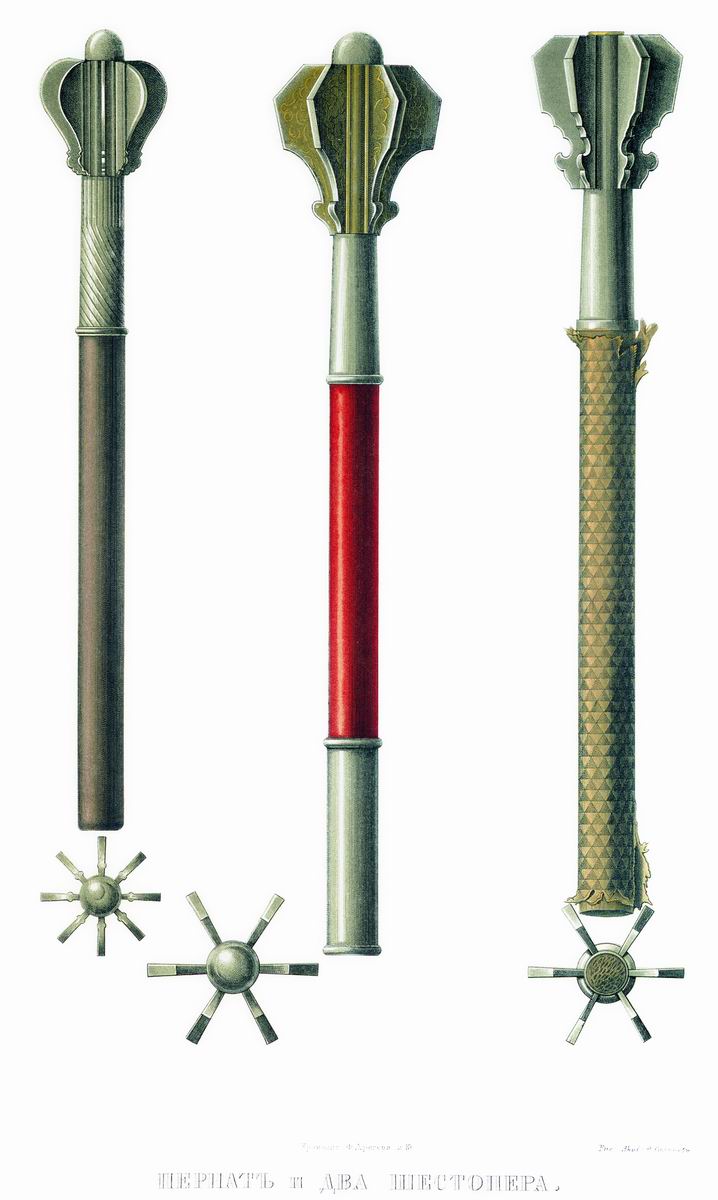
|
Pernach
A pernach (, or , ) is a type of flanged mace originating in the 12th century in the region of Kievan Rus' and later widely used throughout Europe. The name comes from the Slavic word ''перо'' (''pero'') meaning feather, referring to a type of mace resembling an arrow with feathering. Uses against armour and mail Among a variety of similar weapons developed in 12th-century Persian- and Turkic-dominated areas, the pernach became pre-eminent, being capable of penetrating plate armour and plate mail. Ceremonial uses A pernach or shestoper (, "six-feathered") was often carried as a ceremonial mace of rank by certain Eastern European military commanders, including Polish magnates, Ukrainian Cossack colonels and sotniks (cf. centurion). Symbolic uses In Ukraine, it symbolized the authority of polkovnyks (regional leaders or military officers) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mace (bludgeon)
A mace is a blunt weapon, a type of Club (weapon), club or virge that uses a heavy head on the end of a handle to deliver powerful Strike (attack), strikes. A mace typically consists of a strong, heavy, wooden or metal shaft, often reinforced with metal, featuring a head made of stone, bone, copper, bronze, iron, or steel. The head of a mace can be shaped with flanges or knobs to increase the pressure of an impact by focusing the force on a small point. They would bind on metal instead of sliding around it, allowing them to deliver more force to an armored opponent than a traditional mace. This effect increased the potential for the mace to injure an armored opponent through weak spots in the armor, and even damage plate armor by denting it, potentially binding overlapping plates and impeding the wearer's range of motion. Medieval historian and re-enactor Todd Todeschini (AKA Todd Cutler) demonstrated this effect with period accurate equipment in a series of tests on video. Mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
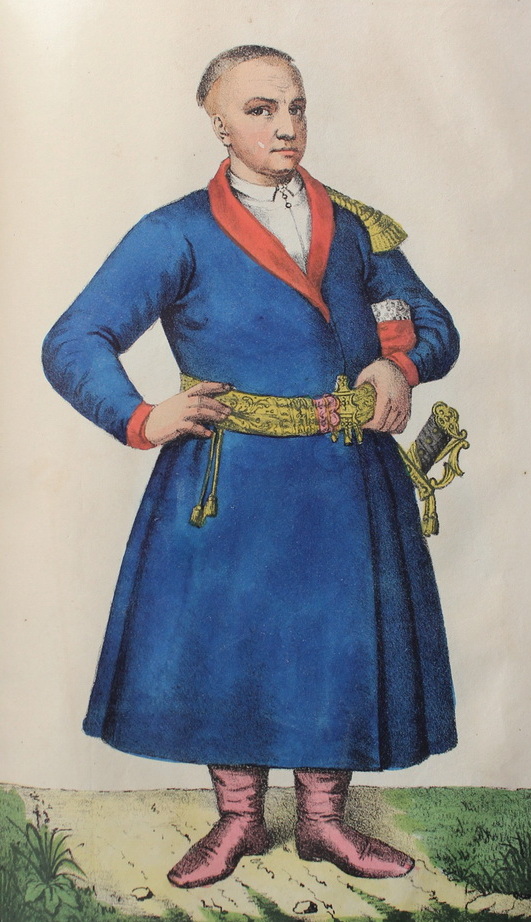
Polkovnyk
(; ) is a military rank used mostly in Slavic-speaking countries which corresponds to a colonel in English-speaking states, ''coronel'' in Spanish and Portuguese-speaking states and '' oberst'' in several German-speaking and Scandinavian countries. It was originally a rank in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Russian Empire. However, in Cossack Hetmanate and Sloboda Ukraine, ''polkovnyk'' was an administrative rank similar to a governor. Usually this word is translated as colonel, however the transliteration is also in common usage, for the sake of the historical and social context. began as a commander of a distinct group of troops (''polk''), arranged for battle. The exact name of this rank maintains a variety of spellings in different languages, but all descend from the Old Slavonic word ''polk'' (literally: regiment sized unit), and include the following in alphabetical order: # Belarus — # Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Montenegro and Serbia — () # Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Weapons
This is a list of weapons that were used during the medieval period. Handheld weapons * Battle axe * Bec de corbin * Bludgeon * Club * Flail * Flanged mace * Horseman's pick * Mace * Morning star * Quarterstaff * Shestopyor, Pernach * War hammer Swords and bladed weapons Swords can have single or double bladed edges or even edgeless. The blade can be curved or straight. * Arming sword * Dagger * Estoc * Falchion * Katana * Knife * Longsword * Messer * Rapier * Sabre or saber (Most sabers belong to the renaissance period, but some sabers can be found in the late medieval period) * Shortsword * Ulfberht (Frankish) *Scythe *War scythe *Poleaxe *Spear *Scimitar Projectile weapons * Bows ** English Longbow *** Daikyu *** English longbow *** Welsh longbow ** Recurved bows *** Hungarian bow *** Perso-Parthian bow ** Short bows and reflex bows *** Gungdo *** Hankyu *** Mongol bow *** Turkish bow ** Crossbows *** Arbalest *** Crossbow *** Repeating crossbow *** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maces (bludgeons)
Mace may refer to: Spices * Mace (spice), a spice derived from the aril of nutmeg * '' Achillea ageratum'', known as English mace, a flowering plant once used as a herb Weapons * Mace (bludgeon), a weapon with a heavy head on a solid shaft used to bludgeon opponents ** Flail (weapon), a spiked weapon on a chain, sometimes called a chain mace or mace-and-chain ** Ceremonial mace, an ornamented mace used in civic ceremonies ** Gada (mace), the blunt mace or club from India *** Kaumodaki, the gada (mace) of the Hindu god Vishnu * Mace (spray), a brand of tear gas, often used by police * MGM-13 Mace, a U.S. tactical surface-to-surface missile * Multi-mission Affordable Capacity Effector, a U.S. air-launched cruise missile Science and technology * Major adverse cardiovascular events, a criterion for evaluating cardiovascular disease treatments such as angioplasty * Malone antegrade continence enema, a surgical procedure used to create a continent pathway proximal to the anus * Major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th-century Introductions
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hetman
''Hetman'' is a political title from Central and Eastern Europe, historically assigned to military commanders (comparable to a field marshal or imperial marshal in the Holy Roman Empire). First used by the Czechs in Bohemia in the 15th century, it was the title of the second-highest military commander after the king in the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from the 16th to 18th centuries. Hetman was also the title of the head of the Cossack state in Ukraine after the Khmelnytsky Uprising of 1648. Throughout much of the history of Romania and the Moldavia, hetmans were the second-highest army rank. In the modern Czech Republic, the title is used for regional governors. Etymology The term ''hetman'' was a Polish borrowing, most likely stemming via Czech from the Turkic title ''ataman'' (literally 'father of horsemen'), however it could also come from the German – captain. Since hetman as a title first appeared in Czechia in the 15th century, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centurion
In the Roman army during classical antiquity, a centurion (; , . ; , or ), was a commander, nominally of a century (), a military unit originally consisting of 100 legionaries. The size of the century changed over time; from the 1st century BC through most of the imperial era it was reduced to 80 men. A centurion was promoted for being an exemplary soldier and was then expected to become a strict commander of his subordinates, to lead his troops by example, and coordinate his century's actions. They were also responsible for handling logistics and supplies, as well as any discipline that was required. In a Roman legion, centuries were grouped into cohorts and commanded by a senior centurion. The prestigious first cohort (a formation of five double-strength centuries of 160 men each) was led by the '' primus pilus,'' who commanded the ''primi ordines'' who were the centurions of the first cohort. A centurion's symbol of office was the vine staff, with which they disciplined e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sotnik
Sotnik or sotnyk (; ; ) was a military rank among the Cossack starshyna (military officers), the Russian ''streltsy'' and Cossack cavalry, the Ukrainian Insurgent Army, the Ukrainian Galician Army, and the Ukrainian People's Army. Administrative rank Holders of the rank also served as leaders of territorial units. In the Cossacks' paramilitary society of the Zaporozhian Host, Cossack Hetmanate, and Sloboda Ukraine, territories were organized along the lines of military organization and commanded by officers. During the Khmelnytsky Uprising and in the Cossack Hetmanate (17th-18th centuries), ''sotnyks'' were leaders of territorial administrative subdivisions called ''sotnyas''. Such sotnyks were subordinated to ''polkovnyks'' (colonel) who were in control of a polk (primary administrative division) and a regiment (military unit). Military ranks The word ''sotnik'' literally means ''commander of a hundred men'' in most Slavonic languages, much like how the Latin term Centurion r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonel
Colonel ( ; abbreviated as Col., Col, or COL) is a senior military Officer (armed forces), officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations. In the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of a regiment in an army. Modern usage varies greatly, and in some cases, the term is used as an Colonel (title), honorific title that may have no direct relationship to military. In some smaller military forces, such as those of Monaco or the Holy See, Vatican, colonel is the highest Military rank, rank. Equivalent naval ranks may be called Captain (naval), captain or ship-of-the-line captain. In the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth's air force ranking system, the equivalent rank is group captain. History and origins By the end of the late medieval period, a group of "companies" was referred to as a "column" of an army. According to Raymond Oliver, , the Spanish began explicitly reorganizing part of thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cossack
The Cossacks are a predominantly East Slavic Eastern Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of eastern Ukraine and southern Russia. Cossacks played an important role in defending the southern borders of Ukraine and Russia, countering the Crimean-Nogai raids, alongside economically developing steppe regions north of the Black Sea and around the Azov Sea. Historically, they were a semi-nomadic and semi-militarized people, who, while under the nominal suzerainty of various Eastern European states at the time, were allowed a great degree of self-governance in exchange for military service. Although numerous linguistic and religious groups came together to form the Cossacks, most of them coalesced and became East Slavic–speaking Orthodox Christians. The rulers of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russian Empire endowed Cossacks with certain special privileges in return for the military duty to serve in the irregular troops: Zaporozhian Cossac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |