|
Pea Protein
Pea protein is a food product and protein supplement derived and extracted from yellow and green split peas, ''Pisum sativum.'' It can be used as a dietary supplement to increase an individual's protein or other nutrient intake, or as a substitute for other food products (e.g. the substitution of dairy milk by pea milk). As a powder, it is used as an food ingredient, ingredient in Food processing, food manufacturing, such as a Thickening agent, thickener, foaming agent, or an Emulsion, emulsifier. It is extracted in a powder form and can be processed and produced in different ways: * As an isolate - through the process of wet fractionation which produces a high protein concentration * As a concentrate - through the process of dry fractionation which produces a low protein concentration * In textured form, which is when it is used in food products as a substitute for other products, such as meat alternatives Pea protein is a food source due to its availability, low allergenicit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chocolate Pea Protein Powder
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cocoa beans that can be a liquid, solid, or paste, either by itself or to flavoring, flavor other foods. Cocoa beans are the processed seeds of the cacao tree (''Theobroma cacao''); unprocessed, they taste intensely bitter. In making chocolate, these seeds Cocoa bean fermentation, are usually fermented to develop the flavor. They are then dried, cleaned, and roasted. The shell is removed to reveal nibs, which are ground to chocolate liquor: unadulterated chocolate in rough form. The liquor can be processed to separate its two components, cocoa solids and cocoa butter, or shaped and sold as unsweetened baking chocolate. By adding sugar, sweetened chocolates are produced, which can be sold simply as dark chocolate (a.k.a., plain chocolate), or, with the addition of milk, can be made into milk chocolate. Making milk chocolate with cocoa butter and without cocoa solids produces white chocolate. In some chocolates, other ingredients ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin
Vitamins are Organic compound, organic molecules (or a set of closely related molecules called vitamer, vitamers) that are essential to an organism in small quantities for proper metabolism, metabolic function. Nutrient#Essential nutrients, Essential nutrients cannot be biosynthesis, synthesized in the organism in sufficient quantities for survival, and therefore must be obtained through the Diet (nutrition), diet. For example, vitamin C can be synthesized by some species but not by others; it is not considered a vitamin in the first instance but is in the second. Most vitamins are not single molecules, but groups of related molecules called vitamers. For example, there are eight vitamers of vitamin E: four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. The term ''vitamin'' does not include the three other groups of essential nutrients: mineral (nutrient), minerals, essential fatty acids, and essential amino acids. Major health organizations list thirteen vitamins: * Vitamin A (all-' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essential Amino Acids
An essential amino acid, or indispensable amino acid, is an amino acid that cannot be synthesized from scratch by the organism fast enough to supply its demand, and must therefore come from the diet. Of the 21 amino acids common to all life forms, the nine amino acids humans cannot synthesize are valine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, threonine, histidine, and lysine. Six other amino acids are considered conditionally essential in the human diet, meaning their synthesis can be limited under special pathophysiological conditions, such as prematurity in the infant or individuals in severe catabolic distress. These six are arginine, cysteine, glycine, glutamine, proline, and tyrosine. Six amino acids are non-essential (dispensable) in humans, meaning they can be synthesized in sufficient quantities in the body. These six are alanine, aspartic acid, asparagine, glutamic acid, serine, and selenocysteine (considered the 21st amino acid). Pyrr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complete Protein
A complete protein or whole protein is a food source of protein that contains an adequate proportion of each of the nine essential amino acids necessary in the human diet. Concept Protein nutrition is complex because any proteinogenic amino acid may be the limiting factor in metabolism. Mixing livestock feeds can optimize for growth, or minimize cost while maintaining adequate growth. Similarly, human nutrition is subject to Liebig's law of the minimum: The lowest level of one of the essential amino acids will be the limiting factor in metabolism. :If the content of a single indispensable amino acid in the diet is less than the individual's requirement, then it will limit the utilization of other amino acids and thus prevent the normal rates of synthesis even when the total nitrogen intake level is adequate. Thus the "limiting amino acid" will determine the nutritional value of the total nitrogen or protein in the diet. Protein sources are thus rated by their limiting amino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicilin
Vicilin is a legumin-associated globulin protein. It is a storage protein found in legumes such as the pea or lentil that protects plants from fungi and microorganism. It is believed to be an allergen in pea and peanut allergy responses. Function of Vicilin Vicilin is a globulin present in legumes that assists the storage of proteins. Vicilins are 7S globulins. Sucrose binding, antifungal capabilities, and oxidative stress are a few of the globulin's functions. Vicilin peptides produced by digestion using trypsin or chymotrypsin offer anti-hypersensitive properties. Vicilin's function was best understood because to the addition of the copper ligand. Vicilin has various significant residues, four of which are involved in copper ion coordination. Vicilin belongs to the cupin family of proteins, in which metal ligand coordination is common, but vicilin is the only seed storage protein in this family known to include copper. This inclusion is crucial for enzymatic activity. Vicili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legumin
Legumin is family of globular proteins obtained from beans, peas, lentils, vetches, Hemp protein, hemp and other leguminous seeds. Garden peas are a common nutritional source for humans that contains legumin. Legumin is similar to the casein of mammalian milk and was called "vegetable casein" since it was considered analogous to the mammalian protein. The primary function of the legumin protein in seeds is storage. Legumin proteins are one of the main storage proteins of Flowering plant, angiosperms and gymnosperms. Legumin is an insoluble hexameric conjugated protein with a high concentration of carbon and oxygen. Properties Structure Legumin is a conjugated protein with six subunits. The individual subunits have a hydrophilic α chain that is initially linked to the smaller hydrophobic β chain with a peptide bond. Both the α and β chains are encoded by the same gene. Each of the six subunits has a mass of ~50-60 kDa. During Translation (biology), translation of the α and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutenin
Glutenin (a type of glutelin) is a major protein within wheat flour, making up 47% of the total protein content. The glutenins are protein aggregates of high- molecular-mass (HMW) and low-molecular-mass (LMW) subunits with molar masses from about 200,000 to a few million, which are stabilized by intermolecular disulfide bonds, hydrophobic interactions and other forces. Glutenin is responsible for the strength and elasticity of dough. Wheat gluten proteins consist of two major fractions: the gliadins and the glutenins. Gliadins are monomer A monomer ( ; ''mono-'', "one" + '' -mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or two- or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization. Classification Chemis ...ic proteins, which can be separated into four groups: alpha-, beta-, gamma- and omega-gliadins. They are structurally similar to LMW glutenins. Glutenins occur as multimeric aggregates of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prolamin
Prolamins are a group of plant storage proteins having a high proline amino acid content. They are found in plants, mainly in the seeds of cereal grains such as wheat ( gliadin), barley ( hordein), rye ( secalin), corn ( zein), sorghum ( kafirin), and oats ( avenin). They are characterised by a high glutamine and proline content, and have poor solubility in water. They solubilise best in strong alcohol (70–80%), light acid, and alkaline solutions. The prolamins of the tribe Triticeae, such as wheat gliadin, and related proteins (see Triticeae glutens) are known to trigger coeliac disease, an autoimmune condition, in genetically predisposed individuals. Maize and sorghum prolamins are sorted by molecular weight into four classes, α, β, γ and δ. Alpha- and delta- prolamins cluster in a broad phylogenetic group (Group 1). The rest cluster into Group 2. Group 1 is widely duplicated in the two plants. A database of Triticeae prolamins (glutens) is available. There does not s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All of the proteins of the albumin family are water- soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins are commonly found in blood plasma and differ from other blood proteins in that they are not glycosylated. Substances containing albumins are called ''albuminoids''. A number of blood transport proteins are evolutionarily related in the albumin family, including serum albumin, alpha-fetoprotein, vitamin D-binding protein and afamin. This family is only found in vertebrates. ''Albumins'' in a less strict sense can mean other proteins that coagulate under certain conditions. See ' for lactalbumin, ovalbumin and plant "2S albumin". Function Albumins in general are transport proteins that bind to various ligands and carry them around. Human types include: * Human serum albumin is the main protein of human blood plasma. It m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globulin
The globulins are a family of globular proteins that have higher molecular weights than albumins and are insoluble in pure water but dissolve in dilute salt solutions. Some globulins are produced in the liver, while others are made by the immune system. Globulins, albumins, and fibrinogen are the major blood proteins. The normal concentration of globulins in human blood is about 2.6-3.5 g/dL. The term "globulin" is sometimes used synonymously with "globular protein". However, albumins are also globular proteins, but are ''not'' globulins. All other serum globular proteins are globulins. Types of globulin All globulins fall into one of three categories: * Alpha globulins * Beta globulins * Gamma globulins (one group of gamma globulins is the immunoglobulins, which are also known as "antibodies") Globulins can be distinguished from one another using serum protein electrophoresis. Globulins exert oncotic pressure. Their deficiency results in loss of carrier functions of gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalate
Oxalate (systematic IUPAC name: ethanedioate) is an anion with the chemical formula . This dianion is colorless. It occurs naturally, including in some foods. It forms a variety of salts, for example sodium oxalate (), and several esters such as dimethyl oxalate (). It is a conjugate base of oxalic acid. At neutral pH in aqueous solution, oxalic acid converts completely to oxalate. Relationship to oxalic acid The dissociation of protons from oxalic acid proceeds in a determined order; as for other polyprotic acids, loss of a single proton results in the monovalent hydrogenoxalate anion . A salt with this anion is sometimes called an acid oxalate, monobasic oxalate, or hydrogen oxalate. The equilibrium constant ( ''K''a) for loss of the first proton is ( p''K''a = 1.27). The loss of the second proton, which yields the oxalate ion, has an equilibrium constant of (p''K''a = 4.28). These values imply, in solutions with neutral pH, no oxalic acid and only t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
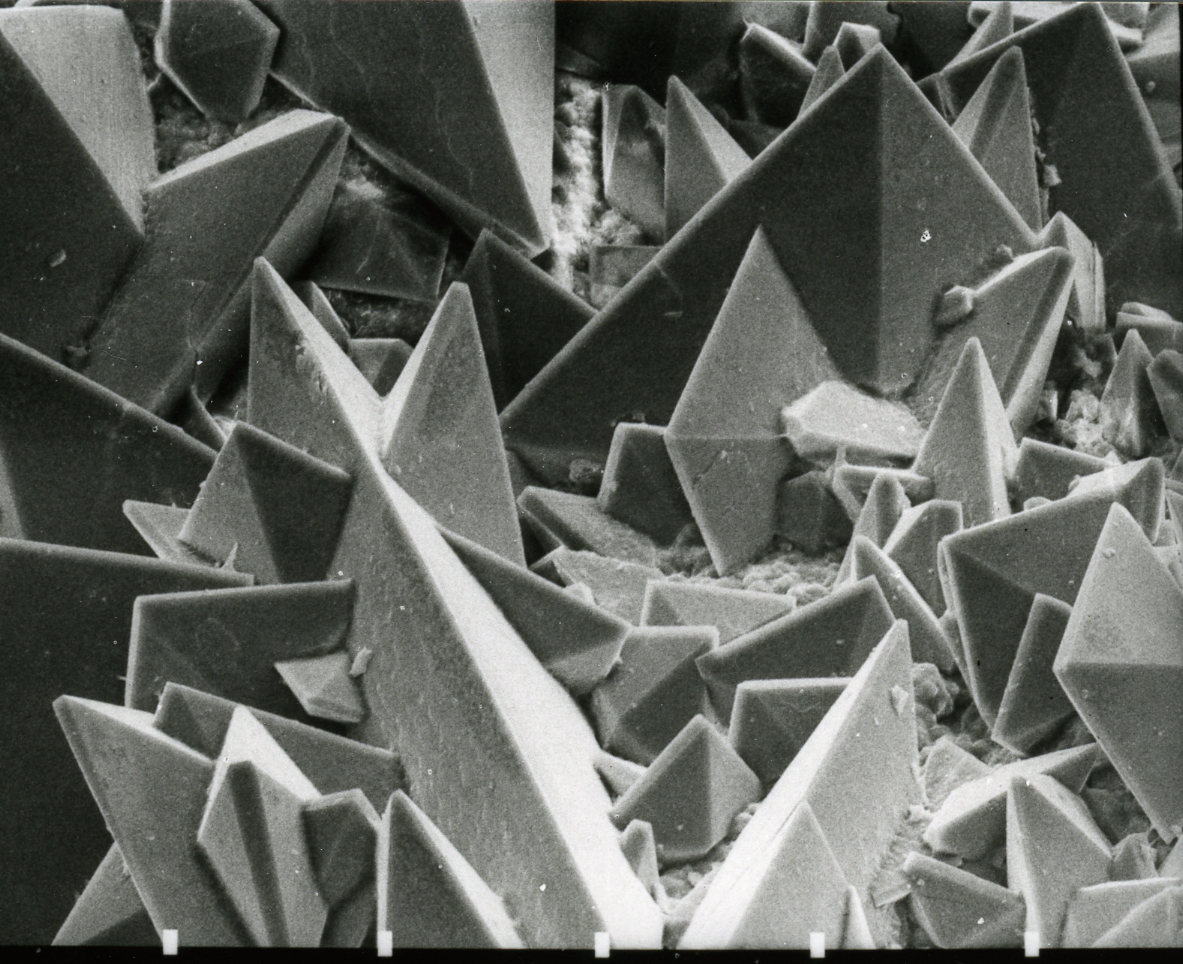
Mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The Geology, geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock (geology), rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral or may be an aggregate (geology), aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |