|
Pedestrian-friendly
In urban planning, walkability is the accessibility of amenities within a reasonable walking distance. It is based on the idea that urban spaces should be more than just transport corridors designed for maximum vehicle throughput. Instead, it should be relatively complete livable spaces that serve a variety of uses, users, and transportation modes and reduce the need for cars for travel. The term "walkability" was primarily invented in the 1960s due to Jane Jacobs' revolution in urban studies. In recent years, walkability has become popular because of its health, economic, and environmental benefits. It is an essential concept of sustainable urban design. Factors influencing walkability include the presence or absence and quality of footpaths, sidewalks or other pedestrian rights-of-way, traffic and road conditions, land use patterns, building accessibility, and safety, among others. Factors One proposed definition for walkability is: "The extent to which the built environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Typology (urban Planning And Architecture)
Typology is the study and classification of object types. In urban planning and architecture, typology refers to the task of identifying and grouping buildings and urban spaces according to the similarity of their essential characteristics. Common examples of essential characteristics include intensity of development (from rural to suburban to urban) and building use (church, hospital, school, apartment, house, etc.) Non-essential characteristics are those which, if modified, would not change the building type. Color, for example, would rarely be considered an essential characteristic of building type. Material, however, may or may not be considered essential depending on how integral the material is to the structure (engineering) and construction (assembly) of the building. Building types may be further divided into subtypes. For example, among religious structures there are churches and mosques, etc.; among churches there are cathedrals and chapels, etc.; among cathedrals the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bike Lanes
Bike lanes (US) or cycle lanes (UK) are types of bikeways (cycleways) with lanes on the roadway for cyclists only. In the United Kingdom, an on-road cycle-lane can be firmly restricted to cycles (marked with a solid white line, entry by motor vehicles is prohibited) or advisory (marked with a broken white line, entry by motor vehicles is permitted). In the United States, a ''designated bicycle lane'' (1988 MUTCD) or ''class II bikeway'' (Caltrans) is always marked by a solid white stripe on the pavement and is for 'preferential use' by bicyclists. There is also a ''class III bicycle route'', which has roadside signs suggesting a route for cyclists, and urging sharing the road. A ''class IV separated bike way'' (Caltrans) is a bike lane that is physically separate from motor traffic and restricted to bicyclists only. Research shows that separated bike lanes improve the safety of bicyclists, and either have positive or non-significant economic effects on nearby businesses. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parking
Parking is the act of stopping and disengaging a vehicle and usually leaving it unoccupied. Parking on one or both sides of a road is often permitted, though sometimes with restrictions. Some buildings have parking facilities for use of the buildings' users. Countries and local governments have rules for design and use of parking spaces. Car parking is essential to car-based travel. Cars are typically stationary around 95 per cent of the time. The availability and price of car parking may support car dependency. Significant amounts of urban land are devoted to car parking; in many North American city centers, half or more of all land is devoted to car parking. Parking facilities Parking facilities can be divided into public parking and private parking. * Public parking is managed by local government authorities and available for all members of the public to drive to and park in. * Private parking is owned by a private entity. It may be available for use by the pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Footpaths
A footpath (also pedestrian way, walking trail, nature trail) is a type of thoroughfare that is intended for use only by pedestrians and not other forms of traffic such as motorized vehicles, bicycles and horses. They can be found in a wide variety of places, from the centre of cities, to farmland, to mountain ridges. Urban footpaths are usually paved, may have steps, and can be called alleys, lanes, steps, etc. National parks, nature preserves, conservation areas and other protected wilderness areas may have footpaths (trails) that are restricted to pedestrians. The term 'footpath' includes pedestrian paths that are next to the road in Irish English, Indian English, Australian English, and New Zealand English (known as 'pavement' in the British English and South African English, or sidewalk in North American English). A footpath can also take the form of a footbridge, linking two places across a river. Origins and history Public footpaths are rights of way originally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mass Transit
Public transport (also known as public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) are forms of transport available to the general public. It typically uses a fixed schedule, route and charges a fixed fare. There is no rigid definition of which kinds of transport are included, and air travel is often not thought of when discussing public transport—dictionaries use wording like "buses, trains, etc." Examples of public transport include city buses, trolleybuses, trams (or light rail) and passenger trains, rapid transit (metro/subway/underground, etc.) and ferries. Public transport between cities is dominated by airlines, coaches, and intercity rail. High-speed rail networks are being developed in many parts of the world. Most public transport systems run along fixed routes with set embarkation/disembarkation points to a prearranged timetable, with the most frequent services running to a headway (e.g., "every 15 minutes" as opposed to being scheduled for a specific time of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and private physical structures such as roads, railways, bridges, airports, public transit systems, tunnels, water supply, sewers, electrical grids, and telecommunications (including Internet connectivity and broadband access). In general, infrastructure has been defined as "the physical components of interrelated systems providing commodities and services essential to enable, sustain, or enhance societal living conditions" and maintain the surrounding environment. Especially in light of the massive societal transformations needed to mitigate and adapt to climate change, contemporary infrastructure conversations frequently focus on sustainable development and green infrastructure. Acknowledging this importance, the international co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Walking
Walking (also known as ambulation) is one of the main gaits of terrestrial locomotion among legged animals. Walking is typically slower than running and other gaits. Walking is defined as an " inverted pendulum" gait in which the body vaults over the stiff limb or limbs with each step. This applies regardless of the usable number of limbs—even arthropods, with six, eight, or more limbs, walk. In humans, walking has health benefits including improved mental health and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease and death. Difference from running The word ''walk'' is descended from the Old English ''wealcan'' 'to roll'. In humans and other bipeds, walking is generally distinguished from running in that only one foot at a time leaves contact with the ground and there is a period of double-support. In contrast, running begins when both feet are off the ground with each step. This distinction has the status of a formal requirement in competitive walking events. For quadrupedal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Multimodal Transport
Multimodal transport (also known as combined transport) is the transportation of goods under a single contract, but performed with at least two different modes of transport; the carrier is liable (in a legal sense) for the entire carriage, even though it is performed by several different modes of transport (by rail, sea and road, for example). The carrier does not have to possess all the means of transport, and in practice usually does not; the carriage is often performed by sub-carriers (referred to in legal language as "actual carriers"). The carrier responsible for the entire carriage is referred to as a multimodal transport operator, or MTO. Article 1.1. of the ''United Nations Convention on International Multimodal Transport of Goods'' (Geneva, 24 May 1980) (which will only enter into force 12 months after 30 countries ratify; as of May 2019, only 6 countries have ratified the treaty) defines multimodal transport as follows: "'International multimodal transport' means the ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
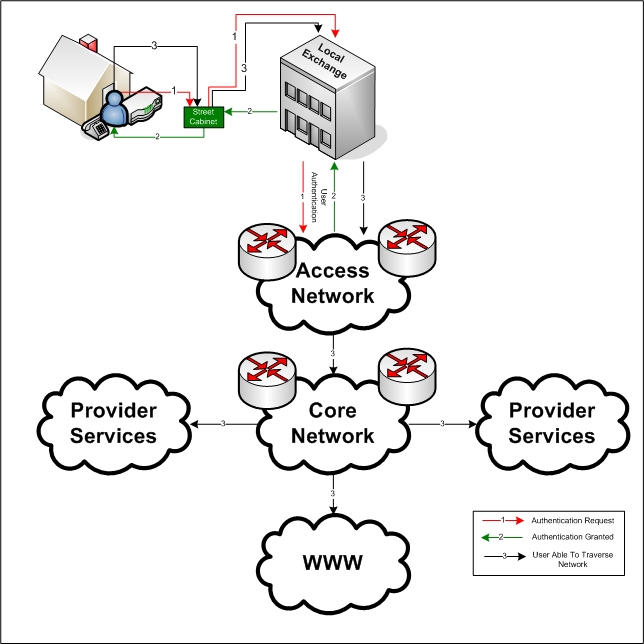
Access Network
An access network is a type of telecommunications telecommunications network, network which connects subscribers to their immediate telecommunications service provider, service provider. It is contrasted with the core network, which connects local providers to one another. The access network may be further divided between feeder plant or distribution network, and drop plant or edge network. Telephone heritage An access network, also referred to as an outside plant, refers to the series of wires, cables and equipment lying between a consumer/business telephone termination point (the point at which a telephone connection reaches the customer) and the local telephone exchange. The local exchange contains banks of automated switching equipment which direct a call or connection to the consumer. The access network is perhaps one of the oldest assets a telecoms operator would own. In 2007–2008 many telecommunication operators experienced increasing problems maintaining the quality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Walk Short Distances - Go By Shanks' Pony Art
Walking (also known as ambulation) is one of the main gaits of terrestrial locomotion among legged animals. Walking is typically slower than running and other gaits. Walking is defined as an "inverted pendulum" gait in which the body vaults over the stiff limb or limbs with each step. This applies regardless of the usable number of limbs—even arthropods, with six, eight, or more limbs, walk. In humans, walking has health benefits including improved mental health and reduced risk of cardiovascular disease and death. Difference from running The word ''walk'' is descended from the Old English language, Old English ''wealcan'' 'to roll'. In humans and other bipeds, walking is generally distinguished from running in that only one foot at a time leaves contact with the ground and there is a period of double-support. In contrast, running begins when both feet are off the ground with each step. This distinction has the status of a formal requirement in Racewalking, competitive walk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Land Lot
In real estate, a land lot or plot of land is a tract or parcel of land owned or meant to be owned by some owner(s). A plot is essentially considered a parcel of real property in some countries or immovable property (meaning practically the same thing) in other countries. Possible owners of a plot can be one or more persons or another legal entity, such as a company, corporation, organization, government, or Trust company, trust. A common form of ownership of a plot is called fee simple in some countries. A small area of land that is empty except for a paved surface or similar improvement, typically all used for the same purpose or in the same state is also often called a plot. Examples are a paved car park or a cultivated garden plot. This article covers plots (more commonly called lots in some countries) as defined parcels of land meant to be owned as units by an owner(s). Like most other types of property, lots or plots owned by private parties are subject to a periodic pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |