|
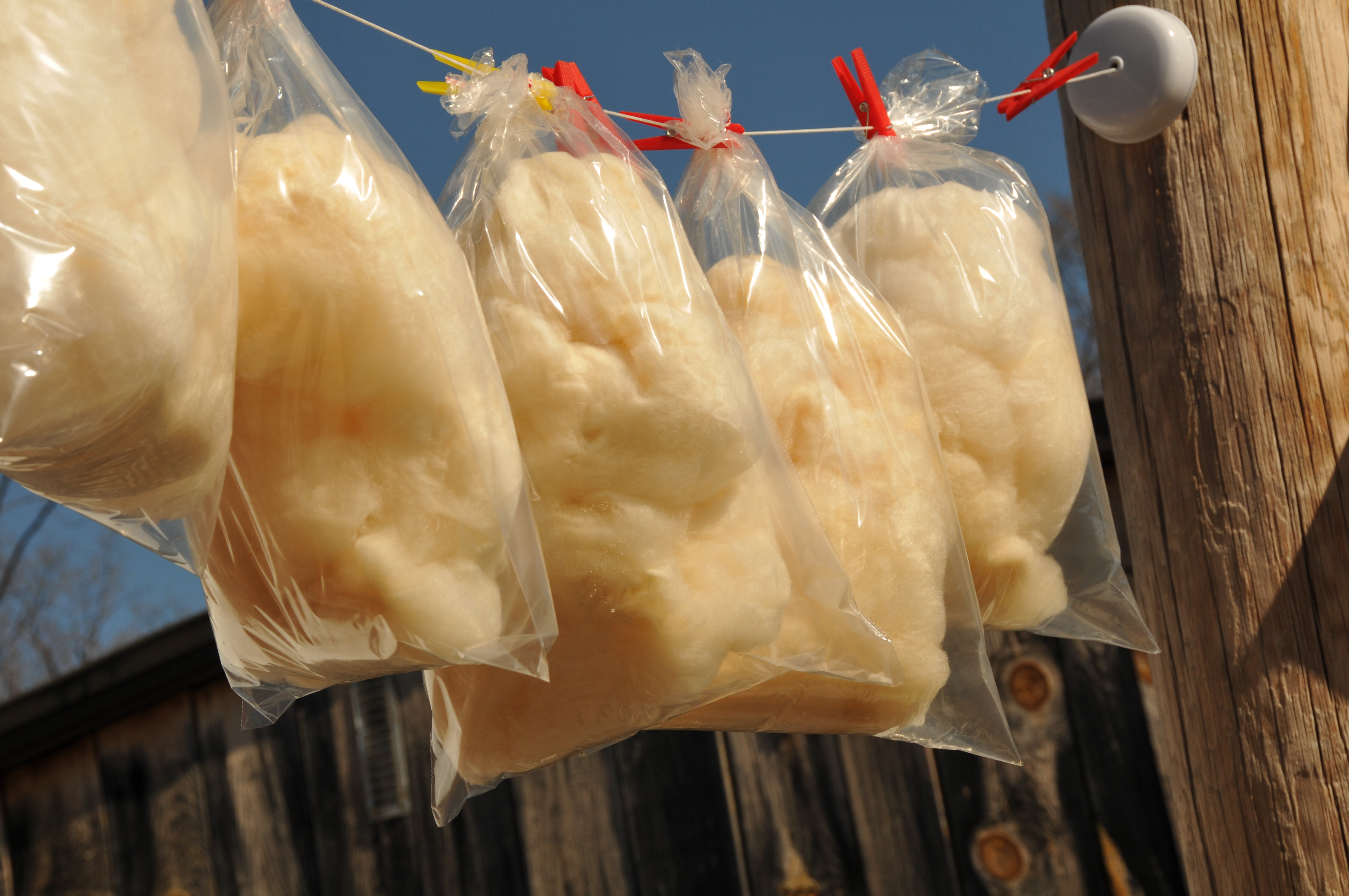
Pashmak
Pashmak () is a form of Iranian candy floss or cotton candy, made from sugar. Pashmak is served on its own or as an accompaniment to fruits, cakes, ice creams, puddings and desserts. It is widely known as Persian Cotton Candy."Shiraz Sights" , at ''BestIranTravel.com'' It is sometimes garnished with ground pistachio nuts. Although the texture is similar to , both method and ingredients are different. Pashmak originated in the Iranian city of known for its various traditional Persian sweets such as Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yazd
Yazd (; ) is a city in the Central District of Yazd County, Yazd province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district. At the 2016 census, its population was 529,673. Since 2017, the historical city of Yazd is recognized as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO. Because of generations of adaptations to its desert surroundings, Yazd is known for its Persian architecture. It is nicknamed the "City of Windcatchers" ( ''Shahr-e Badgirha'') from its many examples. It is also very well known for its Zoroastrian fire temples, ab anbars (cisterns), qanats (underground channels), yakhchals (coolers), Persian handicrafts, handwoven cloth (''Persian termeh''), silk weaving, Persian cotton candy, and its time-honored confectioneries. Yazd is also known as City of Bicycles, because of its early adoption of cycling, and its boasting the highest number of bicycles per capita in Iran. It is reported that bicycle culture in Iran originated in Yazd as a result o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
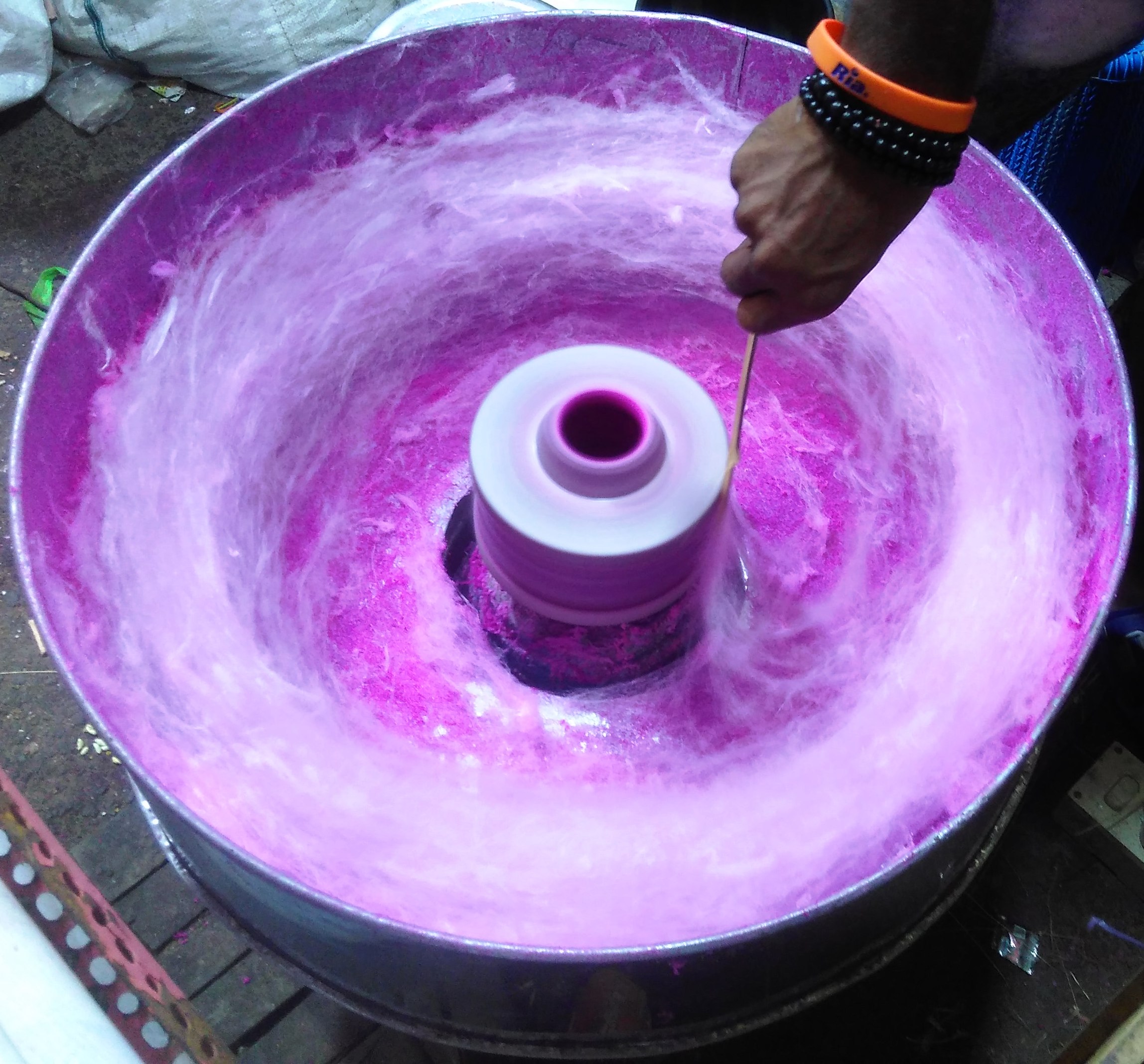
Cotton Candy
Cotton candy, also known as candy floss (candyfloss) and fairy floss, is a spun sugar confection that resembles cotton. It is made by heating and liquefying sugar, and spinning it centrifugally through minute holes, causing it to rapidly cool and re-solidify into fine strands. It usually contains small amounts of food flavoring and it naturally bears the color of the sugar it is made of which is often altered with food coloring. It is often sold at fairs, circuses, carnivals, and festivals, served in a plastic bag, on a stick, or on a paper cone. It is made and sold globally, as ''candy floss'' in the United Kingdom, Ireland, India, New Zealand, Sri Lanka and South Africa, as ''fairy floss'' in Australia, as ''barbe à papa'' 'daddy's beard' in France, as شعر البنات 'girl's hair' in the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia, as غزل البنات "girl's yarn" in Egypt. Similar confections include Korean and Iranian . History Several sources track the origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candy Floss
Cotton candy, also known as candy floss (candyfloss) and fairy floss, is a spun sugar confection that resembles cotton. It is made by heating and liquefying sugar, and spinning it centrifugally through minute holes, causing it to rapidly cool and re-solidify into fine strands. It usually contains small amounts of food flavoring and it naturally bears the color of the sugar it is made of which is often altered with food coloring. It is often sold at fairs, circuses, carnivals, and festivals, served in a plastic bag, on a stick, or on a paper cone. It is made and sold globally, as ''candy floss'' in the United Kingdom, Ireland, India, New Zealand, Sri Lanka and South Africa, as ''fairy floss'' in Australia, as ''barbe à papa'' 'daddy's beard' in France, as شعر البنات 'girl's hair' in the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia, as غزل البنات "girl's yarn" in Egypt. Similar confections include Korean and Iranian . History Several sources track the origin o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton Candy
Cotton candy, also known as candy floss (candyfloss) and fairy floss, is a spun sugar confection that resembles cotton. It is made by heating and liquefying sugar, and spinning it centrifugally through minute holes, causing it to rapidly cool and re-solidify into fine strands. It usually contains small amounts of food flavoring and it naturally bears the color of the sugar it is made of which is often altered with food coloring. It is often sold at fairs, circuses, carnivals, and festivals, served in a plastic bag, on a stick, or on a paper cone. It is made and sold globally, as ''candy floss'' in the United Kingdom, Ireland, India, New Zealand, Sri Lanka and South Africa, as ''fairy floss'' in Australia, as ''barbe à papa'' 'daddy's beard' in France, as شعر البنات 'girl's hair' in the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia, as غزل البنات "girl's yarn" in Egypt. Similar confections include Korean and Iranian . History Several sources track the origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pişmaniye
''Pişmaniye'' is a Turkish confection made by blending flour roasted in butter into pulled-sugar and then forming it into fine strands. It is sometimes garnished with ground pistachio nuts. Although it is sometimes compared to cotton candy, both the ingredients and method of preparation are significantly different. Until recently pişmaniye used to be made at home in most regions of Turkey, but this tradition is now rapidly disappearing. Today the manufacturing process is partially mechanised. Alternative names There are many different Turkish names, used in different provinces, the most common being ''tel helva, çekme helva, tel tel, tepme helva'' and ''keten helva''. Origin and etymology The earliest Turkish reference to pişmaniye is a recipe by Şirvani, a physician writing during the 1430s. The Persian form ''pashmak'', related to and , the origin of the Turkish name ''pişmaniye'', occurs in the poetry of the Iranian poet Ebu Ishak, also known as Bushak (d. 1423 or 142 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ..., fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double sugars, are molecules made of two bonded monosaccharides; common examples are sucrose (glucose + fructose), lactose (glucose + galactose), and maltose (two molecules of glucose). White sugar is almost pure sucrose. In the body, compound sugars are hydrolysed into simple sugars. Longer chains of monosaccharides (>2) are not regarded as sugars and are called oligosaccharides or polysaccharides. Starch is a glucose polymer found in plants, the most abundant source of energy in human foo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sesame
Sesame (; ''Sesamum indicum'') is a plant in the genus '' Sesamum'', also called benne. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cultivated for its edible seeds, which grow in pods. World production in 2018 was , with Sudan, Myanmar, and India as the largest producers. Sesame seed is one of the oldest oilseed crops known, domesticated well over 3,000 years ago. ''Sesamum'' has many other species, most being wild and native to sub-Saharan Africa. ''S. indicum,'' the cultivated type, originated in India. It tolerates drought conditions well, growing where other crops fail. Sesame has one of the highest oil contents of any seed. With a rich, nutty flavor, it is a common ingredient in cuisines around the world. Like other foods, it can trigger allergic reactions in some people and is one of the nine most common allergens outlined by the Food and Drug Administration. Etymology Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afghan Cuisine
Afghan cuisine is influenced by Persian, Central Asian and South Asian cuisines due to Afghanistan's close proximity and cultural ties. The cuisine is halal and mainly based on mutton, beef, poultry and fish with rice and Afghan bread. Accompanying these are common vegetables and dairy products, such as milk, yogurt, whey, and fresh and dried fruits such as apples, apricots, grapes, bananas, oranges, plums, pomegranates, sweet melons, and raisins. The diet of most Afghans revolves around rice-based dishes, while various forms of naan are consumed with most meals. Tea is generally consumed daily in large quantities, and is a major part of hospitality. The culinary specialties reflect the nation's ethnic and geographic diversity. The national dish of Afghanistan is '' Kabuli palaw'', a rice dish cooked with raisins, carrots, nuts, and lamb or beef. Background The cuisine of Afghanistan is ''halal'' and has elements from various places: for example, ''garam masala'' from India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
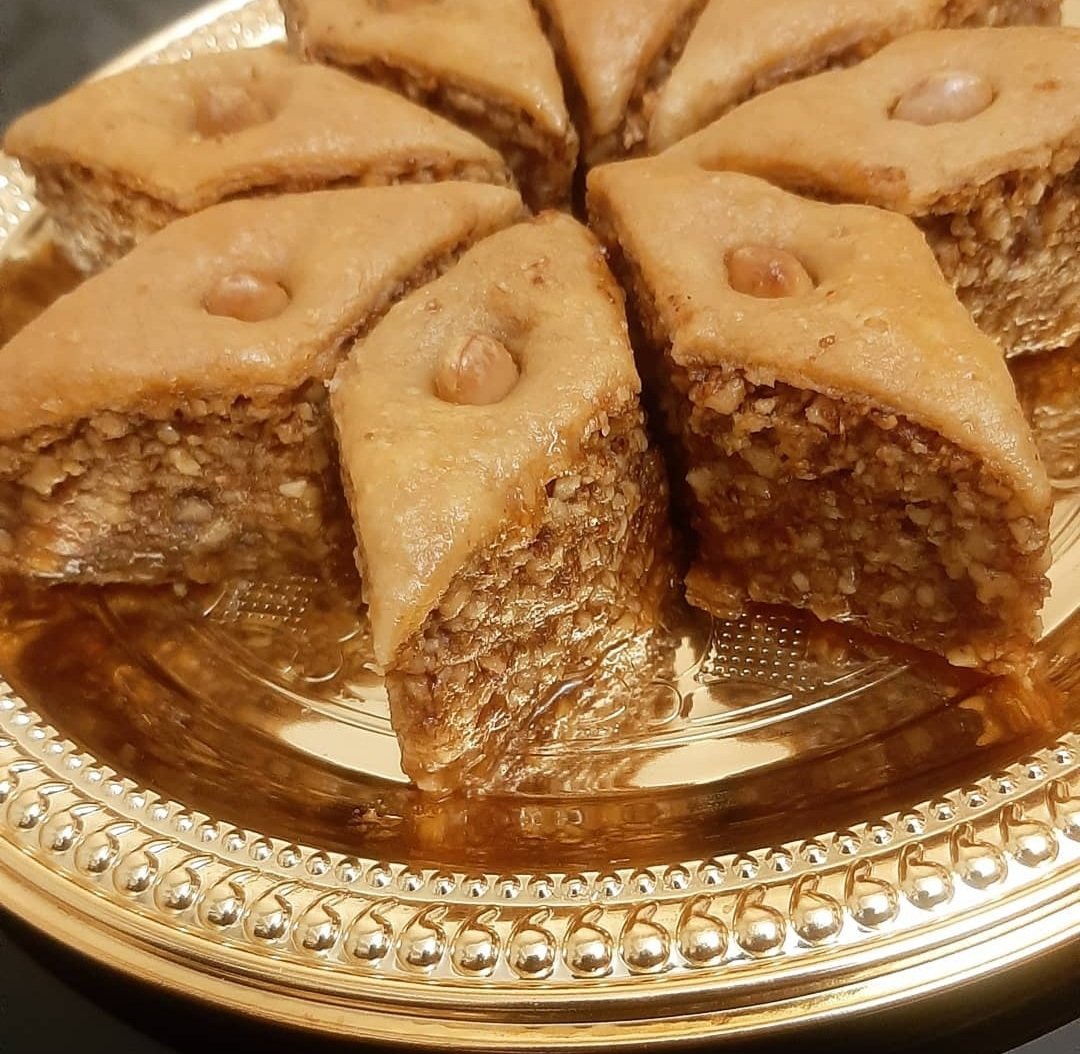
Baghlava
Baklava (, or ; ) is a layered pastry dessert made of filo pastry, filled with chopped nuts, and sweetened with syrup or honey. It was one of the most popular sweet pastries of Ottoman cuisine. There are several theories for the origin of the pre-Ottoman version of the dish. In modern times, it is a common dessert among cuisines of countries in West Asia, Southeast Europe, Central Asia, and North Africa. It is also enjoyed in Pakistan and Afghanistan, where, although not a traditional sweet, it has carved out a niche in urban centers. Etymology The word ''baklava'' is first attested in English in 1650, a borrowing from . The name ''baklava'' is used in many languages with minor phonetic and spelling variations. The earliest known reference to baklava is in a poem by the 15th century mystic Kaygusuz Abdal. The historian Paul D. Buell argues that the word ''baklava'' may come from the Mongolian root ' 'to tie, wrap up, pile up' composed with the Turkic verbal ending ''-v'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qottab
''Qottab'' ( ''qottâb'') is an almond-filled deep-fried Iranian cuisine pastry or cake, prepared with flour, almonds, powdered sugar, vegetable oil, and cardamom. In some cases, ground walnuts are substituted for almonds. The city of Yazd is well known for its ''qottab,'' which is commonly prepard during the Persian new year (Nowruz). Qottab developed from an earlier savoury pastry known as ''sanbosag'', the ancestor of the Ethiopian sambusa and the South Asian samosa. Since the 16th century, the original savoury form of ''sanbosag'' has become rare outside of the region of Laristan and the Persian Gulf Coast. See also * Gosh-e fil * Qutab Qutab () is a traditional dish in Azerbaijani cuisine made from thinly rolled dough that is filled with a variety of ingredients and cooked briefly on a convex griddle called a saj. This versatile and popular dish comes in many variations, with f ... References Iranian pastries Iranian desserts Kerman Almond desserts Deep fri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaz (candy)
Gaz () is an Iranian nougat that originated in the Isfahan region. It is widely known as Persian Nougat in American and European countries. It is made from pistachio, almond kernels, rose-water, egg whites and sap from Persian manna. Etymology The Persian word ''Gaz'' is associated with ''gaz-angobīn'' which translates to 'Honey of Gaz', in reference to a species of Tamarisk, '' T. gallica'' that is native to the Zagros Mountains located to the west of Isfahan. Gaz is traditionally presumed to be the sap of the Tamarisk tree. History Gaz dates backs to 450 years ago in Isfahan, when the sap found on the Tamarisk tree was combined with flour, bread, pistachios, almonds and chocolate in traditional and industrial workshops. The height of this mountain tree reaches a height of two meters and it usually grows in good weather in the Khansar. The product of this tree becomes ready to harvest in the late summer and the shiny and yellow grains come out in the stems like millet. At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safavid Empire
The Guarded Domains of Iran, commonly called Safavid Iran, Safavid Persia or the Safavid Empire, was one of the largest and longest-lasting Iranian empires. It was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often considered the beginning of History of Iran, modern Iranian history, as well as one of the gunpowder empires. The Safavid List of monarchs of Persia, Shāh Ismail I, Ismā'īl I established the Twelver denomination of Shia Islam, Shīʿa Islam as the Safavid conversion of Iran to Shia Islam, official religion of the empire, marking one of the most important turning points in the history of Islam. An Iranian dynasty rooted in the Sufi Safavid order founded by sheikhs claimed by some sources to be of Kurds, Kurdish origin, it heavily intermarried with Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman, Georgians, Georgian, Circassians, Circassian, and Pontic Greeks, Pontic GreekAnthony Bryer. "Greeks and Türkmens: The Pontic Exception", ''Dumbarton Oaks Papers, Vol. 29'' (1975), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |