|
Phene
A phene is an individual genetically determined characteristic or trait which can be possessed by an organism, such as eye colour, height, behavior, tooth shape or any other observable characteristic. Phene - phenotype - phenome distinction The term 'phene' was evidently coined as an obvious parallel construct to 'gene'. Phene is to Phenotype as Gene is to Genotype, and Similarly Phene is to Phenome as Gene is to Genome. More specifically, a Phene is an abstract concept describing a particular characteristic which can be possessed by an organism. Whereas Phenotype refers to a collection of Phenes possessed by a particular organism, and Phenome refers to the entire set of Phenes that exist within an organism or species. Genome wide association studies use "phenes" or "traits" (symptoms) to distinguish groups in the human population. These groups are then employed to identify associations with genetic alleles that are more common in the symptomatic group than in the asymptomati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trait (biology)
A phenotypic trait, simply trait, or character state is a distinct variant of a phenotypic characteristic of an organism; it may be either inherited or determined environmentally, but typically occurs as a combination of the two.Lawrence, Eleanor (2005) ''Henderson's Dictionary of Biology''. Pearson, Prentice Hall. For example, having eye color is a ''character'' of an organism, while blue, brown and hazel versions of eye color are ''traits''. The term ''trait'' is generally used in genetics, often to describe the phenotypic expression of different combinations of alleles in different individual organisms within a single population, such as the famous purple vs. white flower coloration in Gregor Mendel's pea plants. By contrast, in systematics, the term ''character state'' is employed to describe features that represent fixed diagnostic differences among taxa, such as the absence of tails in great apes, relative to other primate groups. Definition A phenotypic trait is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotypic Trait
A phenotypic trait, simply trait, or character state is a distinct variant of a phenotypic characteristic of an organism; it may be either inherited or determined environmentally, but typically occurs as a combination of the two.Lawrence, Eleanor (2005) ''Henderson's Dictionary of Biology''. Pearson, Prentice Hall. For example, having eye color is a ''character'' of an organism, while blue, brown and hazel versions of eye color are ''traits''. The term ''trait'' is generally used in genetics, often to describe the phenotypic expression of different combinations of alleles in different individual organisms within a single population, such as the famous purple vs. white flower coloration in Gregor Mendel's pea plants. By contrast, in systematics, the term ''character state'' is employed to describe features that represent fixed diagnostic differences among taxa, such as the absence of tails in great apes, relative to other primate groups. Definition A phenotypic trait is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
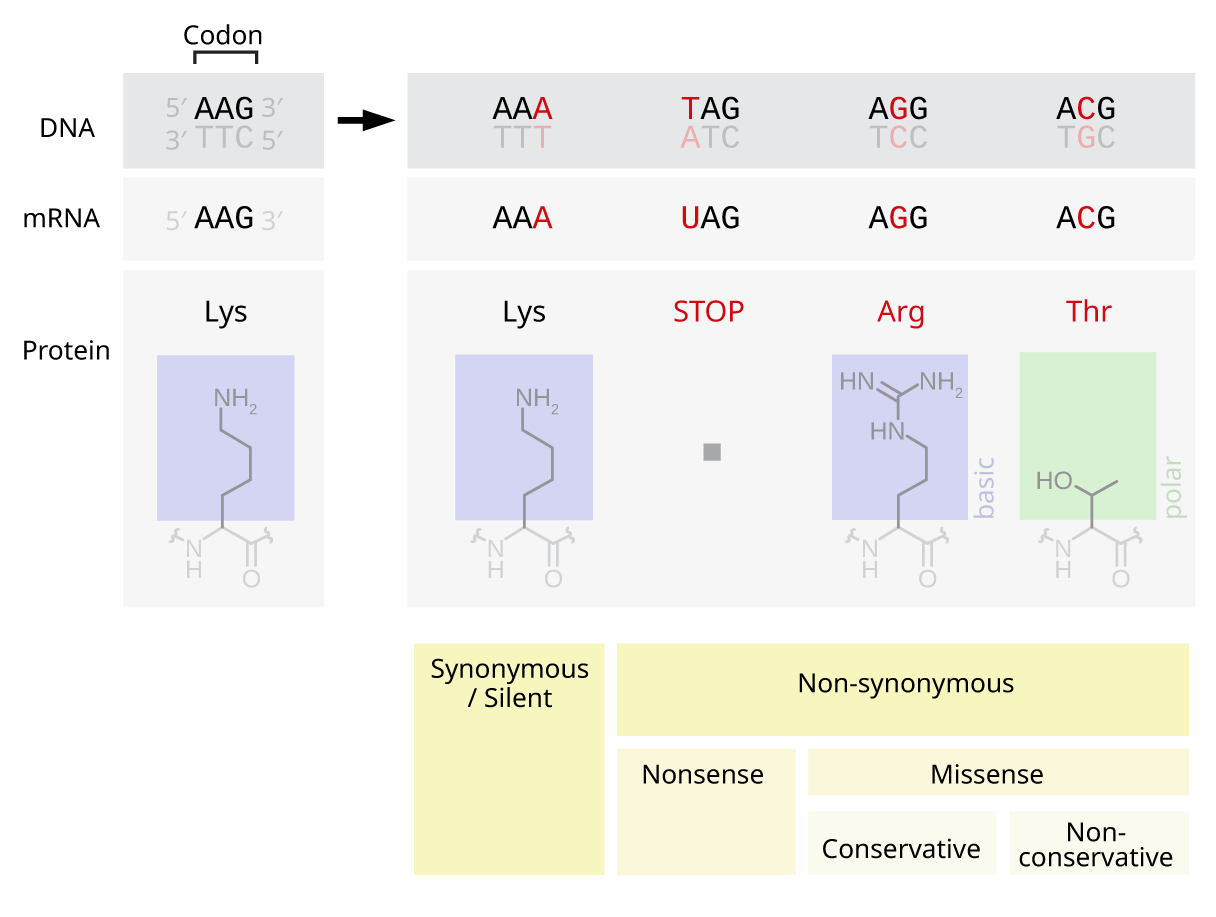
Silent Mutation
Silent mutations, also called synonymous or samesense mutations, are mutations in DNA that do not have an observable effect on the organism's phenotype. The phrase ''silent mutation'' is often used interchangeably with the phrase '' synonymous mutation''; however, synonymous mutations are not always silent, nor vice versa. Synonymous mutations can affect transcription, splicing, mRNA transport, and translation, any of which could alter phenotype, rendering the synonymous mutation non-silent. The substrate specificity of the tRNA to the rare codon can affect the timing of translation, and in turn the co-translational folding of the protein. This is reflected in the codon usage bias that is observed in many species. Mutations that cause the altered codon to produce an amino acid with similar functionality (''e.g.'' a mutation producing leucine instead of isoleucine) are often classified as silent; if the properties of the amino acid are conserved, this mutation does not usually s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Mendelian Inheritance In Man
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) is a continuously updated catalog of human genes and genetic disorders and traits, with a particular focus on the gene-phenotype relationship. , approximately 9,000 of the over 25,000 entries in OMIM represented phenotypes; the rest represented genes, many of which were related to known phenotypes. Versions and history OMIM is the online continuation of Victor A. McKusick's ''Mendelian Inheritance in Man'' (MIM), which was published in 12 editions between 1966 and 1998.McKusick, V. A. ''Mendelian Inheritance in Man. Catalogs of Autosomal Dominant, Autosomal Recessive and X-Linked Phenotypes.'' Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1st ed, 1996; 2nd ed, 1969; 3rd ed, 1971; 4th ed, 1975; 5th ed, 1978; 6th ed, 1983; 7th ed, 1986; 8th ed, 1988; 9th ed, 1990; 10th ed, 1992. Nearly all of the 1,486 entries in the first edition of MIM discussed phenotypes. MIM/OMIM is produced and curated at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Mendelian Inheritance In Animals
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Animals (OMIA) is an online database of genes, inherited disorders and traits in more than 550 animal species. It is modelled on, and is complementary to, Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM). It aims to provide a publicly accessible catalogue of all animal phenes, excluding those in human and mouse, for which species specific resources are already available (OMIM, MLC). Authored by Professor Frank Nicholas of the University of Sydney, with some contribution from colleagues, the database contains textual information and references as well as links to relevant PubMed and Gene records at the NCBI. OMIA is hosted by the University of Sydney, with an Entrez mirror located at the NCBI. See also * Medical classification A medical classification is used to transform descriptions of medical diagnoses or procedures into standardized statistical code in a process known as clinical coding. Diagnosis classifications list diagnosis codes, which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Phenotype
''The Extended Phenotype'' is a 1982 book by the evolutionary biologist Richard Dawkins, in which the author introduced a biological concept of the same name. The book's main idea is that phenotype should not be ''limited'' to biological processes such as protein biosynthesis or tissue growth, but ''extended'' to include all effects that a gene has on its environment, inside or outside the body of the individual organism. Dawkins considers ''The Extended Phenotype'' to be a sequel to ''The Selfish Gene'' (1976) aimed at professional biologists, and as his principal contribution to evolutionary theory. Summary Genes as the unit of selection in evolution The central thesis of ''The Extended Phenotype,'' and of its predecessor by the same author, ''The'' ''Selfish Gene'', is that individual organisms are not the true units of natural selection. Instead, the gene — or the 'active, germ-line replicator' — is the unit upon which the forces of evolutionary selection and adaptat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Death
Cell death is the event of a biological cell ceasing to carry out its functions. This may be the result of the natural process of old cells dying and being replaced by new ones, as in programmed cell death, or may result from factors such as diseases, localized injury, or the death of the organism of which the cells are part. Apoptosis or Type I cell-death, and Autophagy (cellular), autophagy or Type II cell-death are both forms of programmed cell death, while necrosis is a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury. The term "cell necrobiology" has been used to describe the life processes associated with morphological, biochemical, and molecular changes which predispose, precede, and accompany cell death, as well as the consequences and tissue response to cell death. The word is derived from the Greek language, Greek νεκρό meaning "death", βìο meaning "life", and logos, λόγος meaning "the study of". The term was initially coined to bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Genetics
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. Perspectives The main processes involved in the embryonic development of animals are: tissue patterning (via regional specification and patterned cell differentiation); tissue growth; and tissue morphogenesis. * Regional specification refers to the processes that create the spatial patterns in a ball or sheet of initially similar cells. This generally involves the action of cytoplasmic determinants, located within parts of the fertilized egg, and of inductive signals emitted from signaling centers in the embryo. The early stages of regional specification do not generate functional differentiated cells, but cell populations committed to developing to a specific region or part of the organism. These are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres (4-cell stage) are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, (16-cell stage) takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism. The sexual fusion of haploid cells is called karyogamy, the result of which is the formation of a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, diploid cell called the zygote or zygospore. History German zoologists Oscar Hertwig, Oscar and Richard Hertwig made some of the first discoveries on animal zygote formation in the late 19th century. In multicellular organisms The zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In humans and most other Anisogamy, anisogamous organisms, a zygote is formed when an egg cell and sperm, sperm cell come together to create a new unique organism. The formation of a cell potency, totipotent zygote with the potential to produce a whole organism depends on epigenetics, epigenetic reprogramming. DNA demethyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more or less common within a population over successive generations. The process of evolution has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation. The scientific theory of evolution by natural selection was conceived independently by two British naturalists, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, in the mid-19th century as an explanation for why organisms are adapted to their physical and biological environments. The theory was first set out in detail in Darwin's book ''On the Origin of Species''. Evolution by natural selection is established by observable facts about living organisms: (1) more offspring are often produced than can possibly survive; (2) phenotypic variatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermophilic
A thermophile is a type of extremophile that thrives at relatively high temperatures, between . Many thermophiles are archaea, though some of them are bacteria and fungi. Thermophilic eubacteria are suggested to have been among the earliest bacteria. Thermophiles are found in geothermally heated regions of the Earth, such as hot springs like those in Yellowstone National Park and deep sea hydrothermal vents, as well as decaying plant matter, such as peat bogs and compost. They can survive at high temperatures, whereas other bacteria or archaea would be damaged and sometimes killed if exposed to the same temperatures. The enzymes in thermophiles function at high temperatures. Some of these enzymes are used in molecular biology, for example the ''Taq'' polymerase used in PCR. "Thermophile" is derived from the (''thermotita''), meaning heat, and (''philia''), love. Comparative surveys suggest that thermophile diversity is principally driven by pH, not temperature. Clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |