|
Penninic
The Penninic nappes or the Penninicum, commonly abbreviated as Penninic, are one of three nappe stacks and geological zones in which the Alps can be divided. In the western Alps the Penninic nappes are more obviously present than in the eastern Alps (in Austria), where they crop out as a narrow band. The name ''Penninic'' is derived from the Pennine Alps, an area in which rocks from the Penninic nappes are abundant. Of the three nappe stacks the Penninic nappes have the highest metamorphic grade. They contain high grade metamorphic rocks of different paleogeographic origins. They were deposited as sediments on the crust that existed between the European and Apulian plates before the Alps were formed. They are characteristically ophiolite sequences and deep marine sediments, metamorphosed to phyllites, schists and amphibolites. Middle Penninic nappes include the Monte Rosa, Mont Fort, Siviez-Mischabel, Cimes Blanches and Frilihorn, of European origin. Upper Penninic nappe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valais Ocean
The Valais Ocean is a subducted oceanic basin which was situated between the continent Europe and the microcontinent Iberia or so called Briançonnais microcontinent. Remnants of the Valais ocean are found in the western Alps and in tectonic windows of the eastern Alps and are mapped as the so-called "north Penninic" nappes. Tectonic history After the breakup of Pangaea in the early Mesozoic age, the continents of Africa, South America, Europe, and North America began to move away from each other. The breaking up, or rifting, did not take place along one unbroken line; thus, at the southern edge of the European plate, the microcontinent Iberia also began to break away from Europe. In the western part of the rift that separated the two landmasses, oceanic crust was formed in what is at present the Gulf of Biscay, while in the eastern part, the Valais Ocean was formed. When, in the Cretaceous period, Africa again began to move towards Europe, the Valais Ocean became sandwiched b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austroalpine Nappes
The Austroalpine nappes are a geological nappe stack system in the European Alps. They structurally on top of the Penninic (meaning they were thrust over them). The prefix Austro in this term refers to Austria, rather than south/southern. This is because the bulk of the Austroalpine nappes (which constitute the Eastern Alps except for some tectonic windows) is in Austria, although they also reach into Eastern Switzerland. The western boundary of the Eastern Alps is the Lake Constance - Chur – Lake Como line. Geographic position and nappes in the Western Alps The Austroalpine nappes constitute the Eastern Alps, except for some tectonic windows such as the Tauern window, the Rechnitz window (both in Austria) and the Engadin window (Switzerland). They cover eastern Switzerland and the largest part Austria. In the Western Alps the Sesia (Italy) and the Dent Blanche (Switzerland) units form a klippe over the Penninic nappes. They have been labelled as Austroalpine becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia. The Alpine arch extends from Nice on the western Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean to Trieste on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Vienna at the beginning of the Pannonian Basin. The mountains were formed over tens of millions of years as the African and Eurasian tectonic plates collided. Extreme shortening caused by the event resulted in marine sedimentary rocks rising by thrust fault, thrusting and Fold (geology), folding into high mountain peaks such as Mont Blanc and the Matterhorn. Mont Blanc spans the French–Italian border, and at is the highest mountain in the Alps. The Alpine region area contains 82 peaks higher than List of Alpine four-thousanders, . The altitude and size of the range affect the climate in Europe; in the mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
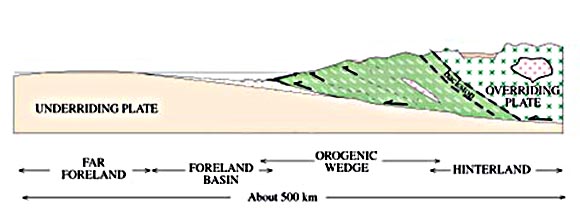
Nappe Stack
In geology, a nappe or thrust sheet is a large sheetlike body of rock that has been moved more than or above a thrust fault from its original position. Nappes form in compressional tectonic settings like continental collision zones or on the overriding plate in active subduction zones. Nappes form when a mass of rock is forced (or "thrust") over another rock mass, typically on a low angle fault plane. The resulting structure may include large-scale recumbent folds, shearing along the fault plane,Twiss, Robert J. and Eldridge M. Moores, ''Structural Geology,'' W. H. Freeman, 1992, p. 236 imbricate thrust stacks, fensters and klippes. The term stems from the French word for ''tablecloth'' in allusion to a rumpled tablecloth being pushed across a table. History Nappes or nappe belts are a major feature of the European Alps, Dinarides, Carpathians and Balkans. Since the 19th century many geologists have uncovered areas with large-scale overthrusts. Some of these were subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dent Blanche Klippe
Dent may refer to: People * Dent (surname) * Dent May, stage name of American musician James Dent May Jr. (born 1985) * Dent Mowrey (1888–1960), American composer, musician and music teacher * Dent Oliver (1918–1973), international speedway rider Places United Kingdom * Dent (fell), near England's Lake District in Cleator Moor, Copeland, Cumbria * Dent, South Lakeland, a village near Sedbergh in Cumbria ** Dent railway station * Dent Fault The Dent Fault is a major fault (geology), fault zone on the boundary between the counties of Cumbria and North Yorkshire in northern England. It is named after the village of Dent, South Lakeland, Dent in Dentdale, on the western margin of the ..., northern England * Dent Group, a group of Upper Ordovician sedimentary and volcanic rocks in northwest England United States * Dent, Idaho, an unincorporated community * Dent, Minnesota, a city * Dent, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Dent, Ohio, a census-designated place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is typically not Foliation (geology), foliated (Layered intrusion, layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphosed limestone, but its use in stonemasonry more broadly encompasses unmetamorphosed limestone. The extraction of marble is performed by quarrying. Marble production is dominated by four countries: China, Italy, India and Spain, which account for almost half of world production of marble and decorative stone. Because of its high hardness and strong wear resistance, and because it will not be deformed by temperature, marble is often used in Marble sculpture, sculpture and construction. Etymology The word "marble" derives from the Ancient Greek (), from (), "crystalline rock, shin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science), crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these minerals Precipitation (chemistry), precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly Dolomite (rock), dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral Dolomite (mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ninth and longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin , 'chalk', which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation . The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high Sea level#Local and eustatic, eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow Inland sea (geology), inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was largely ice-free, although there is some evidence of brief periods of glaciation during the cooler first half, and forests extended to the poles. Many of the dominant taxonomic gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclogite
Eclogite () is a metamorphic rock containing garnet ( almandine- pyrope) hosted in a matrix of sodium-rich pyroxene ( omphacite). Accessory minerals include kyanite, rutile, quartz, lawsonite, coesite, amphibole, phengite, paragonite, zoisite, dolomite, corundum and, rarely, diamond. The chemistry of primary and accessory minerals is used to classify three types of eclogite (A, B, and C). The broad range of eclogitic compositions has led to a longstanding debate on the origin of eclogite xenoliths as subducted, altered oceanic crust. The name ''eclogite'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word for 'choice' (, ), meaning 'chosen rock' on account of its perceived beauty. It was first named by René Just Haüy in 1822 in the second edition of his work ''Traité de minéralogie''. Origins Eclogites typically result from high to ultrahigh pressure metamorphism of mafic rock at low thermal gradients of < as it is subducted to the lower crust to |
Basin (geology)
In geology, a depression is a landform sunken or depressed below the surrounding area. Depressions form by various mechanisms. Types Erosion-related: * Blowout (geomorphology), Blowout: a depression created by Aeolian processes, wind erosion typically in either a partially vegetated Dune, sand dune ecosystem or dry soils (such as a post-glacial loess environment). * Glacial valley: a depression carved by erosion by a glacier. * River valley: a depression carved by fluvial erosion by a river. * Area of subsidence caused by the collapse of an underlying structure, such as sinkholes in karst terrain. * Sink (geography), Sink: an endorheic depression generally containing a wikt:persistent, persistent or intermittent (seasonal) lake, a Salt pan (geology), salt flat (playa) or dry lake, or an ephemeral lake. * Panhole: a shallow depression or basin eroded into flat or gently sloping, cohesive rock.Twidale, C.R., and Bourne, J.A., 2018Rock basins (gnammas) revisited.''Géomorphologie: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock formed by the cementation (geology), cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or deposited at Earth's surface. Sedimentation is any process that causes these particles to settle in place. Geological detritus originates from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or Mass wasting, mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus is formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies (marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur when dissolved minerals precipitate from aqueous solution, water solution. The sedimentary rock cover of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
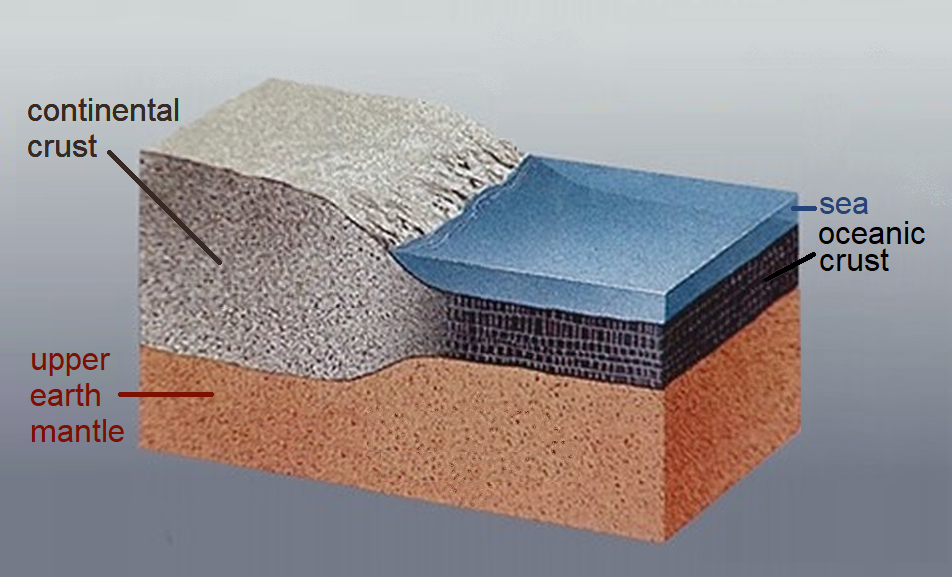
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as '' continental shelves''. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called '' sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. Most continental crust is dry land above sea level. However, 94% of the Zealandia continental crust region is submerged beneath the Pacific Ocean, with New Zealand constituting 93% of the above-water portion. Thickness and density The continental crust consists of various layers, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |