|
Phase Distortion
In signal processing, phase distortion or phase-frequency distortion is distortion, that is, change in the shape of the waveform, that occurs when (a) a filter's phase response is not linear over the frequency range of interest, that is, the Phase (waves), phase shift introduced by a electrical network, circuit or device is not directly proportional to frequency, or (b) the zero-frequency intercept of the phase-frequency characteristic is not 0 or an integral multiple of 2π radians. Audibility of phase distortion Grossly changed phase relationships, without changing amplitudes, can be audible but the degree of audibility of the type of phase shifts expected from typical sound systems remains debated. See also *Audio system measurements *Phase noise References Electrical parameters Audio amplifier specifications {{Sound-tech-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as audio signal processing, sound, image processing, images, Scalar potential, potential fields, Seismic tomography, seismic signals, Altimeter, altimetry processing, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, Data storage, digital storage efficiency, correcting distorted signals, improve subjective video quality, and to detect or pinpoint components of interest in a measured signal. History According to Alan V. Oppenheim and Ronald W. Schafer, the principles of signal processing can be found in the classical numerical analysis techniques of the 17th century. They further state that the digital refinement of these techniques can be found in the digital control systems of the 1940s and 1950s. In 1948, Claude Shannon wrote the influential paper "A Mathematical Theory of Communication" which was publis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distortion
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio signal representing sound or a video signal representing images, in an electronic device or communication channel. Distortion is usually unwanted, and so engineers strive to eliminate or minimize it. In some situations, however, distortion may be desirable. For example, in noise reduction systems like the Dolby noise-reduction system, Dolby system, an audio signal is deliberately distorted in ways that emphasize aspects of the signal that are subject to electrical noise, then it is symmetrically "undistorted" after passing through a noisy communication channel, reducing the noise in the received signal. Distortion is also used as a Distortion (music), musical effect, particularly with electric guitars. The addition of Electronic noise, noise o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Response
In signal processing, phase response is the relationship between the phase of a sinusoidal input and the output signal passing through any device that accepts input and produces an output signal, such as an amplifier An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power su ... or a filter. Amplifiers, filters, and other devices are often categorized by their amplitude and/or phase response. The amplitude response is the ratio of output amplitude to input, usually a function of the frequency. Similarly, phase response is the phase of the output with the input as reference. The input is defined as zero phase. A phase response is not limited to lying between 0° and 360°, as phase can accumulate to any amount of time. See also * Group delay and phase delay References Trigonometry Wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Range
Spectral bands are regions of a given spectrum, having a specific range of wavelengths or frequencies. Most often, it refers to electromagnetic bands, regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. More generally, spectral bands may also be means in the spectra of other types of signals, e.g., noise spectrum. A frequency band is an interval in the frequency domain, limited by a lower frequency and an upper frequency. For example, it may refer to a '' radio band'', such as wireless communication standards set by the International Telecommunication Union. In nuclear physics In nuclear physics, spectral bands refer to the electromagnetic emission of polyatomic systems, including condensed materials, large molecules, etc. Each ''spectral line'' corresponds to the difference in two energy levels of an atom. In molecules, these levels can split. When the number of atoms is large, one gets a continuum of energy levels, the so-called ''spectral bands''. They are often labeled in the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase (waves)
In physics and mathematics, the phase (symbol φ or ϕ) of a wave or other periodic function F of some real variable t (such as time) is an angle-like quantity representing the fraction of the cycle covered up to t. It is expressed in such a scale that it varies by one full turn as the variable t goes through each period (and F(t) goes through each complete cycle). It may be measured in any angular unit such as degrees or radians, thus increasing by 360° or 2\pi as the variable t completes a full period. This convention is especially appropriate for a sinusoidal function, since its value at any argument t then can be expressed as \varphi(t), the sine of the phase, multiplied by some factor (the amplitude of the sinusoid). (The cosine may be used instead of sine, depending on where one considers each period to start.) Usually, whole turns are ignored when expressing the phase; so that \varphi(t) is also a periodic function, with the same period as F, that repeatedly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e.g., voltage sources, current sources, resistances, inductances, capacitances). An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Thus all circuits are networks, but not all networks are circuits (although networks without a closed loop are often referred to as "open circuits"). A resistive network is a network containing only resistors and ideal current and voltage sources. Analysis of resistive networks is less complicated than analysis of networks containing capacitors and inductors. If the sources are constant ( DC) sources, the result is a DC network. The effective resistance and current distribution properties of arbitrary resistor networks can be modeled in terms of their graph measures and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The Audio Engineering Society
The Audio Engineering Society (AES) is a professional body for engineers, scientists, other individuals with an interest or involvement in the professional audio industry. The membership largely comprises engineers developing devices or products for audio, and persons working in audio content production. It also includes acousticians, audiologists, academics, and those in other disciplines related to audio. The AES is the only worldwide professional society devoted exclusively to audio technology. Established in 1948, the Society develops, reviews and publishes engineering standards for the audio and related media industries, and produces the AES Conventions, which are held twice a year alternating between Europe and the US. The AES and individual regional or national ''sections'' also hold ''AES Conferences'' on different topics during the year. History The idea of a society dedicated solely to audio engineering had been discussed for some time before the first meeting, but was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audio System Measurements
Audio system measurements are used to quantify audio system performance. These measurements are made for several purposes. Designers take measurements to specify the performance of a piece of equipment. Maintenance engineers make them to ensure equipment is still working to specification, or to ensure that the cumulative defects of an audio path are within limits considered acceptable. Audio system measurements often accommodate psychoacoustic principles to measure the system in a way that relates to human hearing. Subjectivity and frequency weighting Subjectively valid methods came to prominence in consumer audio in the UK and Europe in the 1970s, when the introduction of compact cassette tape, dbx (noise reduction), dbx and Dolby noise reduction techniques revealed the unsatisfactory nature of many basic engineering measurements. The specification of ITU-R 468 noise weighting, weighted CCIR-468 quasi-peak noise, and flutter measurement, weighted quasi-peak wow and flutter b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
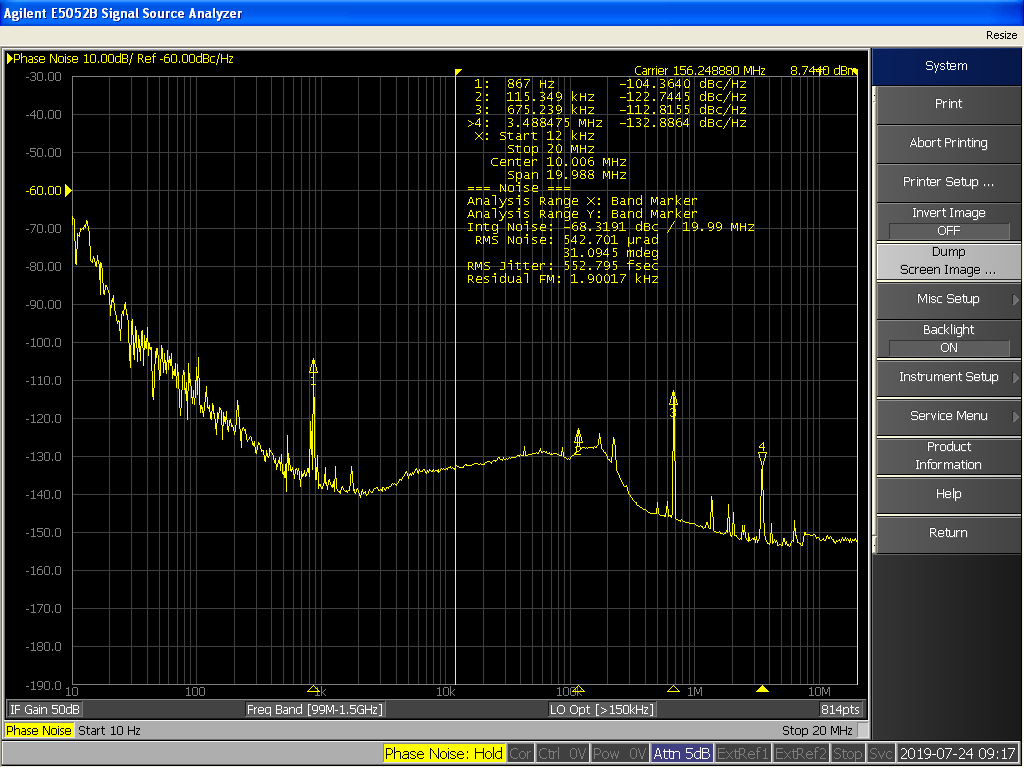
Phase Noise
In signal processing, phase noise is the frequency-domain representation of random fluctuations in the phase of a waveform, corresponding to time-domain deviations from perfect periodicity (jitter). Generally speaking, radio-frequency engineers speak of the phase noise of an oscillator, whereas digital-system engineers work with the jitter of a clock. Definitions An ideal oscillator would generate a pure sine wave. In the frequency domain, this would be represented as a single pair of Dirac delta functions (positive and negative conjugates) at the oscillator's frequency; i.e., all the signal's power is at a single frequency. All real oscillators have phase modulated noise components. The phase noise components spread the power of a signal to adjacent frequencies, resulting in noise sidebands. Consider the following noise-free signal: :x(t)= A\cos(2 \pi f_0 t) Phase noise is added to this signal by adding a stochastic process represented by \phi(t) to the signal a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Parameters
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of either a positive or negative electric charge produces an electric field. The motion of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. In most applications, Coulomb's law determines the force acting on an electric charge. Electric potential is the work done to move an electric charge from one point to another within an electric field, typically measured in volts. Electricity plays a central role in many modern technologies, serving in electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment, and in electronics dealing with electrical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |