|
Pentagonal Cupola
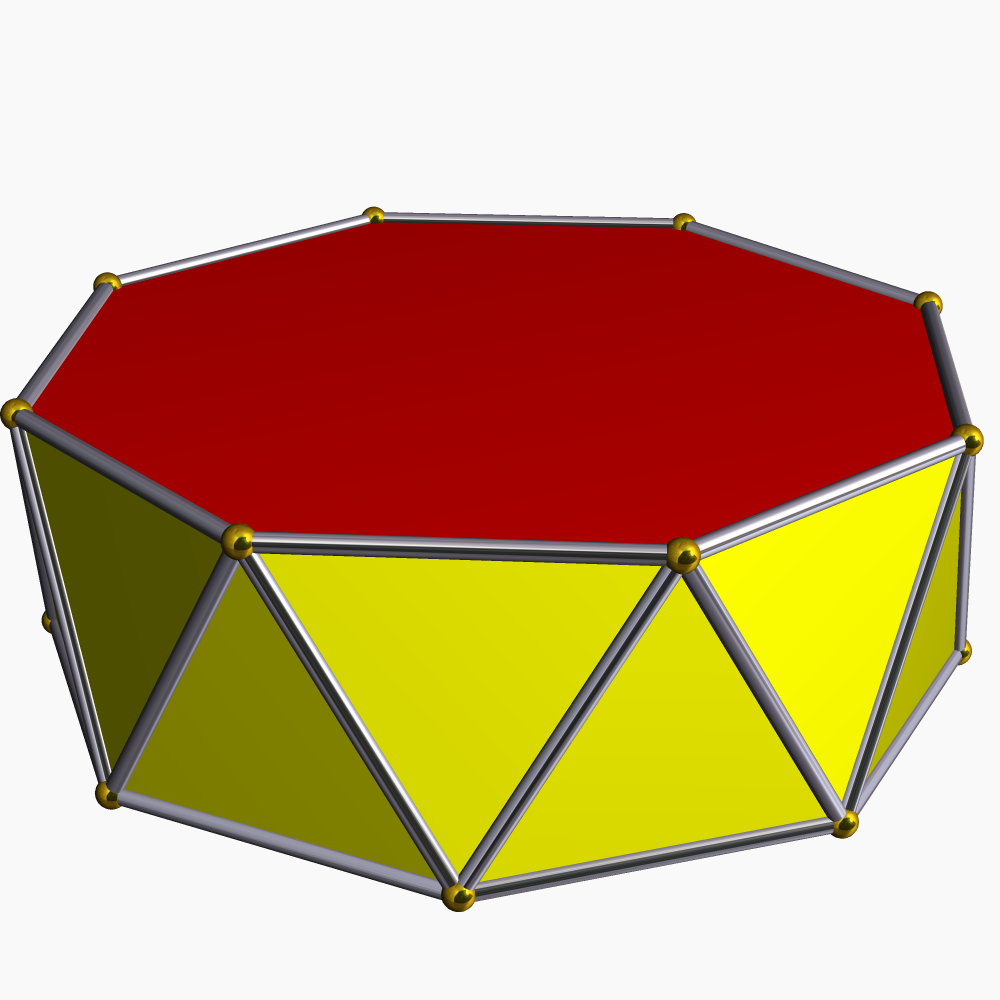
Properties The pentagonal cupola (geometry), cupola's faces are five equilateral triangles, five squares, one regular pentagon, and one regular decagon. It has the property of Convex set, convexity and regular polygonal faces, from which it is classified as the fifth Johnson solid. This cupola produces two or more regular polyhedrons by slicing it with a plane, an elementary polyhedron's example. The following formulae for circumscribed sphere, circumradius R , and height h , surface area A , and volume V may be applied if all face (geometry), faces are regular polygon, regular with edge length a : \begin h &= \sqrta &\approx 0.526a, \\ R &= \fraca &\approx 2.233a, \\ A &= \fraca^2 &\approx 16.580a^2, \\ V &= \fraca^3 &\approx 2.324a^3. \end It has an axis of symmetry passing through the center of both top and base, which is symmetrical by rotating around it at one-, two-, three-, and four-fifth of a full-turn angle. It is also mirror-symmetric relative to any per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnson Solid
In geometry, a Johnson solid, sometimes also known as a Johnson–Zalgaller solid, is a convex polyhedron whose faces are regular polygons. They are sometimes defined to exclude the uniform polyhedrons. There are ninety-two Solid geometry, solids with such a property: the first solids are the Pyramid (geometry), pyramids, Cupola (geometry), cupolas, and a Rotunda (geometry), rotunda; some of the solids may be constructed by attaching with those previous solids, whereas others may not. Definition and background A Johnson solid is a convex polyhedron whose faces are all regular polygons. The convex polyhedron means as bounded intersections of finitely many Half-space (geometry), half-spaces, or as the convex hull of finitely many points. Although there is no restriction that any given regular polygon cannot be a face of a Johnson solid, some authors required that Johnson solids are not Uniform polyhedron, uniform. This means that a Johnson solid is not a Platonic solid, Arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumscribed Sphere
In geometry, a circumscribed sphere of a polyhedron is a sphere that contains the polyhedron and touches each of the polyhedron's Vertex (geometry), vertices. The word circumsphere is sometimes used to mean the same thing, by analogy with the term ''circumcircle''. As in the case of two-dimensional circumscribed circles (circumcircles), the radius of a sphere circumscribed around a polyhedron is called the circumradius of , and the center point of this sphere is called the circumcenter of . Existence and optimality When it exists, a circumscribed sphere need not be the Smallest-circle problem, smallest sphere containing the polyhedron; for instance, the tetrahedron formed by a vertex of a cube and its three neighbors has the same circumsphere as the cube itself, but can be contained within a smaller sphere having the three neighboring vertices on its equator. However, the smallest sphere containing a given polyhedron is always the circumsphere of the convex hull of a subset of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyroelongation
In geometry, a Johnson solid, sometimes also known as a Johnson–Zalgaller solid, is a convex polyhedron whose faces are regular polygons. They are sometimes defined to exclude the uniform polyhedrons. There are ninety-two solids with such a property: the first solids are the pyramids, cupolas, and a rotunda; some of the solids may be constructed by attaching with those previous solids, whereas others may not. Definition and background A Johnson solid is a convex polyhedron whose faces are all regular polygons. The convex polyhedron means as bounded intersections of finitely many half-spaces, or as the convex hull of finitely many points. Although there is no restriction that any given regular polygon cannot be a face of a Johnson solid, some authors required that Johnson solids are not uniform. This means that a Johnson solid is not a Platonic solid, Archimedean solid, prism, or antiprism. A convex polyhedron in which all faces are nearly regular, but some are not pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiprism
In geometry, an antiprism or is a polyhedron composed of two Parallel (geometry), parallel Euclidean group, direct copies (not mirror images) of an polygon, connected by an alternating band of triangles. They are represented by the Conway polyhedron notation, Conway notation . Antiprisms are a subclass of prismatoids, and are a (degenerate) type of snub polyhedron. Antiprisms are similar to Prism (geometry), prisms, except that the bases are twisted relatively to each other, and that the side faces (connecting the bases) are triangles, rather than quadrilaterals. The dual polyhedron of an -gonal antiprism is an -gonal trapezohedron. History In his 1619 book ''Harmonices Mundi'', Johannes Kepler observed the existence of the infinite family of antiprisms. This has conventionally been thought of as the first discovery of these shapes, but they may have been known earlier: an unsigned printing block for the net (geometry), net of a hexagonal antiprism has been attributed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prism (geometry)
In geometry, a prism is a polyhedron comprising an polygon Base (geometry), base, a second base which is a Translation (geometry), translated copy (rigidly moved without rotation) of the first, and other Face (geometry), faces, necessarily all parallelograms, joining corresponding sides of the two bases. All Cross section (geometry), cross-sections parallel to the bases are translations of the bases. Prisms are named after their bases, e.g. a prism with a pentagonal base is called a pentagonal prism. Prisms are a subclass of prismatoids. Like many basic geometric terms, the word ''prism'' () was first used in Euclid's Elements, Euclid's ''Elements''. Euclid defined the term in Book XI as "a solid figure contained by two opposite, equal and parallel planes, while the rest are parallelograms". However, this definition has been criticized for not being specific enough in regard to the nature of the bases (a cause of some confusion amongst generations of later geometry writers). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augmentation (geometry)
In geometry, a Johnson solid, sometimes also known as a Johnson–Zalgaller solid, is a convex polyhedron whose faces are regular polygons. They are sometimes defined to exclude the uniform polyhedrons. There are ninety-two solids with such a property: the first solids are the pyramids, cupolas, and a rotunda; some of the solids may be constructed by attaching with those previous solids, whereas others may not. Definition and background A Johnson solid is a convex polyhedron whose faces are all regular polygons. The convex polyhedron means as bounded intersections of finitely many half-spaces, or as the convex hull of finitely many points. Although there is no restriction that any given regular polygon cannot be a face of a Johnson solid, some authors required that Johnson solids are not uniform. This means that a Johnson solid is not a Platonic solid, Archimedean solid, prism, or antiprism. A convex polyhedron in which all faces are nearly regular, but some are not pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyhedron
In geometry, a polyhedron (: polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional figure with flat polygonal Face (geometry), faces, straight Edge (geometry), edges and sharp corners or Vertex (geometry), vertices. The term "polyhedron" may refer either to a solid figure or to its boundary surface (mathematics), surface. The terms solid polyhedron and polyhedral surface are commonly used to distinguish the two concepts. Also, the term ''polyhedron'' is often used to refer implicitly to the whole structure (mathematics), structure formed by a solid polyhedron, its polyhedral surface, its faces, its edges, and its vertices. There are many definitions of polyhedron. Nevertheless, the polyhedron is typically understood as a generalization of a two-dimensional polygon and a three-dimensional specialization of a polytope, a more general concept in any number of dimensions. Polyhedra have several general characteristics that include the number of faces, topological classification by Eule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Group
In abstract algebra, a cyclic group or monogenous group is a Group (mathematics), group, denoted C_n (also frequently \Z_n or Z_n, not to be confused with the commutative ring of P-adic number, -adic numbers), that is Generating set of a group, generated by a single element. That is, it is a set (mathematics), set of Inverse element, invertible elements with a single associative binary operation, and it contains an element g such that every other element of the group may be obtained by repeatedly applying the group operation to g or its inverse. Each element can be written as an integer Exponentiation, power of g in multiplicative notation, or as an integer multiple of g in additive notation. This element g is called a ''Generating set of a group, generator'' of the group. Every infinite cyclic group is isomorphic to the additive group \Z, the integers. Every finite cyclic group of Order (group theory), order n is isomorphic to the additive group of Quotient group, Z/''n''Z, the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramidal Symmetry
In three dimensional geometry, there are four infinite series of point groups in three dimensions (''n''≥1) with ''n''-fold rotational or reflectional symmetry about one axis (by an angle of 360°/''n'') that does not change the object. They are the finite symmetry groups on a cone. For ''n'' = ∞ they correspond to four frieze groups. Schönflies notation is used. The terms horizontal (h) and vertical (v) imply the existence and direction of reflections with respect to a vertical axis of symmetry. Also shown are Coxeter notation in brackets, and, in parentheses, orbifold notation. Types ;Chiral: *''Cn'', sup>+, (''nn'') of order ''n'' - ''n''-fold rotational symmetry - acro-n-gonal group (abstract group ''Zn''); for ''n''=1: no symmetry (trivial group) ;Achiral: *''Cnh'', +,2 (''n''*) of order 2''n'' - prismatic symmetry or ortho-n-gonal group (abstract group ''Zn'' × ''Dih1''); for ''n''=1 this is denoted by ''Cs'' (1*) and called reflection symmetry, also bilateral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis Of Symmetry
An axis (: axes) may refer to: Mathematics *A specific line (often a directed line) that plays an important role in some contexts. In particular: ** Coordinate axis of a coordinate system *** ''x''-axis, ''y''-axis, ''z''-axis, common names for the coordinate axes of a Cartesian coordinate system ** Axis of rotation ** Axis of symmetry ** Axis of a conic section Politics *Axis powers of World War II, 1936–1945. * Axis of evil (first used in 2002), U.S. President George W. Bush's description of Iran, Iraq, and North Korea *Axis of Resistance (first used in 2002), the Shia alliance of Iran, Syria, and Hezbollah * Axis of Upheaval (first used in 2024), foreign policy neologism of the Anti-western collaboration between Russia, China, Iran, and North Korea * Jakarta-Pyongyang-Peking Axis, diplomatic alignment and alliance between Indonesia, China, and North Korea during Sukarno's Presidency *Political spectrum, sometimes called an axis Science *Axis (anatomy), the second cerv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cupula Pentagonal 3D
A cupula is a small, inverted cup or dome-shaped cap over a structure, including: * Ampullary cupula, a structure in the vestibular system, providing the sense of spatial orientation * Cochlear cupula, a structure in the cochlea * Cupula of the pleura, related to the lungs *The cervical parietal pleura in the thorax *A layer in the otolith organs * The ''cupula optica'', or optic cup, in embryological development of the eye * Cup-like structure fitted over the eye during electrophysiology study * Suprapleural membrane The suprapleural membrane, eponymously known as Sibson's fascia, is a structure described in human anatomy. It is named for Francis Sibson. Anatomy It refers to a thickening of connective tissue that covers the apex of each human lung. It is an ... See also * Cupola (other) * Copula (other) * Cupule (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |