|
Parental Alienation Syndrome
Parental alienation syndrome (PAS) is a term introduced by child psychiatrist Richard Gardner in 1985 to describe signs and symptoms he believed to be exhibited by children who have been alienated from one parent through manipulation by the other parent. Proposed symptoms included extreme but unwarranted fear, and disrespect or hostility towards a parent. Gardner believed that a set of behaviors that he observed in some families involved in child custody litigation could be used to diagnose psychological manipulation or undue influence of a child by a parent, typically by the other parent who may be attempting to prevent an ongoing relationship between a child and other family members after family separation or divorce. Use of the term "syndrome" has not been accepted by either the medical or legal communities and Gardner's research has been broadly criticized by legal and mental health scholars for lacking scientific validity and reliability. Initial description Parental alie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Child And Adolescent Psychiatry
Child and adolescent psychiatry (or pediatric psychiatry) is a branch of psychiatry that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental disorders in children, adolescents, and their families. It investigates the biopsychosocial factors that influence the development and course of psychiatric disorders and treatment responses to various interventions. Child and adolescent psychiatrists primarily use psychotherapy and/or medication to treat mental disorders in the pediatric population. Classification of disorders There are many classifications of disorders. Developmental disorders include autism spectrum disorder and learning disorders, and some attention and behaviors disorders are attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, oppositional defiant disorder, and conduct disorder. Childhood schizophrenia is an example of a psychotic disorder. Major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder, persistent depressive disorder, and disruptive mood dysregulation disorder are unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admissible Evidence
Admissible evidence, in a court of law, is any Testimony, testimonial, Documentary evidence, documentary, or tangible evidence (law), evidence that may be introduced to a Trier of fact, factfinder—usually a judge or jury—to establish or to bolster a point put forth by a party to the proceeding. For evidence to be admissible, it must be relevance (law), relevant and "not excluded by the rules of evidence", which generally means that it must not be unfairly Prejudice (legal term), prejudicial, and it must have some indicia of reliability. The general rule in evidence is that all relevant evidence is admissible and all irrelevant evidence is inadmissible, though some countries (such as the Law of the United States, United States and, to an extent, Australian legal system, Australia) proscribe the prosecution from exploiting evidence False evidence, obtained in violation of constitutional law, thereby rendering relevant evidence inadmissible. This law of evidence, rule of eviden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Case Study
A case study is an in-depth, detailed examination of a particular case (or cases) within a real-world context. For example, case studies in medicine may focus on an individual patient or ailment; case studies in business might cover a particular firm's strategy or a broader market; similarly, case studies in politics can range from a narrow happening over time like the operations of a specific political campaign, to an enormous undertaking like world war, or more often the policy analysis of real-world problems affecting multiple stakeholders. Generally, a case study can highlight nearly any individual, group, organization, event, belief system, or action. A case study does not necessarily have to be one observation ( N=1), but may include many observations (one or multiple individuals and entities across multiple time periods, all within the same case study). Research projects involving numerous cases are frequently called cross-case research, whereas a study of a single case is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anecdotal Evidence
Anecdotal evidence (or anecdata) is evidence based on descriptions and reports of individual, personal experiences, or observations, collected in a non- systematic manner. The term ''anecdotal'' encompasses a variety of forms of evidence. This word refers to personal experiences, self-reported claims, or eyewitness accounts of others, including those from fictional sources, making it a broad category that can lead to confusion due to its varied interpretations. Anecdotal evidence can be true or false but is not usually subjected to the methodology of scholarly method, the scientific method, or the rules of legal, historical, academic, or intellectual rigor, meaning that there are little or no safeguards against fabrication or inaccuracy. However, the use of anecdotal reports in advertising or promotion of a product, service, or idea may be considered a testimonial, which is highly regulated in certain jurisdictions. The persuasiveness of anecdotal evidence compared to that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peer Review
Peer review is the evaluation of work by one or more people with similar competencies as the producers of the work (:wiktionary:peer#Etymology 2, peers). It functions as a form of self-regulation by qualified members of a profession within the relevant Field of study, field. Peer review methods are used to maintain quality standards, improve performance, and provide credibility. In academia, scholarly peer review is often used to determine an academic paper's suitability for publication. Peer review can be categorized by the type and by the field or profession in which the activity occurs, e.g., #Medical, medical peer review. It can also be used as a teaching tool to help students improve writing assignments. Henry Oldenburg (1619–1677) was a German-born British philosopher who is seen as the 'father' of modern scientific peer review. It developed over the following centuries with, for example, the journal ''Nature (journal), Nature'' making it standard practice in 1973. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
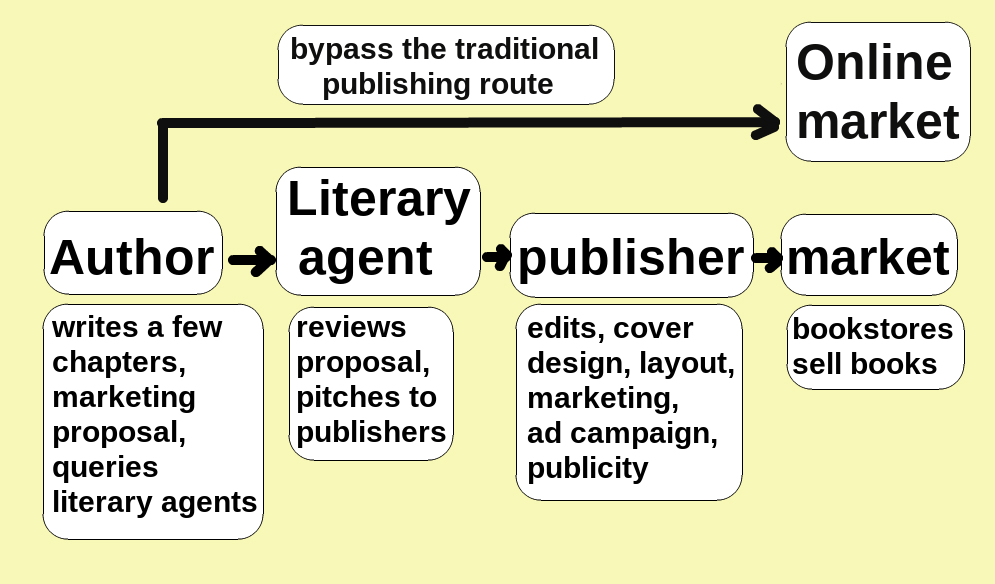
Self-publishing
Self-publishing is an author-driven publication of any media without the involvement of a third-party publisher. Since the advent of the internet, self-published usually depends upon digital platforms and print-on-demand technology, ranging from physical books to Ebook, eBooks. Examples include magazines, print-on-demand books, music albums, pamphlets, brochures, video games, video content, artwork, Zine, zines, and web fiction. Self-publishing is an alternative to traditional publishing that has implications for production, cost and revenue, distribution, and public perception. Types In self-publishing authors publish their own work. While it is possible for an author to single-handedly carry out the whole process independently, many authors engage with professionals for specific services as needed (such as editors or cover designers). A growing number of companies offer a one-stop shop where an author can source a whole range of services required to self-publish a book (som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical Burden Of Proof
The burden of proof (Latin: ''onus probandi'', shortened from ''Onus probandi incumbit ei qui dicit, non ei qui negat'' – the burden of proof lies with the one who speaks, not the one who denies) is the obligation on a party in a dispute to provide sufficient warrant for its position. Holder of the burden When two parties are in a discussion and one makes a claim that the other disputes, the one who makes the claim typically has a ''burden of proof'' to justify or substantiate that claim, especially when it challenges a perceived ''status quo''. This is also stated in Hitchens's razor, which declares that "what may be asserted without evidence may be dismissed without evidence." Carl Sagan proposed a related criterion: "Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence". While certain kinds of arguments, such as logical syllogisms, require mathematical or strictly logical proofs, the standard for evidence to meet the burden of proof is usually determined by context and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothesis
A hypothesis (: hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. A scientific hypothesis must be based on observations and make a testable and reproducible prediction about reality, in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. If a hypothesis is repeatedly independently demonstrated by experiment to be true, it becomes a scientific theory. In colloquial usage, the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, but this is incorrect in the context of science. A working hypothesis is a provisionally-accepted hypothesis used for the purpose of pursuing further progress in research. Working hypotheses are frequently discarded, and often proposed with knowledge (and warning) that they are incomplete and thus false, with the intent of moving research in at least somewhat the right direction, especially when scientists are stuck on an issue and brainstorming ideas. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis'' is used in formal l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnostic And Statistical Manual Of Mental Disorders
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (''DSM''; latest edition: ''DSM-5-TR'', published in March 2022) is a publication by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) for the classification of mental disorders using a common language and standard criteria. It is an internationally accepted manual on the diagnosis and treatment of mental disorders, though it may be used in conjunction with other documents. Other commonly used principal guides of psychiatry include the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), Chinese Classification of Mental Disorders (CCMD), and the ''Psychodynamic Diagnostic Manual''. However, not all providers rely on the DSM-5 as a guide, since the ICD's mental disorder diagnoses are used around the world, and scientific studies often measure changes in symptom scale scores rather than changes in DSM-5 criteria to determine the real-world effects of mental health interventions. It is used by researchers, psychiatric drug regulatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precedent
Precedent is a judicial decision that serves as an authority for courts when deciding subsequent identical or similar cases. Fundamental to common law legal systems, precedent operates under the principle of ''stare decisis'' ("to stand by things decided"), where past judicial decisions serve as case law to guide future rulings, thus promoting consistency and predictability. Precedent is a defining feature that sets common law systems apart from Civil law (legal system), civil law systems. In common law, precedent can either be something courts must follow (binding) or something they can consider but do not have to follow (persuasive). Civil law (legal system), Civil law systems, in contrast, are characterized by comprehensive Code of law, codes and detailed statutes, with no emphasis on precedent, and where judges primarily focus on fact-finding and applying codified law. Courts in common law systems rely heavily on case law, which refers to the collection of precedents and le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Court
Family courts were originally created to be a Court of Equity convened to decide matters and make orders in relation to family law, including custody of children, and could disregard certain legal requirements as long as the petitioner/plaintiff came into court with "clean hands" and the request was reasonable, " quantum meruit". Changes in laws and rules have made this distinction superfluous. Family courts hear all cases that relate to familial and domestic relationships. Each US state and each country has a different system utilized to address family law cases including decisions regarding divorce cases. Family courts have been accused of sentencing disparity both discriminating against women and discriminating against men. In the United States Family courts were first established in the United States starting in the late 1910s at the behest of probation officers invested in the success of specialized domestic relations courts. Members of the National Probation Associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |