|
Phragmites
''Phragmites'' () is a genus of four species of large perennial plant, perennial reed (plant), reed Poaceae, grasses found in wetlands throughout temperate and tropical regions of the world. Taxonomy The World Checklist of Selected Plant Families, maintained by Kew Garden in London, accepts the following four species: * ''Phragmites australis'' (Antonio José Cavanilles, Cav.) Carl Bernhard von Trinius, Trin. ex Steud. – The cosmopolitan common reed * ''Phragmites japonicus'' Steud. – Japan, Korea, Ryukyu Islands, Russian Far East * ''Phragmites karka'' (Anders Johan Retzius, Retz.) Trin. ex Steud. – tropical Africa, southern Asia, Australia, some Pacific Islands, invasive in New Zealand * ''Phragmites mauritianus'' Kunth – central + southern Africa, Madagascar, Mauritius Wildlife in reed beds ''Phragmites'' stands can provide food and shelter resources for a number of birds, insects, and other animals. Habitat benefits are often optimal when stands are thinner, and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmites Mauritianus
''Phragmites'' () is a genus of four species of large perennial reed grasses found in wetlands throughout temperate and tropical regions of the world. Taxonomy The World Checklist of Selected Plant Families, maintained by Kew Garden in London, accepts the following four species: * ''Phragmites australis'' ( Cav.) Trin. ex Steud. – The cosmopolitan common reed * ''Phragmites japonicus'' Steud. – Japan, Korea, Ryukyu Islands, Russian Far East * '' Phragmites karka'' ( Retz.) Trin. ex Steud. – tropical Africa, southern Asia, Australia, some Pacific Islands, invasive in New Zealand * '' Phragmites mauritianus'' Kunth – central + southern Africa, Madagascar, Mauritius Wildlife in reed beds ''Phragmites'' stands can provide food and shelter resources for a number of birds, insects, and other animals. Habitat benefits are often optimal when stands are thinner, and management of stands may promote more suitable habitat benefits. Some evidence suggests that a short term mana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmites Australis
''Phragmites australis'', known as the common reed, is a species of flowering plant in the grass family Poaceae. It is a wetland grass that can grow up to tall and has a cosmopolitan distribution worldwide. Description ''Phragmites australis'' commonly forms extensive stands (known as reed beds), which may be as much as or more in extent. Where conditions are suitable it can also spread at or more per year by horizontal runners, which put down roots at regular intervals. It can grow in damp ground, in standing water up to or so deep, or even as a floating mat. The erect stems grow to tall, with the tallest plants growing in areas with hot summers and fertile growing conditions. The leaves are long and broad. The flowers are produced in late summer in a dense, dark purple panicle, about long. Later the numerous long, narrow, sharp pointed spikelets appear greyer due to the growth of long, silky hairs. These eventually help disperse the minute seeds. Taxonomy Recent stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmites Karka
''Phragmites karka'', the tall reed or common reed, is a species of flowering plant in the Poaceae, grass family. It is native to West Africa. Other Names Distribution This species has a widespread distribution that includes West Africa, Southern Arabian Peninsula, Kenya, South Asia, Southeast Asia and the Pacific Islands. It is also present in New Zealand, where it is categorised as an invasive weed. Description It is a herbaceous, perennial species with a rhizomatous geophyte (underground storage organ) and primarily grows in the tropical regions during the dry season. During the winter, it is deciduous. Plants can grow to 4–10 metres in height, with a diameter of 15-25mm. The species is a fast-growing aquatic plant, often found in swamps, riverbanks and standing water, usually at elevations below 1,000 m. Uses Locally, this species is utilised as a source of building and construction material, and as food. It is often planted near rivers to purify water, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Western Europe, with a population of 14.9 million. London stands on the River Thames in southeast England, at the head of a tidal estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for nearly 2,000 years. Its ancient core and financial centre, the City of London, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as Londinium and has retained its medieval boundaries. The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has been the centuries-long host of Government of the United Kingdom, the national government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. London grew rapidly 19th-century London, in the 19th century, becoming the world's List of largest cities throughout history, largest city at the time. Since the 19th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
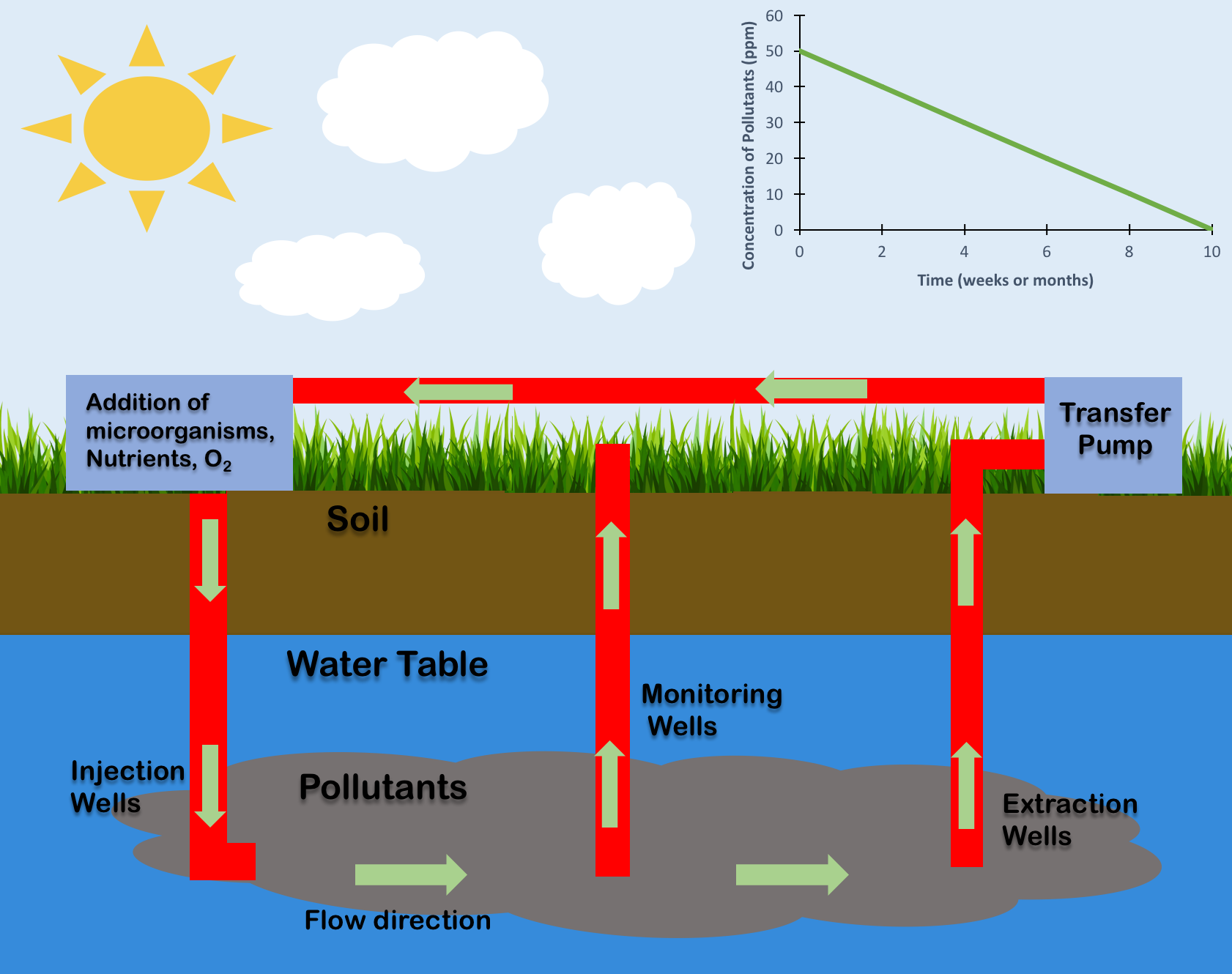
Bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi in mycoremediation, and plants in phytoremediation), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, fuel gasses, industrial effluents etc., in natural or artificial settings. The natural ability of organisms to adsorb, accumulate, and degrade common and emerging pollutants has attracted the use of biological resources in treatment of contaminated environment. In comparison to conventional physicochemical treatment methods bioremediation may offer advantages as it aims to be sustainable, eco-friendly, cheap, and scalable. This technology is rarely implemented however because it is slow or inefficient. Most bioremediation is inadvertent, involving native organisms. Research on bioremediation is heavily focused on stimulating the process by inoculation of a polluted site with organisms or supplying nutrients to promote their growt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constructed Wetland
A constructed wetland is an artificial wetland to treat sewage, greywater, stormwater runoff or Industrial wastewater treatment, industrial wastewater. It may also be designed for land reclamation after mining, or as a Flood mitigation, mitigation step for natural areas lost to land development. Constructed wetlands are engineered systems that use the natural functions of vegetation, soil, and organisms to provide secondary treatment to wastewater. The design of the constructed wetland has to be adjusted according to the type of wastewater to be treated. Constructed wetlands have been used in both centralized and decentralized wastewater systems. Primary treatment is recommended when there is a large amount of suspended solids or soluble organic matter (measured as biochemical oxygen demand and chemical oxygen demand). Similar to natural wetlands, constructed wetlands also act as a biofilter and/or can remove a range of pollutants (such as organic matter, Nutrient pollution, nutri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greywater
Greywater (or grey water, sullage, also spelled gray water in the United States) refers to domestic wastewater generated in households or office buildings from streams without fecal contamination, i.e., all streams except for the wastewater from toilets. Sources of greywater include sinks, showers, baths, washing machines or dishwashers. As greywater contains fewer pathogens than blackwater, it is generally safer to handle and easier to treat and reuse onsite for toilet flushing, landscape or crop irrigation, and other non- potable uses. Greywater may still have some pathogen content from laundering soiled clothing or cleaning the anal area in the shower or bath. The application of greywater reuse in urban water systems provides substantial benefits for both the water supply subsystem, by reducing the demand for fresh clean water, and the wastewater subsystems by reducing the amount of conveyed and treated wastewater. Treated greywater has many uses, such as toilet fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waste Water
Wastewater (or waste water) is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of domestic, industrial, commercial or agricultural activities, surface runoff / storm water, and any sewer inflow or sewer infiltration". In everyday usage, wastewater is commonly a synonym for sewage (also called domestic wastewater or municipal wastewater), which is wastewater that is produced by a community of people. As a generic term, wastewater may also describe water containing contaminants accumulated in other settings, such as: * Industrial wastewater: waterborne waste generated from a variety of industrial processes, such as manufacturing operations, mineral extraction, power generation, or water and wastewater treatment. * Cooling water, is released with potential thermal pollution after use to condense steam or reduce machinery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoremediation
Phytoremediation technologies use living plants to clean up soil, air and water contaminated with hazardous contaminants. It is defined as "the use of green plants and the associated microorganisms, along with proper soil amendments and agronomic techniques to either contain, remove or render toxic environmental contaminants harmless". The term is an amalgam of the Greek ''phyto'' (plant) and Latin ''remedium'' (restoring balance). Although attractive for its cost, phytoremediation has not been demonstrated to redress any significant environmental challenge to the extent that contaminated space has been reclaimed. Phytoremediation is proposed as a cost-effective plant-based approach of environmental remediation that takes advantage of the ability of plants to concentrate elements and compounds from the environment and to detoxify various compounds without causing additional pollution. The concentrating effect results from the ability of certain plants called hyperaccumulators t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem Service
Ecosystem services are the various benefits that humans derive from ecosystems. The interconnected living and non-living components of the natural environment offer benefits such as pollination of crops, clean air and water, decomposition of wastes, and flood control. Ecosystem services are grouped into four broad categories of services. There are ''provisioning services'', such as the production of food and water; ''regulating services'', such as the control of climate and disease; ''supporting services'', such as nutrient cycles and oxygen production; and ''cultural services'', such as recreation, tourism, and spiritual gratification. Evaluations of ecosystem services may include assigning an economic value to them. For example, estuarine and coastal ecosystems are marine ecosystems that perform the four categories of ecosystem services in several ways. Firstly, their provisioning services include marine resources and genetic resources. Secondly, their supporting services inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |