|
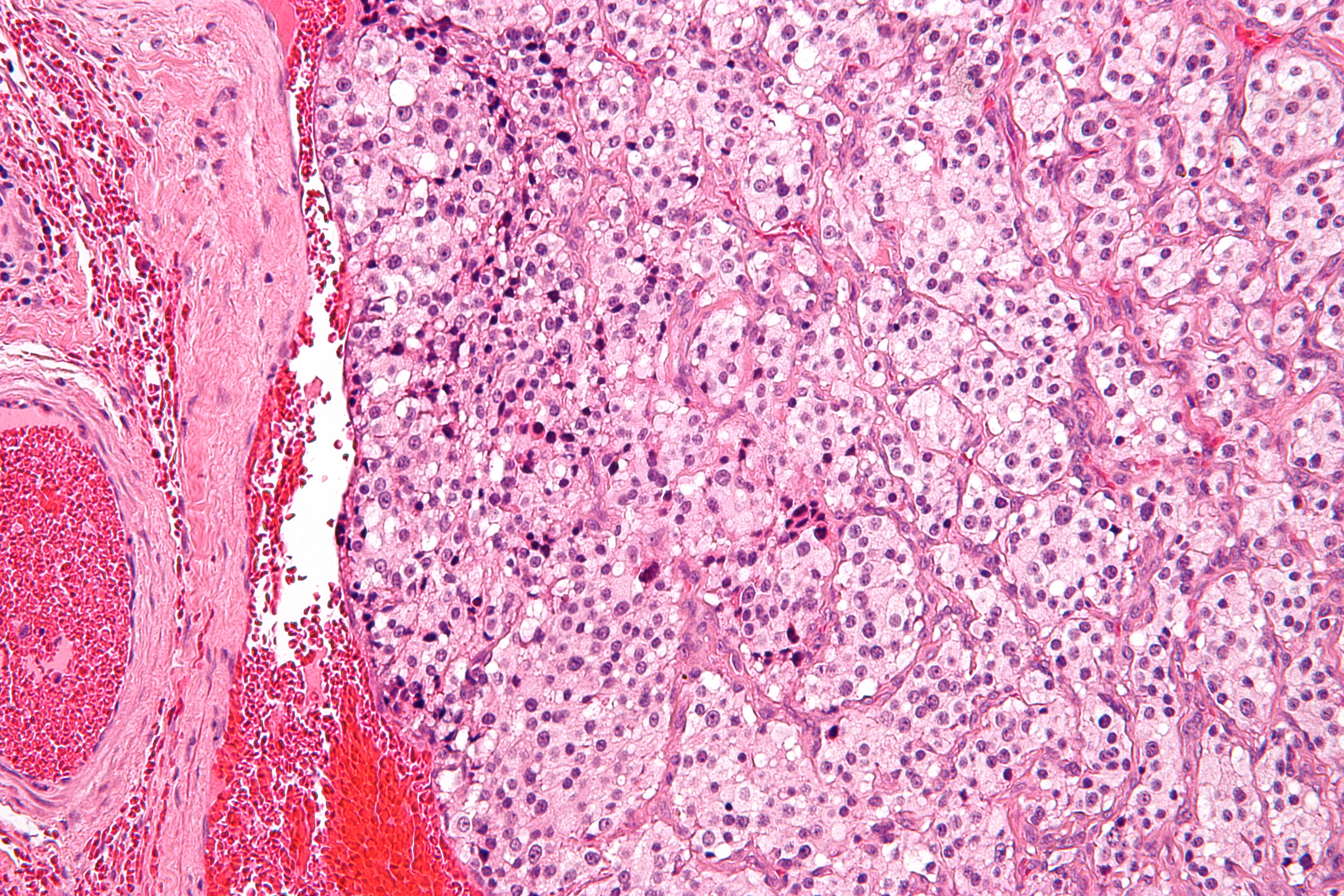
Paraganglioma
A paraganglioma is a rare neuroendocrine tumour, neuroendocrine neoplasm that may develop at various body sites (including the head, neck, thorax and abdomen). When the same type of tumor is found in the adrenal gland, they are referred to as a pheochromocytoma. They are rare tumors, with an overall estimated incidence of 1 in 300,000. There is no test that determines benign from malignant tumors; long-term follow-up is therefore recommended for all individuals with paraganglioma. Signs and symptoms Most paragangliomas are asymptomatic, present as a painless mass, or create symptoms such as hypertension, tachycardia, headache, and palpitations. While all contain neurosecretory granules, only in 1–3% of cases is secretion of hormones such as catecholamines abundant enough to be clinically significant; in that case manifestations often resemble those of pheochromocytomas (intra-medullary paraganglioma). Genetics About 75% of paragangliomas are sporadic; the remaining 25% are here ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor of the adrenal medulla composed of chromaffin cells and is part of the paraganglioma (PGL) family of tumors, being defined as an intra-adrenal PGL. These neuroendocrine tumors can be sympathetic, where they release catecholamines into the bloodstream which cause the most common symptoms, including hypertension (high blood pressure), tachycardia (fast heart rate), sweating, and headaches. Some PGLs may secrete little to no catecholamines, or only secrete paroxysmally (episodically), and other than secretions, PGLs can still become clinically relevant through other secretions or mass effect (most common with head and neck PGL). PGLs of the head and neck are typically parasympathetic and their sympathetic counterparts are predominantly located in the abdomen and pelvis, particularly concentrated at the organ of Zuckerkandl at the bifurcation of the aorta. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of a sympathetic pheochromocytoma are related to sympathetic n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SDHB
Succinate dehydrogenase biquinoneiron-sulfur subunit, mitochondrial (SDHB) also known as iron-sulfur subunit of complex II (Ip) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SDHB'' gene. The succinate dehydrogenase (also called SDH or Complex II) protein complex catalyzes the oxidation of succinate (succinate + ubiquinone => fumarate + ubiquinol). SDHB is one of four protein subunits forming succinate dehydrogenase, the other three being SDHA, SDHC and SDHD. The SDHB subunit is connected to the SDHA subunit on the hydrophilic, catalytic end of the SDH complex. It is also connected to the SDHC/ SDHD subunits on the hydrophobic end of the complex anchored in the mitochondrial membrane. The subunit is an iron-sulfur protein with three iron-sulfur clusters. It weighs 30 kDa. Structure The gene that codes for the SDHB protein is nuclear, not mitochondrial DNA. However, the expressed protein is located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. The location of the gene in hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SDHA
Succinate dehydrogenase complex, subunit A, flavoprotein variant is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SDHA'' gene. This gene encodes a major catalytic subunit of succinate-ubiquinone oxidoreductase, a complex of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. The complex is composed of four nuclear-encoded subunits and is localized in the mitochondrial inner membrane. SDHA contains the FAD binding site where succinate is deprotonated and converted to fumarate. Mutations in this gene have been associated with a form of mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiency known as Leigh Syndrome. A pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 3q29. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Structure The ''SDHA'' gene is located on the p arm of chromosome 5 at locus 15 and is composed of 17 exons. The SDHA protein encoded by this gene is 664 amino acids long and weighs 72.7 kDA. SDHA protein has four subdomains, including capping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Body
The carotid body is a small cluster of peripheral chemoreceptor cells and supporting sustentacular cells situated at the bifurcation of each common carotid artery in its tunica externa. The carotid body detects changes in the composition of arterial blood flowing through it, mainly the partial pressure of arterial oxygen, but also of carbon dioxide. It is also sensitive to changes in blood pH, and temperature. Structure The carotid body is situated on the posterior aspect of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery. The carotid body is made up of two types of cells, called glomus cells: glomus type I cells are peripheral chemoreceptors, and glomus type II cells are sustentacular supportive cells. * Glomus type I cells are derived from the neural crest. They release a variety of neurotransmitters, including acetylcholine, ATP, and dopamine that trigger EPSPs in synapsed neurons leading to the respiratory center. They are innervated by axons of the glossopharyngeal n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Succinate Dehydrogenase Complex Subunit C
Succinate dehydrogenase complex subunit C, also known as succinate dehydrogenase cytochrome b560 subunit, mitochondrial, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SDHC'' gene. This gene encodes one of four nuclear-encoded subunits that comprise succinate dehydrogenase, also known as mitochondrial complex II, a key enzyme complex of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and aerobic respiratory chains of mitochondria. The encoded protein is one of two integral membrane proteins that anchor other subunits of the complex, which form the catalytic core, to the inner mitochondrial membrane. There are several related pseudogenes for this gene on different chromosomes. Mutations in this gene have been associated with pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. Structure The gene that codes for the SDHC protein is nuclear, even though the protein is located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. The location of the gene in hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SDHAF2
Succinate dehydrogenase complex assembly factor 2, formerly known as SDH5 and also known as SDH assembly factor 2 or SDHAF2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SDHAF2 gene. This gene encodes a mitochondrial protein needed for the flavination of a succinate dehydrogenase complex subunit required for activity of the complex. Mutations in this gene are associated with pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Structure ''SDHAF2'' is located on the q arm of chromosome 11 in position 12.2 and spans 16,642 base pairs. The ''SDHAF2'' gene produces a 6.7 kDa protein composed of 65 amino acids. This highly conserved protein is a cofactor of flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). The structure represents a five-helix bundle with a region of well-defined conserved surface residues. This conserved region includes a negatively charged periphery and a positively charged surface, and a patch that is hydrophobic. The region is located in α-helices I, II, and the connecting band. Function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroendocrine Tumour
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung, and the rest of the body. Although there are many kinds of NETs, they are treated as a group of tissue because the cells of these neoplasms share common features, including a similar histological appearance, having special secretory granules, and often producing biogenic amines and polypeptide hormones. The term "neuro" refers to the dense core granules (DCGs), similar to the DCGs in the serotonergic neurons storing monoamines. The term "endocrine" refers to the synthesis and secretion of these monoamines. The neuroendocrine system includes endocrine glands such as the pituitary, the parathyroids and the neuroendocrine adrenals, as well as endocrine islet tissue embedded within glandular tissue such as in the pancreas, and scatter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLC25A11
Mitochondrial 2-oxoglutarate/malate carrier protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC25A11'' gene. Inactivating mutations in this gene predispose to metastasic paraganglioma. See also * Solute carrier family The solute carrier (SLC) group of membrane transport proteins include over 400 members organized into 66 families. Most members of the SLC group are located in the cell membrane. The SLC gene nomenclature system was originally proposed by the HUGO ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * Solute carrier family {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SDHD
Succinate dehydrogenase biquinonecytochrome b small subunit, mitochondrial (CybS), also known as succinate dehydrogenase complex subunit D (SDHD), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SDHD'' gene. Names previously used for SDHD were PGL and PGL1. Succinate dehydrogenase is an important enzyme in both the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain. Hereditary PGL-PCC syndrome is caused by a parental imprint of the SDHD gene. Screening can begin by 6 years of age. Structure The SDHD gene is located on chromosome 11 at locus 11q23 and it spans 8,978 base pairs. There are pseudogenes for this gene on chromosomes 1, 2, 3, 7, and 18. The SDHD gene produces a 17 kDa protein composed of 159 amino acids. The SDHD protein is one of the two integral transmembrane subunits anchoring the four-subunit succinate dehydrogenase (Complex II) protein complex to the matrix side of the mitochondrial inner membrane. The other transmembrane subunit is SDHC. The SDHC/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustentacular Cell
A sustentacular cell is a type of cell primarily associated with structural support, they can be found in various tissues. * Sustentacular cells of the olfactory epithelium (also called supporting cells or Sertoli cells) have been shown to be involved in the phagocytosis of dead neurons, odorant transformation and xenobiotic metabolism. * One type of sustentacular cell is the Sertoli cell, in the testicle. It is located in the walls of the seminiferous tubules and supplies nutrients to sperm. They are responsible for the differentiation of spermatids, the maintenance of the blood-testis barrier, and the secretion of inhibin, androgen-binding protein and Müllerian-inhibiting factor. * The organ of Corti in the inner ear and taste bud Taste buds are clusters of taste receptor cells, which are also known as gustatory cells. The taste receptors are located around the small structures known as papillae found on the upper surface of the tongue, soft palate, upper esopha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medullary Carcinoma Of The Thyroid
Medullary thyroid cancer is a form of thyroid carcinoma which originates from the parafollicular cells (C cells), which produce the hormone calcitonin.Hu MI, Vassilopoulou-Sellin R, Lustig R, Lamont JP"Thyroid and Parathyroid Cancers"in Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (EdsCancer Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach 11 ed. 2008. Medullary tumors are the third most common of all thyroid cancers and together make up about 3% of all thyroid cancer cases. MTC was first characterized in 1959. Approximately 25% of medullary thyroid cancer cases are genetic in nature, caused by a mutation in the RET proto-oncogene. When MTC occurs by itself it is termed sporadic medullary thyroid cancer. Medullary thyroid cancer is seen in people with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2, subtypes 2A and 2B. When medullary thyroid cancer due to a hereditary genetic disorder occurs without other endocrine tumours it is termed familial medullary thyroid cancer. Signs and symptoms The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |