|
Peak Fossil Fuel (other) .
{{Disambig ...
Peak fossil fuel may refer to: * Peak fossil fuel production; see Hubbert peak theory#Hubbert curve. * Peak coal. * Peak gas. * Peak oil Peak oil is the point when global oil production reaches its maximum rate, after which it will begin to decline irreversibly. The main concern is that global transportation relies heavily on gasoline and diesel. Adoption of electric vehicles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubbert Peak Theory
The Hubbert peak theory says that for any given geographical area, from an individual oil-producing region to the planet as a whole, the rate of petroleum production tends to follow a bell-shaped curve. It is one of the primary theories on peak oil. Choosing a particular curve determines a point of maximum production based on discovery rates, production rates, and cumulative production. Early in the curve (pre-peak), the production rate increases due to the discovery rate and the addition of infrastructure. Late in the curve (post-peak), production declines because of resource depletion. The Hubbert peak theory is based on the observation that the amount of oil under the ground in any region is finite; therefore, the rate of discovery, which initially increases quickly, must reach a maximum and then decline. In the US, oil extraction followed the discovery curve after a time lag of 32 to 35 years.Jean Laherrere, "Forecasting production from discovery", ASPO Lisbon May 19–20, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Coal
Use of coal is expected to peak in the mid-2020s. Historically, it was widely believed that the supply-side would eventually drive peak coal due to the depletion of coal reserves. However, since the increasing global efforts to limit climate change, peak coal has been driven by demand. This is due in large part to the rapid expansion of natural gas and renewable energy. As of 2024 over 40% of all energy sector CO2 emissions are from coal, and many countries have pledged to coal phase-out, phase-out coal. The peak of coal's share in the global energy mix was in 2008, when coal accounted for 30% of global energy production. Coal consumption is declining in the United States and Europe, as well as developed economies in Asia. However production increased in Coal in India, India, Coal in Indonesia, Indonesia and Coal in China, China, which offset the falls in other regions. Global coal consumption reached an all time high in 2023 at 8.5 billion tons, but is expected to reach a new re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
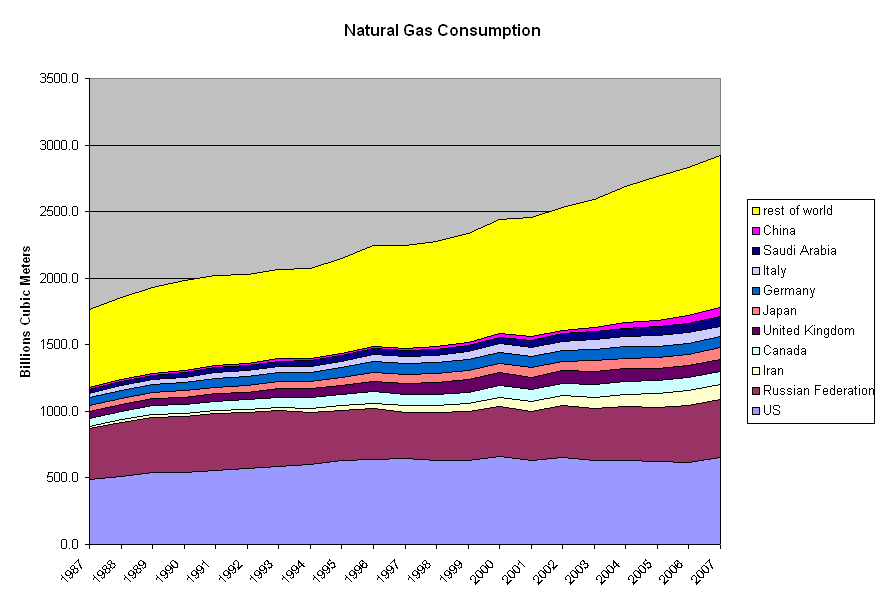
Peak Gas
Peak gas is the point in time when the maximum global natural gas (fossil gas) production rate will be reached, after which the rate of production will enter its terminal decline. Although demand is peaking in the United States and Europe, it continues to rise globally due to consumers in Asia, especially China. Natural gas is a fossil fuel formed from plant matter over the course of millions of years. Natural gas derived from fossil fuels is a non-renewable energy source; however, methane can be renewable in other forms such as biogas. Peak coal was in 2013, and peak oil is forecast to occur before peak gas. One forecast is for natural gas demand to peak in 2035. The concept of peak gas follows from Hubbert peak theory, which is most commonly associated with peak oil. Hubbert saw gas, coal and oil as natural resources, each of which would peak in production and eventually run out for a region, a country, or the world. Gas demand The world gets almost one quarter of its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |