|
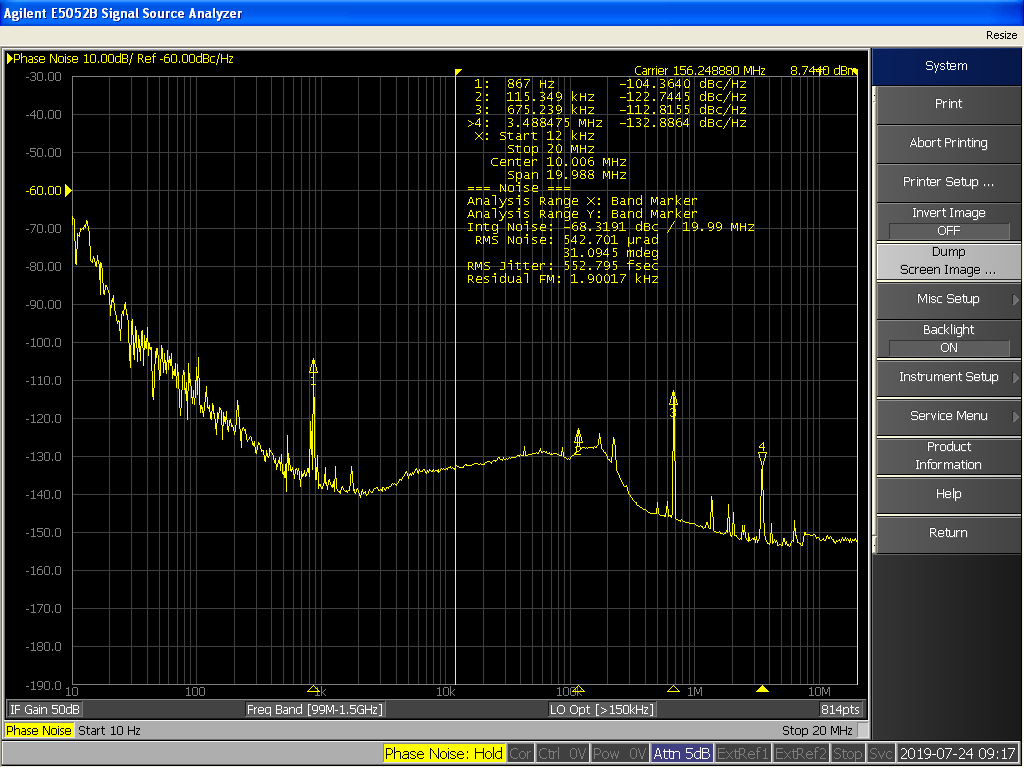
Phase Noise
In signal processing, phase noise is the frequency-domain representation of random fluctuations in the phase of a waveform, corresponding to time-domain deviations from perfect periodicity (jitter). Generally speaking, radio-frequency engineers speak of the phase noise of an oscillator, whereas digital-system engineers work with the jitter of a clock. Definitions An ideal oscillator would generate a pure sine wave. In the frequency domain, this would be represented as a single pair of Dirac delta functions (positive and negative conjugates) at the oscillator's frequency; i.e., all the signal's power is at a single frequency. All real oscillators have phase modulated noise components. The phase noise components spread the power of a signal to adjacent frequencies, resulting in noise sidebands. Consider the following noise-free signal: :x(t)= A\cos(2 \pi f_0 t) Phase noise is added to this signal by adding a stochastic process represented by \phi(t) to the signal a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Noise Measured In Ssa
Phase or phases may refer to: Science *State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist *Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform *Phase space, a mathematical space in which each possible state of a physical system is represented by a point also referred to as a "microscopic state" **Phase space formulation, a formulation of quantum mechanics in phase space *Phase (waves), the position of a point in time (an instant) on a waveform cycle **Instantaneous phase, generalization for both cyclic and non-cyclic phenomena *AC phase, the phase offset between alternating current electric power in multiple conducting wires **Single-phase electric power, distribution of AC electric power in a system where the voltages of the supply vary in unison **Three-phase electric power, a common method of AC electric power generation, transmission, and distribution *Phase problem, the loss of information (the phase) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidebands
In radio communications, a sideband is a band (radio), band of frequencies higher than or lower than the carrier frequency, that are the result of the modulation process. The sidebands carry the information transmitted by the radio signal. The sidebands comprise all the spectral components of the modulated signal except the carrier. The signal components above the carrier frequency constitute the upper sideband (USB), and those below the carrier frequency constitute the lower sideband (LSB). All forms of modulation produce sidebands. Sideband creation We can illustrate the creation of sidebands with one trigonometric identity: :\cos(A)\cdot \cos(B) \equiv \tfrac\cos(A+B) + \tfrac\cos(A-B) Adding \cos(A) to both sides: :\cos(A)\cdot [1+\cos(B)] = \tfrac\cos(A+B) + \cos(A) + \tfrac\cos(A-B) Substituting (for instance) A \triangleq 1000\cdot t and B \triangleq 100\cdot t, where t represents time: :\underbrace_\cdot \underbrace_ = \underbrace_ + \und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Noise
In signal processing, white noise is a random signal having equal intensity at different frequencies, giving it a constant power spectral density. The term is used with this or similar meanings in many scientific and technical disciplines, including physics, acoustical engineering, telecommunications, and statistical forecasting. White noise refers to a statistical model for signals and signal sources, not to any specific signal. White noise draws its name from white light, although light that appears white generally does not have a flat power spectral density over the visible band. In discrete time, white noise is a discrete signal whose samples are regarded as a sequence of serially uncorrelated random variables with zero mean and finite variance; a single realization of white noise is a random shock. In some contexts, it is also required that the samples be independent and have identical probability distribution (in other words independent and identically distribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RF Design
''Defense Electronics'' (formerly ''RF Design'') is a Penton Media trade magazine A trade magazine, also called a trade journal or trade paper (colloquially or disparagingly a trade rag), is a magazine or newspaper whose target audience is people who work in a particular tradesman, trade or industry. The collective term ... that covers radio frequency design. ''RF Design'' was started in 1978 and was published by Penton Media on a quarterly basis. References External links *http://defenseelectronicsmag.com/ Business magazines published in the United States Electrical and electronic engineering magazines Engineering magazines Magazines established in 1978 Magazines published in Tennessee Professional and trade magazines Quarterly magazines published in the United States {{business-mag-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flicker Noise
Flicker noise is a type of electronic noise with a 1/''f'' power spectral density. It is therefore often referred to as 1/''f'' noise or pink noise, though these terms have wider definitions. It occurs in almost all electronic devices and can show up with a variety of other effects, such as impurities in a conductive channel, generation and recombination noise in a transistor due to base current, and so on. Properties 1/''f'' noise in current or voltage is usually related to a direct current, as resistance fluctuations are transformed to voltage or current fluctuations by Ohm's law. There is also a 1/''f'' component in resistors with no direct current through them, likely due to temperature fluctuations modulating the resistance. This effect is not present in manganin, as it has negligible temperature coefficient of resistance. In electronic devices, it shows up as a low-frequency phenomenon, as the higher frequencies are overshadowed by white noise from other sources. In o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Oscillator
In electronics, the term local oscillator (LO) refers to an electronic oscillator when used in conjunction with a Frequency mixer, mixer to change the frequency of a signal. This frequency conversion process, also called Heterodyne, heterodyning, produces the sum and difference frequencies from the frequency of the local oscillator and frequency of the input signal. Processing a signal at a fixed frequency gives a radio receiver improved performance. In many receivers, the function of local oscillator and mixer is combined in one stage called a "Pentagrid converter, converter" - this reduces the space, cost, and power consumption by combining both functions into one active device. The term ''local'' refers to the fact that the frequency is generated within the circuit and is not reliant on any external signals, although the frequency of the oscillator may be tuned according to external signals. Applications Local oscillators are used in the superheterodyne receiver, the most c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Device Under Test
A device under test (DUT), also known as equipment under test (EUT) and unit under test (UUT), is a manufactured product undergoing testing, either at first manufacture or later during its life cycle as part of ongoing functional testing and calibration checks. This can include a test after repair to establish that the product is performing in accordance with the original product specification. Electronics testing In the electronics industry a DUT is any electronic assembly under test. For example, cell phones coming off of an assembly line may be given a final test in the same way as the individual chips were earlier tested. Each cell phone under test is, briefly, the DUT. For circuit boards, the DUT is often connected to the test equipment using a bed of nails tester of pogo pins. Semiconductor testing In semiconductor testing, the device under test is a die on a wafer or the resulting packaged part. A connection system is used, connecting the part to automatic or manual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrum Analyzer
A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure the power of the spectrum of known and unknown signals. The input signal that most common spectrum analyzers measure is electrical; however, spectral compositions of other signals, such as acoustic pressure waves and optical light waves, can be considered through the use of an appropriate transducer. Spectrum analyzers for other types of signals also exist, such as optical spectrum analyzers which use direct optical techniques such as a monochromator to make measurements. By analyzing the spectra of electrical signals, dominant frequency, power, distortion, harmonics, bandwidth, and other spectral components of a signal can be observed that are not easily detectable in time domain waveforms. These parameters are useful in the characterization of electronic devices, such as wireless transmitters. The display of a spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root-mean-square
In mathematics, the root mean square (abbrev. RMS, or rms) of a set of values is the square root of the set's mean square. Given a set x_i, its RMS is denoted as either x_\mathrm or \mathrm_x. The RMS is also known as the quadratic mean (denoted M_2), a special case of the generalized mean. The RMS of a continuous function is denoted f_\mathrm and can be defined in terms of an integral of the square of the function. In estimation theory, the root-mean-square deviation of an estimator measures how far the estimator strays from the data. Definition The RMS value of a set of values (or a continuous-time waveform) is the square root of the arithmetic mean of the squares of the values, or the square of the function that defines the continuous waveform. In the case of a set of ''n'' values \, the RMS is : x_\text = \sqrt. The corresponding formula for a continuous function (or waveform) ''f''(''t'') defined over the interval T_1 \le t \le T_2 is : f_\text = \sqrt , and the RMS fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leeson's Equation
Leeson's equation is an empirical expression that describes an oscillator's phase noise spectrum. Leeson's expression for single-sideband (SSB) phase noise in dBc/Hz (decibels relative to output level per hertz) and augmented for flicker noise: : L(f_\text) = 10 \log_ \bigg \frac \bigg( \bigg(\frac\bigg)^2 + 1\bigg)\bigg(\frac + 1\bigg) \bigg/math> where is the output frequency, is the loaded quality factor, is the offset from the output frequency (Hz), is the corner frequency, is the noise factor of the amplifier, is the Boltzmann constant, is absolute temperature, and is the available power at the sustaining amplifier input.https://www.ieee.li/pdf/essay/phase_noise_basics.pdf There is often misunderstanding around Leeson's equation, even in text books. In the 1966 paper, Leeson stated correctly that " is the signal level at the oscillator active element input" (often referred to as the power through the resonator now, strictly speaking it is the available power at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1/f Noise
Pink noise, noise, fractional noise or fractal noise is a signal or process with a frequency spectrum such that the power spectral density (power per frequency interval) is inversely proportional to the frequency of the signal. In pink noise, each octave interval (halving or doubling in frequency) carries an equal amount of noise energy. Pink noise sounds like a waterfall. It is often used to tune loudspeaker systems in professional audio. Pink noise is one of the most commonly observed signals in biological systems. The name arises from the pink appearance of visible light with this power spectrum. This is in contrast with white noise which has equal intensity per frequency interval. Definition Within the scientific literature, the term "1/f noise" is sometimes used loosely to refer to any noise with a power spectral density of the form S(f) \propto \frac, where is frequency, and , with exponent usually close to 1. One-dimensional signals with are usually called pink ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autocorrelation
Autocorrelation, sometimes known as serial correlation in the discrete time case, measures the correlation of a signal with a delayed copy of itself. Essentially, it quantifies the similarity between observations of a random variable at different points in time. The analysis of autocorrelation is a mathematical tool for identifying repeating patterns or hidden periodicities within a signal obscured by noise. Autocorrelation is widely used in signal processing, time domain and time series analysis to understand the behavior of data over time. Different fields of study define autocorrelation differently, and not all of these definitions are equivalent. In some fields, the term is used interchangeably with autocovariance. Various time series models incorporate autocorrelation, such as unit root processes, trend-stationary processes, autoregressive processes, and moving average processes. Autocorrelation of stochastic processes In statistics, the autocorrelation of a real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |