|
Percutaneous Nephrostomy
{{More citations needed, date=January 2021 In surgery, a percutaneous procedurei.e. Granger et al., 2012 is any medical procedure or method where access to inner organs or other tissue is done via needle-puncture of the skin, rather than by using an "open" approach where inner organs or tissue are exposed (typically with the use of a scalpel). The percutaneous approach is commonly used in vascular procedures such as angioplasty and stenting. This involves a needle catheter getting access to a blood vessel, followed by the introduction of a wire through the lumen (pathway) of the needle. It is over this wire that other catheters can be placed into the blood vessel. This technique is known as the modified Seldinger technique. More generally, "percutaneous", via its Latin roots means, 'by way of the skin'. An example would be percutaneous drug absorption from topical medications. More often, percutaneous is typically used in reference to placement of medical devices using a nee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery such as gastric bypass), to reconstruct or alter aesthetics and appearance (cosmetic surgery), or to remove unwanted tissue (biology), tissues (body fat, glands, scars or skin tags) or foreign bodies. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure or surgical operation, or simply "surgery" or "operation". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments, operating theater, surgical facility or surgical nurse. Most surgical procedures are performed by a pair of operators: a surgeon who is the main operator performing the surgery, and a surgical assistant who provides in-procedure manual assistance during surgery. Modern surgical opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topical
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes including creams, foams, gels, lotions, and ointments. Many topical medications are epicutaneous, meaning that they are applied directly to the skin. Topical medications may also be inhalational, such as asthma medications, or applied to the surface of tissues other than the skin, such as eye drops applied to the conjunctiva, or ear drops placed in the ear, or medications applied to the surface of a tooth. The word ''topical'' derives from Greek τοπικός ''topikos'', "of a place". Justification Topical drug delivery is a route of administering drugs via the skin to provide topical therapeutic effects. As skin is one of the largest and most superficial organs in the human body, pharmacists utilise it to deliver various dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthroscopic Surgery
Arthroscopy (also called arthroscopic or keyhole surgery) is a minimally invasive surgery, surgical procedure on a joint in which an examination and sometimes treatment of damage is performed using an arthroscope, an endoscope that is inserted into the joint through a small incision. Arthroscopic procedures can be performed during Anterior cruciate ligament, ACL reconstruction. The advantage over traditional open surgery is that the joint does not have to be opened up fully. For knee arthroscopy only two small incisions are made, one for the arthroscope and one for the surgical instruments to be used in the knee cavity. This reduces Healing, recovery time and may increase the rate of success due to less trauma to the connective tissue. It has gained popularity due to evidence of faster recovery times with less scarring, because of the smaller incisions. Irrigation fluid (most commonly 'normal' Normal saline, saline) is used to distend the joint and make a surgical space. The surg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.MedlinePlus > Laparoscopy Update Date: 21 August 2009. Updated by: James Lee, MD // No longer valid Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive procedure, bandaid surgery, or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique. There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery versus an exploratory laparotomy. These include reduced pain due to smaller incisions, reduced hemorrhaging, and shorter recovery time. The key element is the use of a laparoscope, a long fiber optic cable system that allows viewing of the affected area by snaking the cable from a more distant, but more easily accessible location. Laparoscopic surgery includes operations within the abdominal or pelvic cavities, whereas keyhole surgery perfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
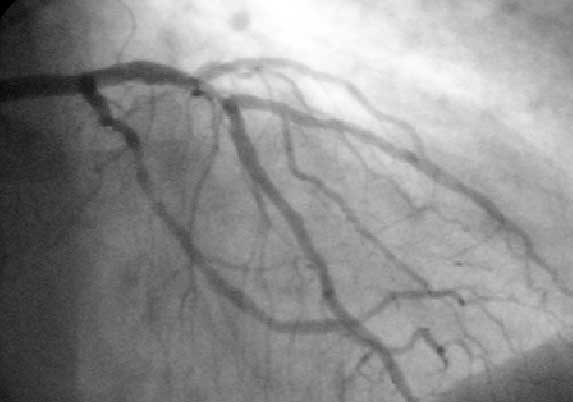
Angioplasty
Angioplasty, also known as balloon angioplasty and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure, minimally invasive endovascular surgery, endovascular Medical procedure, procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins, typically to treat arterial atherosclerosis. A deflated balloon attached to a catheter (a balloon catheter) is passed over a guide-wire into the stenosis, narrowed blood vessel, vessel and then inflated to a fixed size. The balloon forces expansion of the blood vessel and the surrounding muscular wall, allowing an improved blood flow. A stent may be inserted at the time of ballooning to ensure the vessel remains open, and the balloon is then deflated and withdrawn. Angioplasty has come to include all manner of Blood vessel, vascular interventions that are typically performed percutaneously. Uses and indications Coronary angioplasty A coronary angioplasty is a therapeutic procedure to treat the stenotic (narrow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interventional Radiology
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as Fluoroscopy, x-ray fluoroscopy, CT scan, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures Minimally invasive procedure, through very small incisions or body orifices. Diagnostic IR procedures are those intended to help make a diagnosis or guide further medical treatment, and include image-guided biopsy of a tumor or injection of an Radiocontrast agent, imaging contrast agent into a hollow structure, such as a blood vessel or a Bile duct, duct. By contrast, Therapy, therapeutic IR procedures provide direct treatment—they include catheter-based medicine delivery, medical device placement (e.g., stents), and angioplasty of narrowed structures. The main benefits of IR techniques are that they can reach the deep structures of the body through a body orifice or tiny incisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
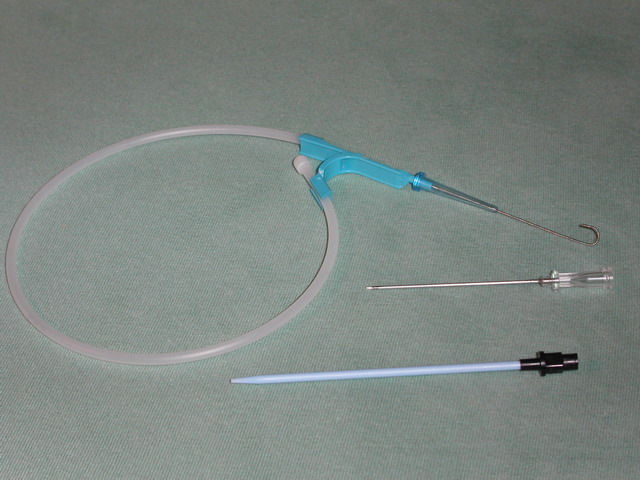
Introducer Sheath
The Seldinger technique, also known as Seldinger wire technique, is a medical procedure to obtain safe access to blood vessels and other hollow organs. It is named after Sven Ivar Seldinger (1921–1998), a Swedish radiologist who introduced the procedure in 1953. Uses The Seldinger technique is used for angiography, insertion of chest drains and central venous catheters, insertion of PEG tubes using the push technique, insertion of the leads for an artificial pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, and numerous other interventional medical procedures. Complications The initial puncture is with a sharp instrument, and this may lead to hemorrhage or perforation of the organ in question. Infection is a possible complication, and hence asepsis is practiced during most Seldinger procedures. Loss of the guidewire into the cavity or blood vessel is a significant and generally preventable complication. Description The desired vessel or cavity is punctured with a sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sven Ivar Seldinger
Sven Ivar Seldinger (19 April 1921 – 21 February 1998), was a radiology, radiologist from Mora Municipality, Sweden. In 1953, he introduced the Seldinger technique to obtain safe access to blood vessels and other hollow organ (anatomy), organs. Biography Sven Ivar Seldinger was born on 19 April 1921 in Dalarna, Dalarna, Sweden. He was born to a family who had long run the local Mora Mechanical Workshop. He first began his medical training in 1940 at the Karolinska Institute. After graduating medical school in 1948, he went on to specialize in radiology. While attending at the Karolinska Hospital he came up with an idea of how to administer a catheter that would be able to reach every human artery. He was qualified with the title of Docent in Radiology in 1967 after successfully defending his thesis on percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography. He was later able to demonstrate, using "phantom experiments", how one could insert a catheter into the femoral artery and reach both the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seldinger Technique
The Seldinger technique, also known as Seldinger wire technique, is a medical procedure to obtain safe access to blood vessels and other hollow organ (anatomy), organs. It is eponym, named after Sven Ivar Seldinger (1921–1998), a Sweden, Swedish radiology, radiologist who introduced the procedure in 1953. Uses The Seldinger technique is used for angiography, insertion of chest drains and central venous catheters, insertion of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy, PEG tubes using the push technique, insertion of the leads for an artificial pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, and numerous other interventional medical procedures. Complications The initial puncture is with a sharp instrument, and this may lead to hemorrhage or perforation of the organ in question. Infection is a possible complication, and hence asepsis is practiced during most Seldinger procedures. Loss of the guidewire into the cavity or blood vessel is a significant and generally preventable com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trocar
A trocar (or trochar) is a medical device, medical or veterinary medicine, veterinary device used in minimally invasive surgery. Trocars are typically made up of an Wiktionary:awl, awl (which may be metal or plastic with a pointed or tapered tip), a cannula (essentially a rigid hollow tube) and often a seal (mechanical), seal. Some trocars also include a valve mechanism to allow for insufflation (medicine), insufflation. Trocars are designed for placement through the chest and abdominal walls during thoracoscopy, thoracoscopic and laparoscopic surgery, and each trocar functions as a portal (architecture), portal for the subsequent insertion of other endoscopic instruments such as forceps, grasper, surgical scissors, scissors, surgical staple, stapler, electrocautery, suction (medicine), suction tip, etc. — hence the more commonly used colloquial jargon "port". Trocars also allow passive evacuation of excess gas or fluid from organs within the body. Etymology The word ''trocar' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumen (anatomy)
In biology, a lumen (: lumina) is the inside space of a tubular structure, such as an artery or intestine. It comes . It can refer to: *the interior of a vessel, such as the central space in an artery, vein or capillary through which blood flows *the interior of the gastrointestinal tract *the pathways of the bronchi in the lungs *the interior of renal tubules and urinary collecting ducts *the pathways of the female genital tract, starting with a single pathway of the vagina, splitting up in two lumina in the uterus, both of which continue through the fallopian tubes *the fluid-filled cavity forming in the blastocyst during pre-implantation development called the blastocoel In cell biology, lumen is a membrane-defined space that is found inside several organelles, cellular components, or structures, including thylakoid, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondrion, and microtubule. Transluminal procedures ''Transluminal procedures'' are procedures occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catheter
In medicine, a catheter ( ) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Catheters are manufactured for specific applications, such as cardiovascular, urological, gastrointestinal, neurovascular and ophthalmic procedures. The process of inserting a catheter is called ''catheterization''. In most uses, a catheter is a thin, flexible tube (''soft'' catheter) though catheters are available in varying levels of stiffness depending on the application. A catheter left inside the body, either temporarily or permanently, may be referred to as an "indwelling catheter" (for example, a peripherally inserted central catheter). A permanently inserted catheter may be referred to as a "permcath" (originally a trademark). Catheters can be inserted into a body cavity, duct, or vessel, brain, skin or adipose tissue. Functional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |