|
Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma refers to a group of T-cell lymphomas that develop away from the thymus or bone marrow. Examples include: * Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas * Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma * Extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type * Enteropathy type T-cell lymphoma * Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma * Anaplastic large cell lymphoma * Peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified In ICD-10 ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), a medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO). It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social cir ..., cutaneous T-cell lymphomas are classified separately. References External links Non-Hodgkin lymphoma {{Oncology-stub} ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-cell Lymphoma
T-cell lymphoma is a rare form of cancerous lymphoma affecting T cell, T-cells. Lymphoma arises mainly from the uncontrolled proliferation of lymphocytes, such as T-cells, and can become cancerous. T-cell lymphoma is categorized under Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and represents less than 15% of all Non-Hodgkin's diseases in the category. T-cell lymphomas are often categorised based on their growth patterns as either aggressive (fast-growing) or indolent (slow-growing). Although the cause of T-cell lymphoma is not definitive, it has been associated with various risk factors and viruses such as Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and Human T cell leukemia virus-1, human T-cell leukemia virus-1 (HTLV1). The prognosis and treatment of T-cell lymphoma can vary drastically based on the specific type of lymphoma and its growth patterns. Due to their rarity and high variability between the different subtypes, the prognosis of T-cell lymphoma is significantly worse than other Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymus
The thymus (: thymuses or thymi) is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule. The thymus is made up of immature T cells called thymocytes, as well as lining cells called epithelial cells which help the thymocytes develop. T cells that successfully develop react appropriately with Major histocompatibility complex, MHC immune receptors of the body (called ''positive selection'') and not against proteins of the body (called ''negative selection''). The thymus is the largest and most active during the neonatal and pre-adolescent periods. By the early teens, the Thymic involuti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
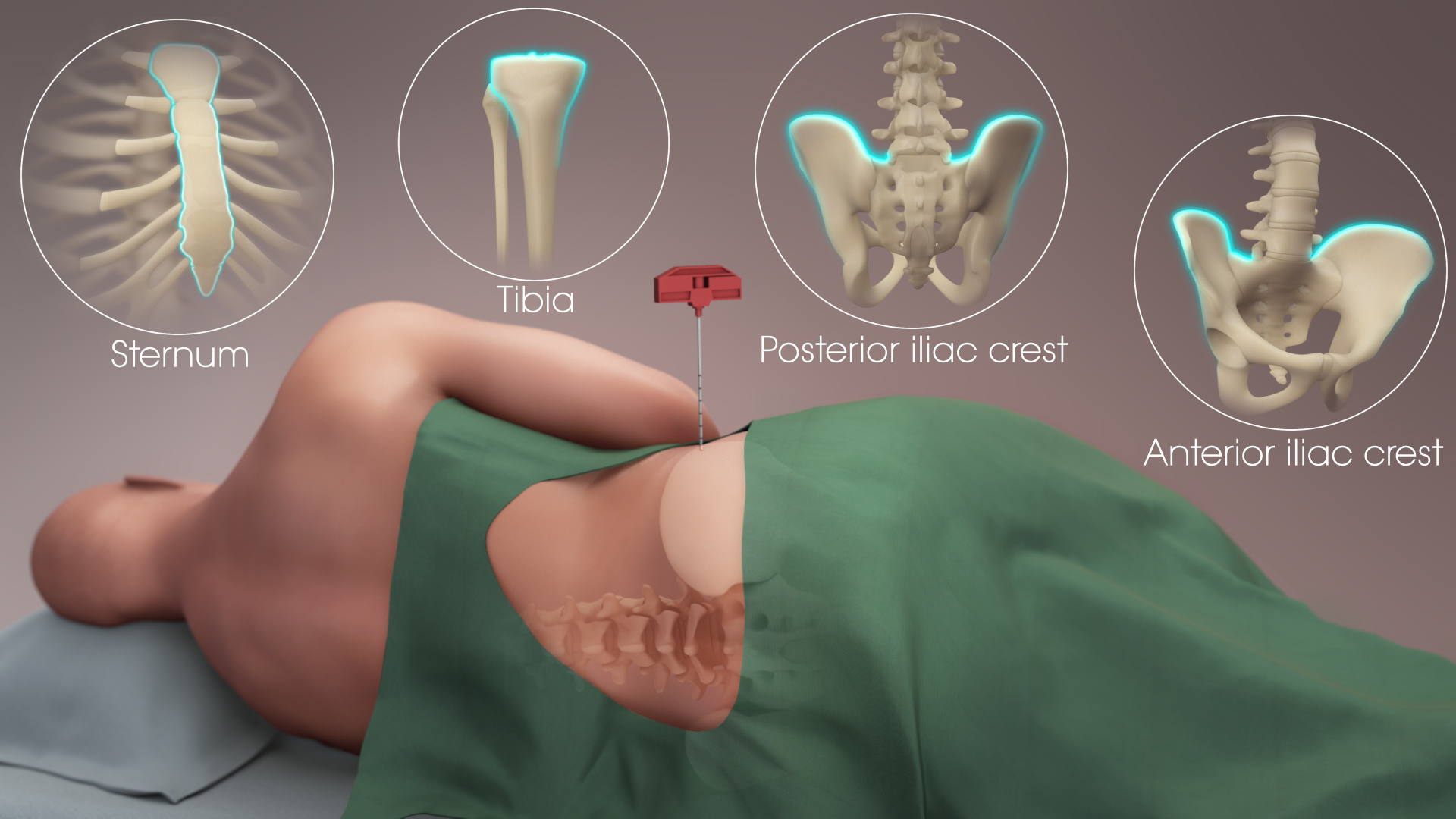
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of Blood cell, hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the Rib cage, ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and Pelvis, bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a person weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the Circulatory system, systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of Hematopoietic cell, hematopoietic cells, including both Myeloid tissue, myeloid and Lymphocyte, lymphoid lineages, are create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutaneous T-cell Lymphomas
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a class of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is a type of cancer of the immune system. Unlike most non-Hodgkin lymphomas (which are generally B-cell-related), CTCL is caused by a mutation of T cells. The cancerous T cells in the body initially migrate to the skin, causing various lesions to appear. These lesions change shape as the disease progresses, typically beginning as what appears to be a rash which can be very itchy and eventually forming plaques and tumor A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...s before metastasis, spreading to other parts of the body. Signs and symptoms The presentation depends if it is mycosis fungoides or Sézary syndrome, the most common, though not the only types. Among the symptoms for the aforementioned type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL, sometimes misspelled AILT, formerly known as "angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy with dysproteinemia") is a mature T-cell lymphoma of blood or lymph vessel immunoblasts characterized by a polymorphous lymph node infiltrate showing a marked increase in follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) and high endothelial venules (HEVs) and systemic involvement. Signs and symptoms Patients with AITL usually present at an advanced stage and show systemic involvement. The clinical findings typically include a pruritic skin rash and possibly edema, ascites, pleural effusions, and arthritis. Causes AITL was originally thought to be a premalignant condition, termed angioimmunoblastic lymphadenopathy, and this atypical reactive lymphadenopathy carried a risk for transformation into a lymphoma. It is postulated that the originating cell for AITL is a mature (post-thymic) CD4+ T-cell that arises ''de novo'', or that the disease has a premalignant subtype. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extranodal Natural Killer/T-cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type
Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTCL-NT) (also termed angiocentric lymphoma, nasal-type NK lymphoma, NK/T-cell lymphoma, polymorphic/malignant midline reticulosis, and lethal midline granuloma) is a rare type of lymphoma that commonly involves midline areas of the nasal cavity, oral cavity, and/or pharynx. At these sites, the disease often takes the form of massive, necrotic, and extremely disfiguring lesions. However, ENKTCL-NT can also involve the eye, larynx, lung, gastrointestinal tract, skin, and various other tissues. ENKTCL-NT mainly affects adults; it is relatively common in Asia and to lesser extents Mexico, Central America, and South America but is rare in Europe and North America. In Korea, ENKTCL-NT often involves the skin and is reported to be the most common form of cutaneous lymphoma after mycosis fungoides. ENKTCL-NT is classified as an Epstein–Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disease. It is due to the malignant transformation of either one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enteropathy Type T-cell Lymphoma
Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (EATL), previously termed enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma, type I and at one time termed enteropathy-type T-cell lymphoma (ETTL), is a complication of coeliac disease in which a malignant T-cell lymphoma develops in areas of the small intestine affected by the disease's intense inflammation. While a relatively rare disease, it is the most common type of primary gastrointestinal T-cell lymphoma. EATL had been defined as a single type of small intestine lymphoma, but in 2008, the World Health Organization (WHO) divided the disease into two subtypes: 1) EATL type I, which occurs in individuals with coeliac disease, a chronic immune disorder causing inflammatory responses to dietary gluten primarily in the upper reaches (i.e. jejunum and duodenum) of the small intestine; and 2) EATL type II, a disorder similar to EATL type I that occurs without coeliac disease. While type I and II EATL share many similar features, post-2008 studies found so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous T-cell Lymphoma
Subcutaneous T-cell lymphoma (also known as a "panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma") is a cutaneous condition that most commonly presents in young adults, and is characterized by subcutaneous nodules. Common symptoms include fever, fatigue, and pancytopenia. Diagnosis Classification Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma is a subtype of peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) is defined as a diverse group of aggressive lymphomas that develop from mature-stage white blood cells called T-cells and natural killer cells (NK cells) (see figure for an overview of PTCL subtypes). PTCL is a type of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL). NHL affects two particular types of white blood cells: B-cells and T-cells. PTCL specifically affects T-cells, and results when T-cells develop and grow abnormally. Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma is a rare type of lymphoma that infiltrates the subcutaneous fat but does not involve the skin. There are two subtypes – a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL) refers to a group of non-Hodgkin lymphomas in which aberrant T cells proliferate uncontrollably. Considered as a single entity, ALCL is the most common type of peripheral lymphoma and represents ~10% of all peripheral lymphomas in children. The incidence of ALCL is estimated to be 0.25 cases per 100,000 people in the United States of America. There are four distinct types of anaplastic large-cell lymphomas that on microscopic examination share certain key histopathological features and tumor marker proteins. However, the four types have very different clinical presentations, gene abnormalities, prognoses, and/or treatments. ALCL is defined based on microscopic histopathological examination of involved tissues which shows the presence of at least some ALCL-defining pleomorphic cells. These "hallmark" cells have abnormal kidney-shaped or horseshoe-shaped nuclei, prominent Golgi, and express the CD30 tumor marker protein on their surface mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma Not Otherwise Specified
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS), is a subtype of peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) is defined as a diverse group of aggressive lymphomas that develop from mature-stage white blood cells called T-cells and natural killer cells (NK cells) (see figure for an overview of PTCL subtypes). PTCL is a type of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL). PTCL specifically affects T-cells rather than B-cells, and results when T-cells develop and grow abnormally. About 30% of PTCL-NOS cases exhibit malignant T cells that are infected with the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). When associated with EBV, PTCL-NOS is classified as one of the Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative diseases (see Epstein-Barr virus-associated peripheral T cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified) but the relationship of EBV to the development and progression of Epstein-Barr virus-associated PTCL-NOS is unclear. PTCL-NOS, the most common subtype of PTCL, is aggressive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICD-10
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), a medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO). It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases. Work on ICD-10 began in 1983, was endorsed by the Forty-third World Health Assembly in 1990, and came into effect in member states on January 1, 1993. ICD-10 was replaced by ICD-11 on January 1, 2022. While WHO manages and publishes the base version of the ICD, several member states have modified it to better suit their needs. In the base classification, the code set allows for more than 14,000 different codes and permits the tracking of many new diagnoses compared to the preceding ICD-9. Through the use of optional sub-classifications, ICD-10 allows for specificity regarding the cause, manifestation, location, severity, and type of injury or disease. The adapted versions may differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |