|
Pannage
Pannage is the practice of releasing livestock- pigs in a forest, so that they can feed on fallen acorns, beechmast, chestnuts or other nuts. Historically, it was a right or privilege granted to local people on common land or in royal forests across much of Europe. H. R. Loyn, ''Anglo-Saxon England and the Norman Conquest'', 2nd ed. 1991:369. The practice was historically referred to as ''Eichelmast'' or ''Eckerich'' in German-speaking Europe while the fee to feed one's livestock in such a way was historically referred to as ''žirovina'' in Croatia and Slovenia. Pannage had two useful purposes in the Middle Ages. While rooting around looking for nuts, pigs also turned the soil and broke it. Pig-rooting prevented soil compaction and released nutrients for plant growth. It also fattened pigs for slaughter. Especially in the eastern shires of England, pannage was so prominent a value in the economic importance of woodland that it was often employed, as in ''Domesday Book'' (10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
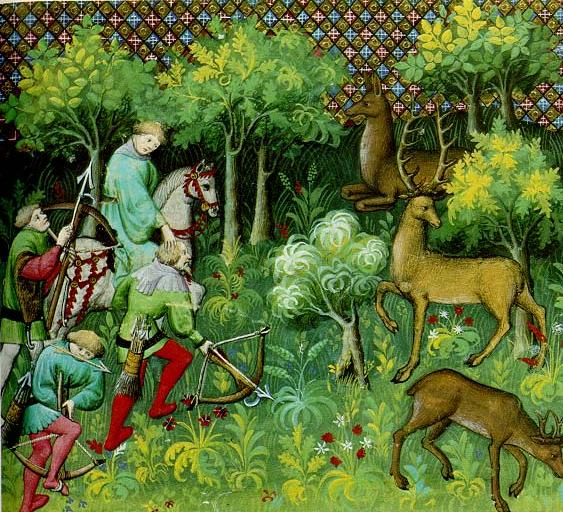
Royal Forest
A royal forest, occasionally known as a kingswood (), is an area of land with different definitions in England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland. The term ''forest'' in the ordinary modern understanding refers to an area of wooded land; however, the original medieval sense was closer to the modern idea of a "preserve" – i.e. land legally set aside for specific purposes such as royal hunting – with less emphasis on its composition. There are also differing and contextual interpretations in Continental Europe derived from the Carolingian and Merovingian legal systems. In Anglo-Saxon England, though the kings were great huntsmen, they never set aside areas declared to be "outside" (Latin ''foris'') the law of the land. Historians find no evidence of the Anglo-Saxon monarchs (c. 500 to 1066) creating forests. However, under the Norman kings (after 1066), by royal prerogative forest law was widely applied. The law was designed to protect the " venison and the vert". In this sense, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannage
Pannage is the practice of releasing livestock- pigs in a forest, so that they can feed on fallen acorns, beechmast, chestnuts or other nuts. Historically, it was a right or privilege granted to local people on common land or in royal forests across much of Europe. H. R. Loyn, ''Anglo-Saxon England and the Norman Conquest'', 2nd ed. 1991:369. The practice was historically referred to as ''Eichelmast'' or ''Eckerich'' in German-speaking Europe while the fee to feed one's livestock in such a way was historically referred to as ''žirovina'' in Croatia and Slovenia. Pannage had two useful purposes in the Middle Ages. While rooting around looking for nuts, pigs also turned the soil and broke it. Pig-rooting prevented soil compaction and released nutrients for plant growth. It also fattened pigs for slaughter. Especially in the eastern shires of England, pannage was so prominent a value in the economic importance of woodland that it was often employed, as in ''Domesday Book'' (10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
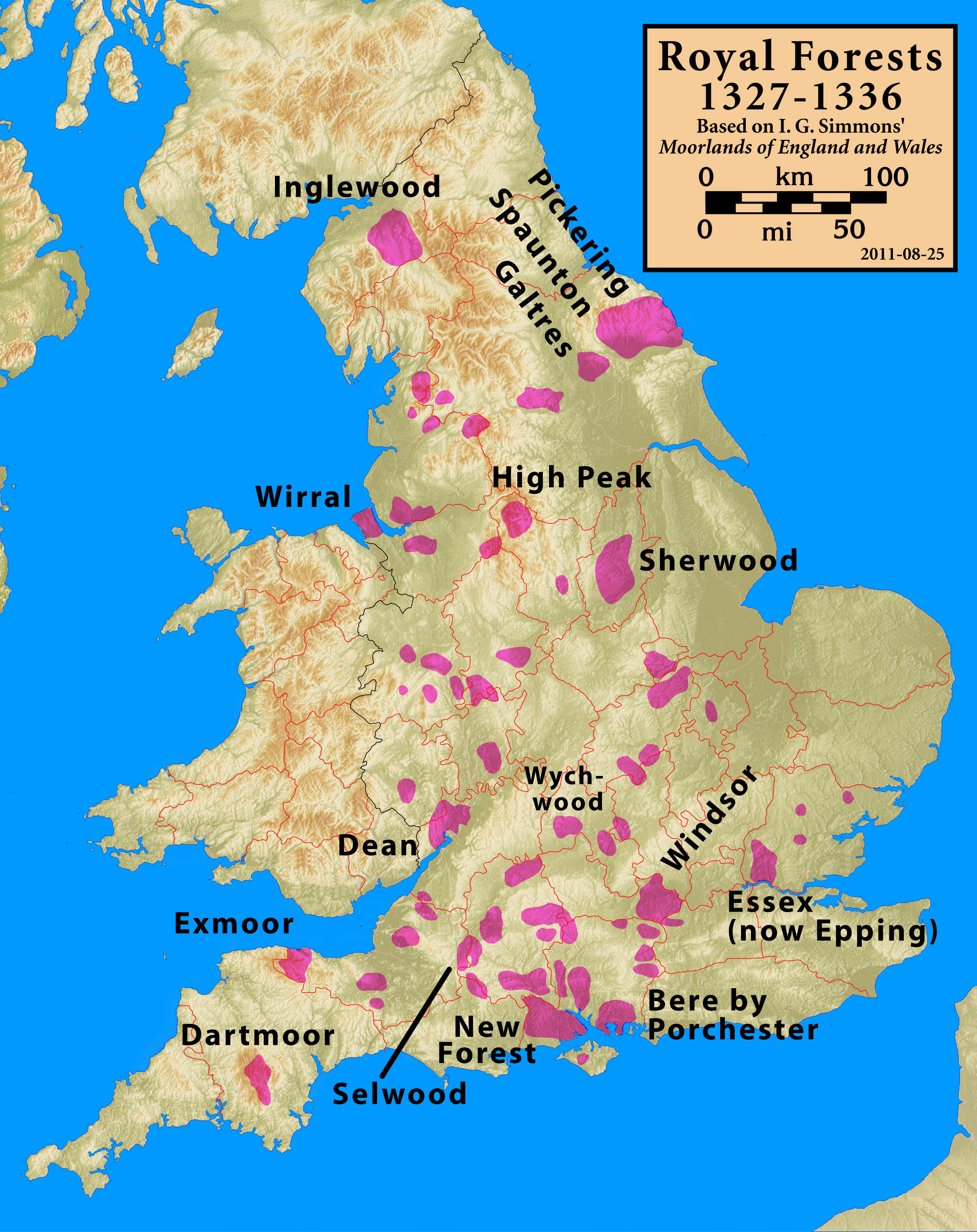
New Forest
The New Forest is one of the largest remaining tracts of unenclosed pasture land, heathland and forest in Southern England, covering southwest Hampshire and southeast Wiltshire. It was proclaimed a royal forest by William the Conqueror, featuring in the Domesday Book. It is the home of the New Forest Commoners, whose ancient rights of common pasture are still recognised and exercised, enforced by official Verderer (New Forest), verderers and Agister (New Forest), agisters. In the 18th century, the New Forest became a source of timber for the Royal Navy. It remains a habitat for many rare birds and mammals. The boundaries of the forest have varied over time and depend on the purpose of delimiting them. It is a biological and geological Site of Special Scientific Interest. Several areas are Geological Conservation Review sites, including Mark Ash Wood, Shepherd’s Gutter, Cranes Moor, Studley Wood, and Wood Green. There are also a number of Nature Conservation Review sites. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Land
Common land is collective land (sometimes only open to those whose nation governs the land) in which all persons have certain common rights, such as to allow their livestock to graze upon it, to collect wood, or to cut turf for fuel. A person who has a right in, or over, common land jointly with another or others is usually called a commoner. In Great Britain, common land or former common land is usually referred to as a common; for instance, Clapham Common and Mungrisdale Common. Due to enclosure, the extent of common land is now much reduced from the hundreds of square kilometres that existed until the 17th century, but a considerable amount of common land still exists, particularly in upland areas. There are over 8,000 registered commons in England alone. Origins Originally in medieval England the common was an integral part of the manor, and was thus part of the estate held by the lord of the manor under a grant from the Crown or a superior peer (who in turn held hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norton, Buckland And Stone
Norton, Buckland and Stone is a small rural civil parish east of Teynham and west of the centre of Faversham in the borough of Swale, Kent, England. It is bypassed by the M2 to the south and traverses the historic A2, on the route of the Roman road of Watling Street. In 2011 the parish had a population of 467. Norton Ash and Lewson Street History and Buildings In 1798, Edward Hasted records that Norton, was written in "ancient" records as 'Northtune'. The manor was previously owned by Odo, Earl of Kent (as the Bishop of Bayeux), at the time of the Domesday Book in 1086. It was recorded as 'Nortone'. The parish had three churches, and three mills without tallage (land tax),and two fisheries of twelve pence. Wood for the pannage (grazing) of forty hogs. But after his trial (for fraud) in 1076. His assets were re-apportioned including Badlesmere. The parish returned to the crown who passed it to 'Hugo de Port'. Then it passed to John de Campania (of Newenham), with a rent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nose Ring (animals)
A nose ring is inserted into the nose of an animal. Nose rings are used to control bulls and occasionally cows, and to help wean young cattle by preventing suckling. Nose rings are used on pigs to discourage rooting. Some nose rings are installed through a pierced hole in the nasal septum or rim of the nose and remain there, while others are temporary tools. History Historically, the use of nose rings for controlling animals dates to the dawn of recorded human civilization. They were used in ancient Sumer and are seen on the Standard of Ur, where they were used on both bovines and equines. There are theories that the rod-and-ring symbol are a shepherd's crook and a nose rope. Calf-weaning nose ring Calf-weaning nose rings, sometimes called weaners, are pain-based anti-suckling devices. These nose rings (usually made of plastic) clip onto the nose without piercing it, and are reusable. They provide an alternative to separating calves from their mothers during the weaning per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transhumance
Transhumance is a type of pastoralism or Nomad, nomadism, a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In montane regions (''vertical transhumance''), it implies movement between higher pastures in summer and lower valleys in winter. Herders have a permanent home, typically in valleys. Generally only the herds travel, with a certain number of people necessary to tend them, while the main population stays at the base. In contrast, movement in plains or plateaus ''(horizontal transhumance)'' is more susceptible to disruption by climatic, economic, or political change. Traditional or fixed transhumance has occurred throughout the inhabited world, particularly Europe and western Asia. It is often important to pastoralist societies, as the dairy products of transhumance flocks and herds (milk, butter, yogurt and cheese) may form much of the diet of such populations. In many languages there are words for the higher summer pastures, and frequently these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pig Farming
Pig farming, pork farming, pig production or hog farming is the raising and breeding of domestic pigs as livestock, and is a branch of animal husbandry. Pigs are farmed principally for food (e.g. pork: bacon, ham, gammon (meat), gammon) and leather#From other animals, skins. Pigs are amenable to many different styles of farming: Intensive pig farming, intensive commercial units, commercial free range enterprises, or extensive farming (being allowed to wander around a village, town or city, or tethered in a simple shelter or kept in a pen outside the owner's house). Historically, farm pigs were kept in small numbers and were closely associated with the residence of the owner, or in the same village or town. They were valued as a source of meat and fat, and for their ability to convert inedible food into meat and manure, and were often fed household food waste when kept on a homestead. Pigs have been farmed to dispose of municipal food waste, garbage on a large scale. All these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Agriculture
Agriculture began independently in different parts of the globe, and included a diverse range of Taxon, taxa. At least eleven separate regions of the Old World, Old and New World were involved as independent centers of origin. The development of agriculture about 12,000 years ago changed the way humans lived. They switched from nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyles to permanent settlements and farming. Wild cereal, grains were collected and eaten from at least 104,000 years ago. However, domestication did not occur until much later. The earliest evidence of small-scale cultivation of edible grasses is from around 21,000 BC with the Ohalo II people on the shores of the Sea of Galilee. By around 9500 BC, the eight Neolithic founder crops – emmer wheat, einkorn wheat, barley, hulled barley, peas, lentils, Vicia ervilia, bitter vetch, chickpeas, and flax – were cultivated in the Levant. Rye may have been cultivated earlier, but this claim remains controversial. Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verderer (New Forest)
In the New Forest a verderer is an unpaid officer whose duty is to regulate and protect the interests of the New Forest commoners, and to preserve the natural beauty and good traditional character of the Forest. There are ten verderers, together constituting the Court of Verderers (or Court of Swainmote). The Court of Verderers The Court has ancient origins but in its present form is a corporate body set up under the New Forest Act 1887 and reconstituted in 1949. It consists of ten verderers, five of whom are elected by the commoners, and four of whom are appointed respectively by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, the Forestry Commission, the National Park Authority, and Natural England. The remaining position is held by the Official Verderer who serves as chair of the Court and who is appointed by the Sovereign. The Court has the same status as a Magistrates Court, and acting under its authority the verderers are responsible for regulating commoning w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are called cows and mature male cattle are bulls. Young female cattle are called heifers, young male cattle are oxen or bullocks, and castrated male cattle are known as steers. Cattle are commonly raised for meat, for dairy products, and for leather. As draft animals, they pull carts and farm implements. Cattle are considered sacred animals within Hinduism, and it is illegal to kill them in some Indian states. Small breeds such as the miniature Zebu are kept as pets. Taurine cattle are widely distributed across Europe and temperate areas of Asia, the Americas, and Australia. Zebus are found mainly in India and tropical areas of Asia, America, and Australia. Sanga cattle are found primarily in sub-Saharan Africa. These types, sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |