|
Phenyltoloxamine
Phenyltoloxamine is an antihistamine with sedative and analgesic effects. It is available in combination with other drugs such as paracetamol (acetominophen). Common use Phenyltoloxamine is widely used in preparations as an enhancing agent for some analgesics and antitussives (acetaminophen, dihydrocodeine, codeine, hydrocodone). It is widely used in certain parts of the world as cough suppressant usually with codeine, and sometimes by itself or in addition to dextromethorphan as it, like diphenhydramine, possesses antitussive action of its own and is particularly useful in semi-productive coughs because of its moderate drying action. Phenyltoloxamine is used in combination with paracetamol, aspirin and other salicylates and other drugs in proprietary preparations available over the counter for backache, muscle strains and similar conditions. Adverse effects Common adverse effects are those associated with most anticholinergics, with effects being more pronounced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydrocodeine
Dihydrocodeine is a semi-synthetic opioid analgesic prescribed for pain or severe dyspnea, or as an antitussive, either alone or compounded with paracetamol (acetaminophen) (as in co-dydramol) or aspirin. It was developed in Germany in 1908 and first marketed in 1911. Commonly available as tablets, solutions, elixirs, and other oral forms, dihydrocodeine is also available in some countries as an injectable solution for deep subcutaneous and intra-muscular administration. As with codeine, intravenous administration should be avoided, as it could result in anaphylaxis and life-threatening pulmonary edema. In the past, dihydrocodeine suppositories were used. Dihydrocodeine is available in suppository form on prescription. Dihydrocodeine is used as an alternative to codeine. It was first described in 1911 and approved for medical use in 1948. Dihydrocodeine was developed during the search for more effective cough medication, especially to help reduce the spread of tuberculosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides relief from nasal congestion, sneezing, or hives caused by pollen, dust mites, or animal allergy with few side effects. Antihistamines are usually for short-term treatment. Chronic allergies increase the risk of health problems which antihistamines might not treat, including asthma, sinusitis, and lower respiratory tract infection. Consultation of a medical professional is recommended for those who intend to take antihistamines for longer-term use. Although people typically use the word "antihistamine" to describe drugs for treating allergies, doctors and scientists use the term to describe a class of drug that opposes the activity of histamine receptors in the body. In this sense of the word, antihistamines are subclassified acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
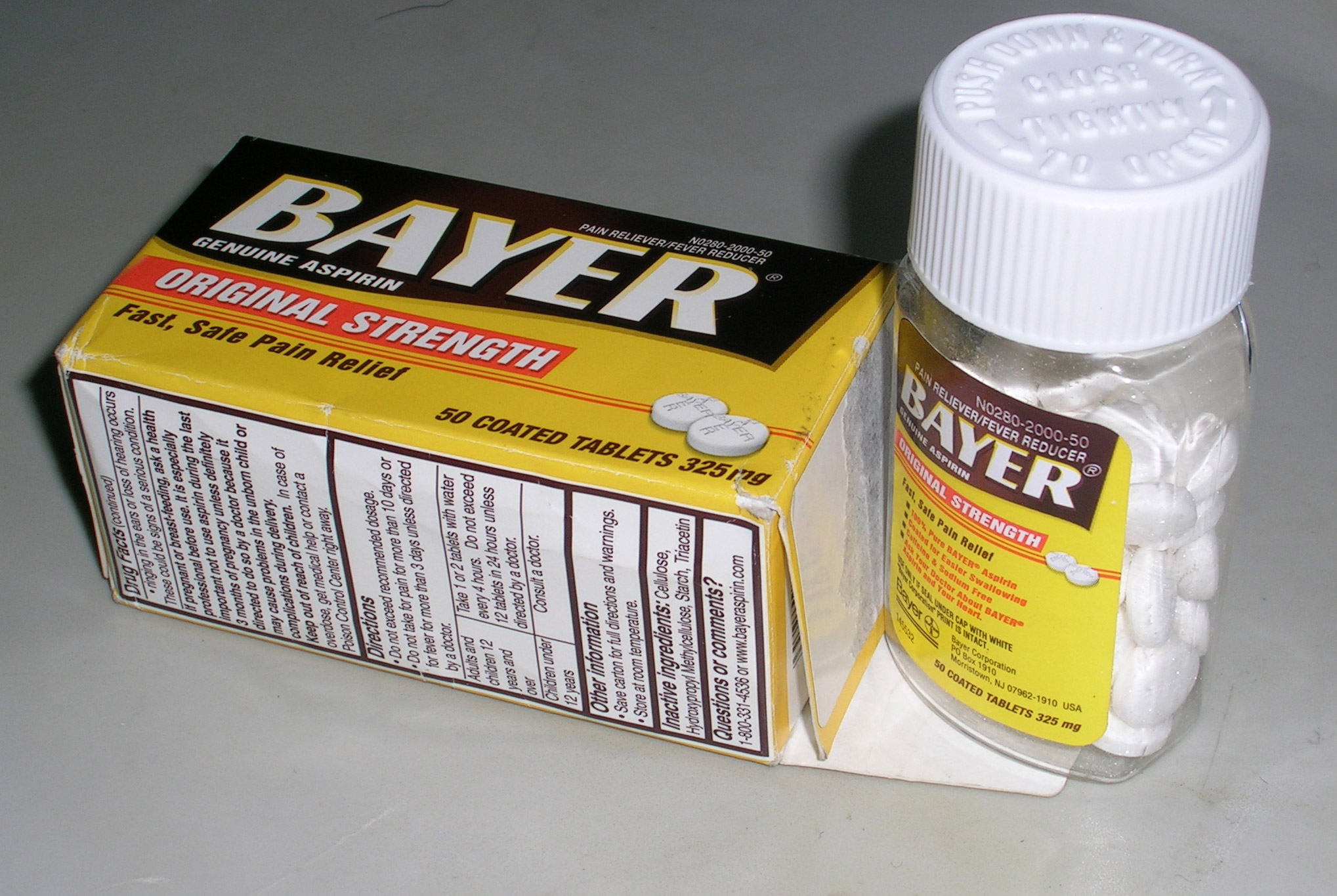
Aspirin
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and/or inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease, pericarditis, and rheumatic fever. Aspirin is also used long-term to help prevent further heart attacks, ischaemic strokes, and blood clots in people at high risk. For pain or fever, effects typically begin within 30 minutes. Aspirin works similarly to other NSAIDs but also suppresses the normal functioning of platelets. One common adverse effect is an upset stomach. More significant side effects include stomach ulcers, stomach bleeding, and worsening asthma. Bleeding risk is greater among those who are older, drink alcohol, take other NSAIDs, or are on other blood thinners. Aspirin is not recommended in the last part of pregnancy. It is not generally recommended in children with infections because of the ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscarinic Antagonists
A muscarinic receptor antagonist (MRA) is a type of anticholinergic agent that blocks the activity of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. The muscarinic receptor is a protein involved in the transmission of signals through certain parts of the nervous system, and muscarinic receptor antagonists work to prevent this transmission from occurring. Notably, muscarinic antagonists reduce the activation of the parasympathetic nervous system. The normal function of the parasympathetic system is often summarised as "rest-and-digest", and includes slowing of the heart, an increased rate of digestion, narrowing of the airways, promotion of urination, and sexual arousal. Muscarinic antagonists counter this parasympathetic "rest-and-digest" response, and also work elsewhere in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. Drugs with muscarinic antagonist activity are widely used in medicine, in the treatment of low heart rate, overactive bladder, respiratory problems such as asthma an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H1 Receptor Antagonists
H1 antagonists, also called H1 blockers, are a class of medications that block the action of histamine at the H1 receptor, helping to relieve allergic reactions. Agents where the main therapeutic effect is mediated by negative modulation of histamine receptors are termed antihistamines; other agents may have antihistaminergic action but are not true antihistamines. In common use, the term "antihistamine" refers only to H1-antihistamines. Virtually all H1-antihistamines function as inverse agonists at the histamine H1-receptor, as opposed to neutral antagonists, as was previously believed. Medical uses H1-antihistamines are clinically used in the treatment of histamine-mediated allergic conditions. These indications may include:Rossi S (Ed.) (2004). ''Australian Medicines Handbook 2004''. Adelaide: Australian Medicines Handbook. * Allergic rhinitis * Allergic conjunctivitis * Allergic dermatological conditions ( contact dermatitis) * Rhinorrhea (runny nose) * Urticari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylamino Compounds
Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around 40%. An estimated 270,000 tons were produced in 2005. Structure and synthesis The molecule consists of a nitrogen atom with two methyl substituents and one proton. Dimethylamine is a weak base and the pKa of the ammonium CH3--CH3 is 10.73, a value above methylamine (10.64) and trimethylamine (9.79). Dimethylamine reacts with acids to form salts, such as dimethylamine hydrochloride, an odorless white solid with a melting point of 171.5 °C. Dimethylamine is produced by catalytic reaction of methanol and ammonia at elevated temperatures and high pressure: :2 CH3OH + NH3 → (CH3)2NH + 2 H2O Natural occurrence Dimethylamine is found quite widely distributed in animals and plants, and is present in many foods at the lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenhydramine
Diphenhydramine (DPH) is an antihistamine and sedative mainly used to treat allergies, insomnia, and symptoms of the common cold. It is also less commonly used for tremor in parkinsonism, and nausea. It is taken by mouth, injected into a vein, injected into a muscle, or applied to the skin. Maximal effect is typically around two hours after a dose, and effects can last for up to seven hours. Common side effects include sleepiness, poor coordination and an upset stomach. Its use is not recommended in young children or the elderly. There is no clear risk of harm when used during pregnancy; however, use during breastfeeding is not recommended. It is a first generation H1-antihistamine and ethanolamine and works by blocking certain effects of histamine, which produces its antihistamine and sedative effects. Diphenhydramine is also a potent anticholinergic, which means it also works as a deliriant at higher than recommended doses as a result. Its sedative and deliriant eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Over-the-counter Drug
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are medicines sold directly to a consumer without a requirement for a prescription from a healthcare professional, as opposed to prescription drugs, which may be supplied only to consumers possessing a valid prescription. In many countries, OTC drugs are selected by a regulatory agency to ensure that they contain ingredients that are safe and effective when used without a physician's care. OTC drugs are usually regulated according to their active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) rather than final products. By regulating APIs instead of specific drug formulations, governments allow manufacturers the freedom to formulate ingredients, or combinations of ingredients, into proprietary mixtures. The term ''over-the-counter'' (''OTC'') refers to a medication that can be purchased without a medical prescription. In contrast, prescription drugs require a prescription from a doctor or other health care professional and should only be used by the prescri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Controlled Substance
A controlled substance is generally a drug or chemical whose manufacture, possession and use is regulated by a government, such as illicitly used drugs or prescription medications that are designated by law. Some treaties, notably the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, the Convention on Psychotropic Substances, and the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, provide internationally agreed-upon "schedules" of controlled substances, which have been incorporated into national laws; however, national laws usually significantly expand on these international conventions. Some precursor chemicals used for the production of illegal drugs are also controlled substances in many countries, even though they may lack the pharmacological effects of the drugs themselves. Substances are classified according to schedules and consist primarily of potentially psychoactive substances and anabolic steroids. The controlled substance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developing World
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. The term low and middle-income country (LMIC) is often used interchangeably but refers only to the economy of the countries. The World Bank classifies the world's economies into four groups, based on gross national income per capita: high, upper-middle, lower-middle, and low income countries. Least developed countries, landlocked developing countries and small island developing states are all sub-groupings of developing countries. Countries on the other end of the spectrum are usually referred to as high-income countries or developed countries. There are controversies over this term's use, which some feel it perpetuates an outdated concept of "us" and "them". In 2015, the World Bank declared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Countries
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.Western Civilization Our Tradition; James Kurth; accessed 30 August 2011 The Western world is also known as the Occident (from the word ''occidēns'' "setting down, sunset, west") in contrast to the known as the Orient ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adverse Effects
An adverse effect is an undesired harmful effect resulting from a medication or other intervention, such as surgery. An adverse effect may be termed a " side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. The term complication is similar to adverse effect, but the latter is typically used in pharmacological contexts, or when the negative effect is expected or common. If the negative effect results from an unsuitable or incorrect dosage or procedure, this is called a medical error and not an adverse effect. Adverse effects are sometimes referred to as " iatrogenic" because they are generated by a physician/treatment. Some adverse effects occur only when starting, increasing or discontinuing a treatment. Adverse effects can also be caused by placebo treatments (in which case the adverse effects are referred to as nocebo effects). Using a drug or other medical intervention which is contraindicated may increase the risk of adverse effects. Adverse effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)