|
Phenelzine
Phenelzine, sold under the brand name Nardil among others, is a non-selective and irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine family which is primarily used as an antidepressant and anxiolytic to treat depression and anxiety. Along with tranylcypromine and isocarboxazid, phenelzine is one of the few non-selective and irreversible MAOIs still in widespread clinical use. Synthesis of phenelzine was first described by Emil Votoček and Otakar Leminger in 1932. Medical uses Phenelzine is primarily used in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Patients with atypical depression respond particularly well to phenelzine. The medication is also useful in treatment-resistant depression, where patients do not respond favorably to first and second-line treatments for depression. In addition to being a recognized treatment for major depressive disorder, phenelzine is also effective in treating dysthymia, bipolar depression, panic disorder, social anxiet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor
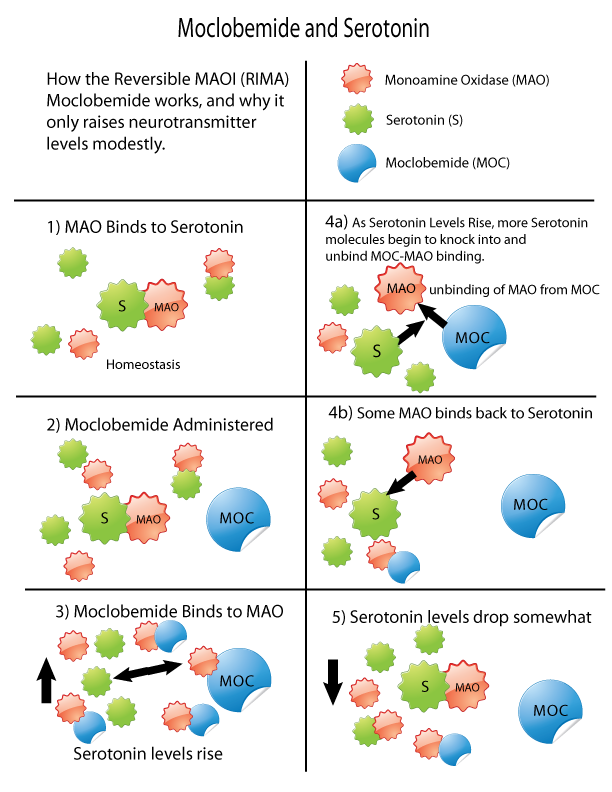
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a drug class, class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that binding selectivity, selectively and Enzyme inhibitor#Reversible inhibitors, reversibly enzyme inhibitor, inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the medication, treatment of major depressive disorder, depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction. Common side effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, akathisia, sexual dysfunction, and emotional blunting. There is an increased risk of Suicidal ideation, suicidal thinking and Suicide, behavior when taken by children, adolescents, and young adults. Antidepressant discontinuation syndrome, Discontinuation syndrome, which resembles recurrent Depression (mood), depression in the case of the Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, SSRI class, may occur after stopping the intake of any antidepressant. Research regarding the effectiveness of antidepressants for depression in adults is controversial and has found both benefits and drawbacks. Meanwhile, evidence of benefit in children and adolescents is unclear, even though antidepressant use has considerably increased in children and adolescents in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Anxiety Disorder
Social anxiety disorder (SAD), also known as social phobia, is an anxiety disorder characterized by sentiments of fear and anxiety in social situations, causing considerable distress and impairing ability to function in at least some aspects of daily life. These fears can be triggered by perceived or actual scrutiny from others. Individuals with social anxiety disorder fear negative evaluations from other people. Physical symptoms often include excessive blushing, excessive sweating, trembling, palpitations, rapid heartbeat, muscle tension, shortness of breath, and nausea. Panic attacks can also occur under intense fear and discomfort. Some affected individuals may use alcohol or other drugs to reduce fears and inhibitions at social events. It is common for those with social phobia to self-medicate in this fashion, especially if they are undiagnosed, untreated, or both; this can lead to alcohol use disorder, eating disorders or other kinds of substance use disorder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isocarboxazid
Isocarboxazid, sold under the brand name Marplan among others, is a non-selective irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class used as an antidepressant. Along with phenelzine and tranylcypromine, it is one of only three classical MAOIs still available for clinical use in the treatment of psychiatric disorders in the United States, though it is not as commonly employed in comparison to the others. Isocarboxazid is primarily used to treat mood and anxiety disorders. It has also been investigated in the treatment of schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease, and other dementia-related disorders. Isocarboxazid, as well as other MAOIs, increase the levels of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, melatonin, and phenethylamine in the brain. Classical MAOIs, including isocarboxazid, are used only rarely due to prominent food and drug interactions and have been largely superseded by newer antidepressants such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiolytic
An anxiolytic (; also antipanic or anti-anxiety agent) is a medication or other intervention that reduces anxiety. This effect is in contrast to anxiogenic agents which increase anxiety. Anxiolytic medications are used for the treatment of anxiety disorders and their related psychological and physical symptoms. Nature of anxiety Anxiety is a naturally-occurring emotion and response. When anxiety levels exceed the tolerability of a person, anxiety disorders may occur. People with anxiety disorders can exhibit fear responses, such as defensive behaviors, high levels of alertness, and negative emotions. Those with anxiety disorders may have concurrent psychological disorders, such as depression. Anxiety disorders are classified using six possible clinical assessments: Different types of anxiety disorders will share some general symptoms while having their own distinctive symptoms. This explains why people with different types of anxiety disorders will respond differently to diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes of administration, such as Injection (medicine), injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth". The expression is used in medicine to describe a treatment that is taken orally (but not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Depression
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that each last from days to weeks, and in some cases months. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called ''mania''; if it is less severe and does not significantly affect functioning, it is called ''hypomania''. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy, or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually, but not always, a reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying, have a negative outlook on life, and demonstrate poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high. Over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, with about one-third attempting suicide in their lifetime. Among those with the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panic Disorder
Panic disorder is a mental disorder, specifically an anxiety disorder, characterized by reoccurring unexpected panic attacks. Panic attacks are sudden periods of intense fear that may include palpitations, sweating, shaking, shortness of breath, numbness, or a sense of impending doom. The maximum degree of symptoms occurs within minutes. There may be ongoing worries about having further attacks and avoidance of places where attacks have occurred in the past. The exact cause of panic disorder is not fully understood, however there are a number of factors linked to the disorder such as a stressful or traumatic life event, having close family members with the disorder and an imbalance of neurotransmitters. Diagnosis involves ruling out other potential causes of anxiety including other mental disorders, medical conditions such as heart disease or hyperthyroidism, and drug use. Screening for the condition may be done using a questionnaire. Panic disorder is usually treated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulimia
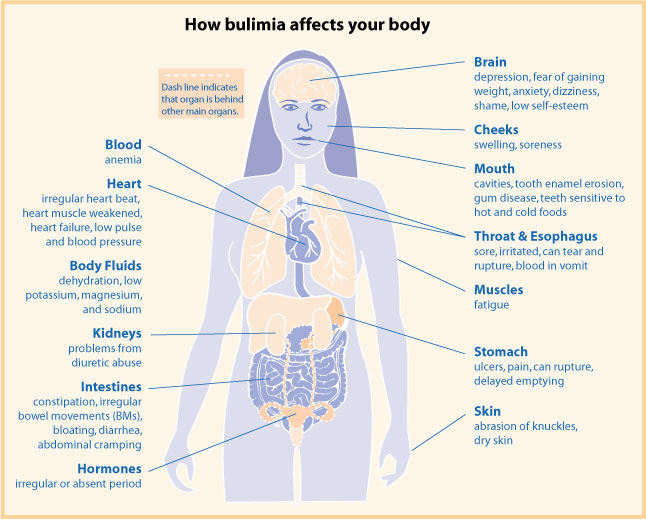
Bulimia nervosa, also known simply as bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating (eating large quantities of food in a short period of time, often feeling out of control) followed by compensatory behaviors, such as self-induced vomiting or fasting, to prevent weight gain. Other efforts to lose weight may include the use of diuretics, laxatives, stimulants, water fasting, or excessive exercise. Most people with bulimia are at normal weight and have higher risk for other mental disorders, such as depression, anxiety, borderline personality disorder, bipolar disorder, and problems with drugs to alcohol. There is also a higher risk of suicide and self-harm. Bulimia is more common among those who have a close relative with the condition. The percentage risk that is estimated to be due to genetics is between 30% and 80%. Other risk factors for the disease include psychological stress, cultural pressure to attain a certain body type, poor self-esteem, and obesit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treatment-resistant Depression
Treatment-resistant depression (TRD) is often defined as major depressive disorder in which an affected person does not respond adequately to at least two different antidepressant medications at an adequate dose and for an adequate duration. Inadequate response has most commonly been defined as less than 25% reduction in depressive symptoms following treatment with an antidepressant. Many clinicians and researchers question the construct validity and clinical utility of treatment-resistant depression as currently conceptualized. There is ongoing debate as to whether inadequate response to other treatment modalities, such as psychotherapy, should be included in defining TRD. Treatment resistance is becoming more prominent with nearly 30% of individuals with major depressive disorder being termed treatment-resistant as defined above. There are many factors that may contribute to inadequate treatment, such as: a history of repeated or severe adverse childhood experiences, early d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |