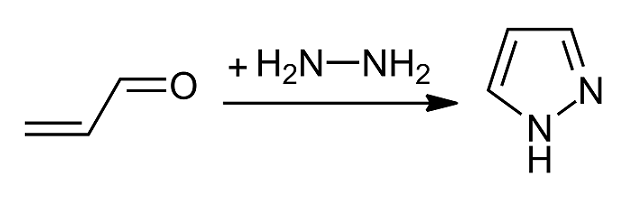|
Penflufen
Penflufen is a fungicide which was produced and patented by Bayer AG in 2006 and is used for crop protection from fungi. Penflufen is a pyrazole-amide based succinate-dehydrogenase inhibitor, which blocks the electron transport at complex II in the mitochondrial respiration chain. The European Chemical Agency (ECHA) has also approved the use of penflufen in wood preservation despite labelling it a suspected carcinogen A carcinogen () is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and biologic agents such as viruse .... References Fungicides Pyrazoles Anilides Fluoroarenes Amides {{Agriculture-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungicide
Fungicides are pesticides used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in losses of yield and quality. Fungicides are used both in agriculture and to fight fungal infections in animals, including humans. Fungicides are also used to control oomycetes, which are not taxonomically/genetically fungi, although sharing similar methods of infecting plants. Fungicides can either be contact, translaminar or systemic. Contact fungicides are not taken up into the plant tissue and protect only the plant where the spray is deposited. Translaminar fungicides redistribute the fungicide from the upper, sprayed leaf surface to the lower, unsprayed surface. Systemic fungicides are taken up and redistributed through the xylem vessels. Few fungicides move to all parts of a plant. Some are locally systemic, and some move upward. Most fungicides that can be bought retail are sold in liquid form, the active ingredient being present at 0.08% i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayer AG
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include: pharmaceuticals, consumer healthcare products, agricultural chemicals, seeds and biotechnology products. The company is a component of the EURO STOXX 50 stock market index. Bayer was founded in 1863 in Barmen as a partnership between dye salesman Friedrich Bayer (1825–1880) and dyer Friedrich Weskott (1821–1876). The company was established as a dyestuffs producer, but the versatility of aniline chemistry led Bayer to expand its business into other areas. In 1899, Bayer launched the compound acetylsalicylic acid under the trademarked name Aspirin. Aspirin is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2021, it was the 34th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the kingdom (biology)#Six kingdoms (1998), traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrazole
Pyrazole is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula . It is a heterocycle characterized as an azole with a 5-membered ring of three carbon atoms and two adjacent nitrogen atoms, which are in Arene substitution pattern, ortho-substitution. Pyrazoles are also a class of compounds that have the ring C3N2 with adjacent nitrogen atoms. Pyrazole itself has few applications but many substituted pyrazoles are of commercial interest. Notable drugs containing a pyrazole ring are celecoxib (celebrex) and the anabolic steroid stanozolol. Properties Pyrazole is a weak base, with p''K''b 11.5 (p''K''a of the conjugate acid 2.49 at 25 °C). According to X-ray crystallography, the compound is planar. The two C-N distances are similar, both near 1.33 Å History The term pyrazole was given to this class of compounds by German Chemist Ludwig Knorr in 1883. In a classical method developed by German chemist Hans von Pechmann in 1898, pyrazole was synthesized from acetylene and di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a chemical compound, compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl functional group, groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the Polymer backbone, main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, as in asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a Derivative (chemistry), derivative of a carboxylic acid () with the hydroxyl group () replaced by an amino group (); or, equivalently, an acyl group, acyl (alkanoyl) group () joined to an amino group. Common amides are formamide (), acetamide (), benzamide (), and dimethylformamide (). Some uncommon examples of amides are ''N''-chloroacetamide () and chloroformamide (). Amides are qualified as primary (chemistry), primary, secondary (chemistry), secondary, and tertiary (chemistry), tertiary according to the number of acyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Succinate Dehydrogenase
Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) or succinate-coenzyme Q reductase (SQR) or respiratory complex II is an enzyme complex, found in many bacterial cells and in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes. It is the only enzyme that participates in both the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. Histochemical analysis showing high succinate dehydrogenase in muscle demonstrates high mitochondrial content and high oxidative potential. In step 6 of the citric acid cycle, SQR catalyzes the oxidation of succinate to fumarate with the reduction of ubiquinone to ubiquinol. This occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane by coupling the two reactions together. Structure Subunits Mitochondrial and many bacterial SQRs are composed of four structurally different subunits: two hydrophilic and two hydrophobic. The first two subunits, a flavoprotein (SDHA) and an iron-sulfur protein (SDHB), form a hydrophilic head where enzymatic activity of the complex takes place. SD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Transport
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules which transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. Many of the enzymes in the electron transport chain are embedded within the membrane. The flow of electrons through the electron transport chain is an exergonic process. The energy from the redox reactions creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In aerobic respiration, the flow of electrons terminates with molecular oxygen as the final electron acceptor. In anaerobic respiration, other electron acceptors are used, such as sulfate. In an electron transport chain, the redox reactions are driven by the difference in the Gibbs free energy of reactants and products. The free energy released when a higher-e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondria
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'', meaning a thread-like granule, was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase popularized by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 ''Scientific American'' article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). The multicellular animal '' Henneguya salminicola'' is known to have retained mitochondrion-related organelles despite a complete loss of their mitochondrial genome. A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microspo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Chemical Agency
The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA; ) is an agency of the European Union working for the safe use of chemicals. It manages the technical and administrative aspects of the implementation of the European Union regulation called Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH). ECHA is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's chemicals legislation. ECHA has to ascertain that companies comply with the legislation, advances the safe use of chemicals, provides information on chemicals and addresses chemicals of concern. It is located in Helsinki, Finland and is operational since 2007. ECHA is an independent and mature regulatory agency established by REACH. It is not a subsidiary entity of the European Commission. The agency is headed by Executive Director Sharon McGuinness. Establishment The ECHA was created by European Union regulation dating from 18 December 2006 to manage the then-new legislation to regulate the manu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Preservation
Wood preservation refers to any method or process, or even technique, used to protect the wood and extend its service life. Most wood species are susceptible to both biological (''biotic'') and non-biological (''abiotic'') factors that cause decay and/or deterioration. Only a limited number of wood species possess natural durability, and even those may not be suitable for all environments. In general, wood benefits from appropriate preservation measures. In addition to structural design considerations, a variety of chemical preservatives and treatment processes — commonly known as timber treatment, lumber treatment, pressure treatment or modification treatment — are used to enhance the durability of wood and wood-based products, including engineered wood. These treatments may involve physical, chemical, thermal, and/or biological methodology aimed at protecting wood from degradation. They increase its resistance to biological agents such as fungi, termites, and insects, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogen
A carcinogen () is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and biologic agents such as viruses and bacteria. Most carcinogens act by creating mutations in DNA that disrupt a cell's normal processes for regulating growth, leading to uncontrolled cellular proliferation. This occurs when the cell's DNA repair processes fail to identify DNA damage allowing the defect to be passed down to daughter cells. The damage accumulates over time. This is typically a multi-step process during which the regulatory mechanisms within the cell are gradually dismantled allowing for unchecked cellular division. The specific mechanisms for carcinogenic activity is unique to each agent and cell type. Carcinogens can be broadly categorized, however, as activation-dependent and activation-independent which relate to the agent's ability to engage dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungicides
Fungicides are pesticides used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in losses of yield and quality. Fungicides are used both in agriculture and to fight fungal infections in animals, including humans. Fungicides are also used to control oomycetes, which are not taxonomically/genetically fungi, although sharing similar methods of infecting plants. Fungicides can either be contact, translaminar or systemic. Contact fungicides are not taken up into the plant tissue and protect only the plant where the spray is deposited. Translaminar fungicides redistribute the fungicide from the upper, sprayed leaf surface to the lower, unsprayed surface. Systemic fungicides are taken up and redistributed through the xylem vessels. Few fungicides move to all parts of a plant. Some are locally systemic, and some move upward. Most fungicides that can be bought retail are sold in liquid form, the active ingredient being present at 0.08% i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |