbonyl C-atoms are weakly electrophilic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
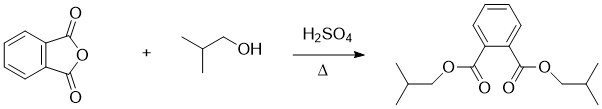
Diisobutyl Phthalate
Diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP) is a phthalate ester having the structural formula . It is formed by the esterification of isobutanol and phthalic anhydride. This and other phthalates are used as plasticizers due to their flexibility and durability. They are found in many industrial and personal products, such as lacquers, nail polish and cosmetics. DIBP can be absorbed via oral ingestion and dermal exposure. When it comes to excretion, DIBP is first converted into the hydrolytic monoester monoisobutyl phthalate (MIBP). The primary excretory route is urine, with Bile duct, biliary excretion being noted in minor amounts. DIBP has lower density and freezing point than the related compound dibutyl phthalate (DBP). Industry use It is used as a plasticizer additive in a range of plastic and rubber materials. It has low volatility, which makes it ideal for use in products that require long-lasting flexibility, e.g. automotive parts, wire and cable insulation, and flooring. It is dense and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethyl Phthalate
Dimethyl phthalate (DMP) is an organic compound and phthalate ester. it is a colourless and oily liquid that is soluble in organic solvents, but which is only poorly soluble in water (~4 g/L). It is used in a variety of products and is most commonly used as insect repellent such as ectoparasiticide for mosquitoes and flies for animal livestock. The short-chain or low molecular weight phthalate is also frequently used in consumer products such as cosmetics, ink, soap, household cleaning supplies, etc. Other uses of DMP include solid rocket propellants (as a stabilizer) and plastics. The U.S Environmental Protection Agency has classified Dimethyl phthalate as not classifiable for human carcinogenicity. Its oral LD50 is 4390 to 8200 mg/kg bw/d in rats and the dermal LD50 is 38000 mg/kg bw in rats and more than 4800 mg/kg bw in guinea pigs. Synthesis Dimethyl phthalate is manufactured commercially via the esterification of phthalic anhydride with methanol. The react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethyl Phthalate
Diethyl phthalate (DEP) is a phthalate ester. It is a colourless liquid without significant odour but with a bitter disagreeable taste. Synthesis and applications Diethyl phthalate is produced by the reaction of ethanol with phthalic anhydride, in the presence of a strong acid catalyst: It finds some use as a specialist plasticiser in PVC, it has also been used as a blender and fixative in perfume. Biodegradation Biodegradation by microorganisms Biodegradation of DEP in soil occurs by sequential hydrolysis of the two diethyl chains of the phthalate to produce monoethyl phthalate, followed by phthalic acid. This reaction occurs very slowly in an abiotic environment. Thus there exists an alternative pathway of biodegradation which includes transesterification or demethylation by microorganisms, if the soil is also contaminated with methanol, that would produce another three intermediate compounds, ethyl methyl phthalate, dimethyl phthalate and monomethyl phthalate. This bio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding, molded, Extrusion, extruded, or Compression molding, pressed into a diverse range of solid forms. This adaptability, combined with a wide range of other properties such as low weight, durability, flexibility, chemical resistance, low toxicity, and low-cost production, has led to their widespread use around the world. While most plastics are produced from natural gas and petroleum, a growing minority are produced from renewable resources like polylactic acid. Between 1950 and 2017, 9.2 billion metric tons of plastic are estimated to have been made, with more than half of this amount being produced since 2004. In 2023 alone, preliminary figures indicate that over 400 million metric tons of plastic were produced worldwide. If global trends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Di-n-butyl Phthalate
Dibutyl phthalate (DBP) is an organic compound of phthalate which is commonly used as a plasticizer because of its low toxicity and wide liquid range. With the chemical formula C6H4(CO2C4H9)2, it is a colorless oil, although impurities often render commercial samples yellow.Peter M. Lorz, Friedrich K. Towae, Walter Enke, Rudolf Jäckh, Naresh Bhargava, Wolfgang Hillesheim "Phthalic Acid and Derivatives" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2007, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Dibutyl phthalate has high dielectric constant. Production and use DBP is produced by the reaction of ''n''-butanol with phthalic anhydride. DBP is an important plasticizer that enhances the utility of some major engineering plastics, such as PVC. Such modified PVC is widely used in plumbing for carrying sewage and other corrosive materials. Degradation Hydrolysis of DBP leads to phthalic acid and 1-butanol. Monobutyl phthalate (MBP) is its major metabolite. Biodegradation Biodegradation by microorg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diisodecyl Phthalate
Diisodecyl phthalate (DIDP) is a commonly used plasticizer used in the production of plastic and plastic coating to increase flexibility. It is a mixture of compounds derived from the esterification of phthalic acid and isomeric decyl alcohols. The coating on furnishings, cookware, pharmaceutical pills, food wrappers and many other products may have DIDP or other phthalates in them. There has been recent concern in the US and European Union for their toxicity and bioaccumulative quality. The European Union has set a maximum specific migration limit (SML) from food contact materials Food contact materials or food contacting substances (FCS) are materials that are intended to be in contact with food. These can be things that are quite obvious like a glass or a can for soft drinks as well as machinery in a food factory or a ... of 9 mg/kg food for the sum of diisodecyl phthalates and diisononyl phthalates. DIDP has been listed since 2007 under Proposition 65 as a subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |