|
Persona (psychology)
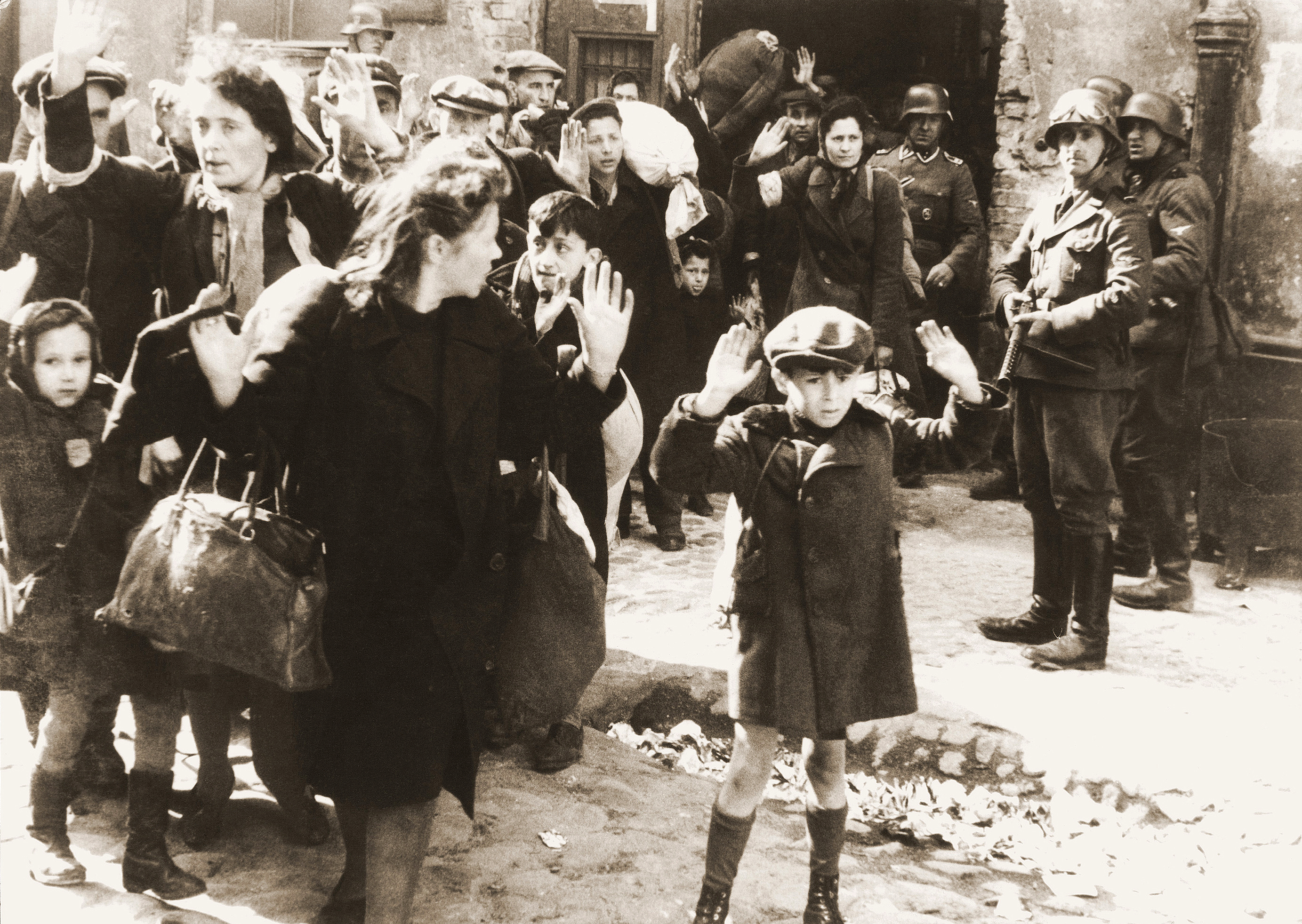
The persona, for Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung, is the social face an individual presents to the world—"a kind of mask, designed on the one hand to make a definite impression upon others, and on the other to conceal the true nature of the individual." Jung's persona Identification According to Jung, the development of a viable social persona is a vital part of adapting to, and preparing for, adult life in the external social world. "A strong ego relates to the outside world through a flexible persona; identifications with a specific persona (doctor, scholar, artist, etc.) inhibits psychological development." For Jung, "the danger is that eoplebecome identical with their personas—the professor with his textbook, the tenor with his voice." The result could be "the shallow, brittle, conformist kind of personality which is 'all persona', with its excessive concern for 'what people think'"—an unreflecting state of mind "in which people are utterly unconscious of any distinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Jung
Carl Gustav Jung ( ; ; 26 July 1875 – 6 June 1961) was a Swiss psychiatrist, psychotherapist, and psychologist who founded the school of analytical psychology. A prolific author of Carl Jung publications, over 20 books, illustrator, and correspondent, Jung was a complex and convoluted academic, best known for his concept of Jungian archetypes, archetypes. Alongside contemporaries Sigmund Freud, Freud and Alfred Adler, Adler, Jung became one of the most influential psychologists of the early 20th century and has fostered not only scholarship, but also popular interest. Jung's work has been influential in the fields of psychiatry, anthropology, archaeology, literature, philosophy, psychology, and religious studies. He worked as a research scientist at the Burghölzli psychiatric hospital in Zurich, under Eugen Bleuler. Jung established himself as an influential mind, developing a friendship with Sigmund Freud, founder of psychoanalysis, conducting a The Freud/Jung Letters, leng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jungian Archetypes
Jungian archetypes are a concept from psychology that refers to a universal, inherited idea, pattern of thought, or image that is present in the collective unconscious of all human beings. As the psychic counterpart of instinct (i.e., archetypes are innate, symbolic, psychological expressions that manifest in response to patterned biological instincts), archetypes are thought to be the basis of many of the common themes and symbols that appear in stories, myths, and dreams across different cultures and societies. Some examples of archetypes include those of the mother, the child, the trickster, and Flood myth, the flood, among others. The concept of the collective unconscious was first proposed by Carl Jung, a Swiss Psychiatry, psychiatrist and Analytical Psychology, analytical psychologist. According to Jung, archetypes are innate patterns of thought and behavior that strive for Self-realization, realization within an individual's environment. This process of Self-actualization, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical Psychology
Analytical psychology (, sometimes translated as analytic psychology; also Jungian analysis) is a term referring to the psychological practices of Carl Jung. It was designed to distinguish it from Freud's psychoanalytic theories as their seven-year collaboration on psychoanalysis was drawing to an end between 1912 and 1913. The evolution of his science is contained in his monumental ''opus'', the '' Collected Works'', written over sixty years of his lifetime. The history of analytical psychology is intimately linked with the biography of Jung. At the start, it was known as the "Zurich school", whose chief figures were Eugen Bleuler, Franz Riklin, Alphonse Maeder and Jung, all centred in the Burghölzli hospital in Zurich. It was initially a theory concerning psychological complexes until Jung, upon breaking with Sigmund Freud, turned it into a generalised method of investigating archetypes and the unconscious, as well as into a specialised psychotherapy. Analytical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
True Self And False Self
The true self (also known as real self, authentic self, original self and vulnerable self) and the false self (also known as fake self, idealized self, superficial self and pseudo self) are a psychological dualism conceptualized by English psychoanalyst Donald Winnicott. Winnicott used "true self" to denote a sense of self based on spontaneous authentic experience and a feeling of being alive, having a real self with little to no contradiction. "False self", by contrast, denotes a sense of self created as a defensive facade, which in extreme cases can leave an individual lacking spontaneity and feeling dead and empty behind an inconsistent and incompetent appearance of being real, such as in narcissism. Characteristics In his work, Winnicott saw the "true self" as stemming from self-perception in early infancy, such as awareness of tangible aspects of being alive, like blood pumping through veins and lungs inflating and deflating with breathing—what Winnicott called ''simply bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persona (series)
''Persona'', previously marketed as ''Shin Megami Tensei: Persona'' outside of Japan, is a video game franchise primarily developed by Atlus and owned by Sega. Centered around a series of Japanese role-playing game, Japanese role-playing video games, ''Persona'' is a spin-off from Atlus' ''Megami Tensei'' franchise. The first entry in the series, ''Revelations: Persona'', was released in 1996 for the PlayStation (console), PlayStation. The series has seen several more games since, with the most recent main entry being 2024's ''Persona 3 Reload.'' ''Persona'' began as a spin-off based on the positively-received high school setting of ''Shin Megami Tensei If...'' (1994). ''Persona'' core features include a group of students as the main cast, a silent protagonist similar to the mainline ''Megami Tensei'' franchise, and combat using #Personas, Personas. Beginning with ''Persona 3'' in 2006, the main series came to focus more on, and become renowned for, the immersive Dating sim, soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persona (1966 Film)
''Persona'' is a 1966 Swedish avant-garde psychological drama film written, directed, and produced by Ingmar Bergman and starring Bibi Andersson and Liv Ullmann. The story revolves around a young nurse named Alma (Andersson) and her patient, well-known stage actress Elisabet Vogler (Ullmann), who has suddenly stopped speaking. They move to a cottage, where Alma cares for Elisabet, confides in her, and begins having trouble distinguishing herself from her patient. Characterized by elements of psychological horror, ''Persona'' has been the subject of much critical analysis, interpretation, and debate. The film's exploration of duality, insanity, and Identity (social science), personal identity has been interpreted as reflecting the Jungian theory of ''persona (psychology), persona'' and dealing with issues related to filmmaking, vampirism, homosexuality, motherhood, abortion, and other subjects. The experimental style of its prologue, storytelling, and end has also been noted. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masking (behavior)
In psychology and sociology, masking, also known as social camouflaging, is a defensive behavior in which an individual conceals their natural personality or behavior in response to social pressure, abuse, or harassment. Masking can be strongly influenced by environmental factors such as authoritarian parents, social rejection, and emotional abuse, emotional, physical abuse, physical, or sexual abuse, sexual abuse. Masking can be a behavior individuals adopt subconsciously as coping mechanisms or a trauma response, or it can be a conscious behavior an individual adopts to Assimilation (psychology), fit in within perceived societal norms. Masking is interconnected with maintaining Performativity, performative behavior within social structures and cultures. Masking is mostly used to conceal a negative affectivity, negative emotion (usually sadness, frustration, and anger) with a positive emotion or indifferent affect. Developmental studies have shown that this ability begins as earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bad Faith (existentialism)
In existentialism, bad faith () is the psychological phenomenon whereby individuals act inauthentically, by yielding to the external pressures of society to adopt false values and disown their innate freedom as sentient human beings. Bad faith also derives from the related concepts of self-deception and '' ressentiment''. Freedom and choice A critical claim in existentialist thought is that individuals are always free to make choices and guide their lives towards their own chosen goal or "project". This claim suggests that individuals cannot escape this freedom, even in overwhelming circumstances. For instance, even an empire's colonized victims possess choices: to submit to rule, to negotiate, to commit suicide, to resist nonviolently, or to counter-attack. Although external circumstances may limit individuals, called facticity, they cannot force a person to follow one of the remaining courses over another. In this sense, the individual still has some freedom of choice. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akrasia
Akrasia (/əˈkreɪziə/; from Ancient Greek ἀκρασία, literally meaning "lack of self-control" or "powerlessness," derived from ἀ- "without" + κράτος "power, rule") refers to the phenomenon of acting against one's better judgment—the state in which an individual intentionally performs an action while simultaneously believing that a different course of action would be better. Sometimes translated as "weakness of will" or "incontinence," akrasia describes the paradoxical human experience of knowingly choosing what one judges to be the inferior option. History In Plato's '' Protagoras'' dialogue, Socrates asks precisely how it is possible that, ''if'' one judges action A to be the best course of action, why one would do anything other than A. Classical answers In Plato's ''Protagoras'', Socrates presents a radical thesis that fundamentally denies the existence of akrasia. His famous declaration, "No one goes willingly toward the bad" (οὐδεὶς ἑκὼν κ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anima And Animus
The anima and animus are a pair of Dualism in cosmology, dualistic, Jungian archetypes which form a syzygy (other)#Philosophy, syzygy, or union of opposing forces. Carl Jung described the animus as the Unconscious mind, unconscious masculine side of a woman, and the anima as the unconscious feminine side of a man, each transcending the personal Psyche (psychology), psyche. They are considered Animism, animistic parts within the Self in Jungian psychology, Self, with Jung viewing parts of the self as part of the infinite set of archetypes within the collective unconscious. Anima and animus are described in analytical psychology and archetypal psychology, under the umbrella of transpersonal psychology. Modern Jungian clinical theory under these frameworks considers a syzygy-without-its-partner to be like Yin and Yang , yin without Yin and Yang , yang. The goal is to become integrated over time into a well-functioning whole, similar to positive psychology's understanding o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
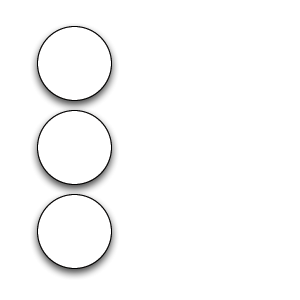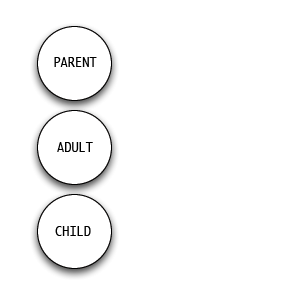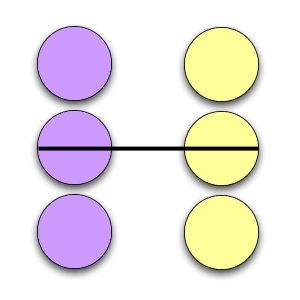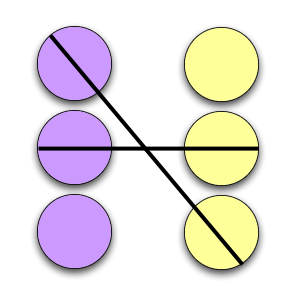
Transactional Analysis
Transactional analysis is a psychoanalytic theory and method of therapy wherein social interactions (or "transactions") are analyzed to determine the id, ego, and superego, ego state of the communicator (whether parent-like, childlike, or adult-like) as a basis for understanding behavior. In transactional analysis, the communicator is taught to alter the ego state as a way to solve emotional problems. The method deviates from Freudian psychoanalysis, which focuses on increasing awareness of the contents of subconsciously held ideas. Eric Berne developed the concept and paradigm of transactional analysis in the late 1950s. History Eric Berne presented transactional analysis to the world as a Phenomenology (philosophy), phenomenological approach, supplementing Freud's philosophical construct with observable data. His theory built on the science of Wilder Penfield and René Spitz along with the neo-psychoanalytic thought of people such as Paul Federn, Edoardo Weiss, and Erik Erikson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |