|
Palatine
A palatine or palatinus (Latin; : ''palatini''; cf. derivative spellings below) is a high-level official attached to imperial or royal courts in Europe since Roman Empire, Roman times."Palatine" . From the ''Oxford English Dictionary''. Retrieved November 19, 2008. The term ''palatinus'' was first used in Ancient Rome for Chamberlain (office), chamberlains of the Emperor due to their association with the Palatine Hill. The imperial palace guard, after the rise of Constantine I, were also called the ''Scholae Palatinae'' for the same reason. In the Early Middle Ages the title became attached to courts beyond the imperial one; one of the highest level of officials in the papal administration were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Count Palatine
A count palatine (Latin ''comes palatinus''), also count of the palace or palsgrave (from German ''Pfalzgraf''), was originally an official attached to a royal or imperial palace or household and later a nobleman of a rank above that of an ordinary count. The title originated in the Late Roman Empire. In the Middle Ages especially and into modern times, it is associated with the Holy Roman Empire,"palatine, adj.1 and n.1". OED Online. June 2019. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/136245?redirectedFrom=count+palatine& (accessed July 31, 2019). especially Electoral Palatinate. The office, jurisdiction or territory of a count palatine was a county palatine or palatinate. In England the forms earl palatine and palatine earldom are rare alternative terms. Importance of a count palatine in medieval Europe ''Comes palatinus'' This Latin title is the original, but is also pre-feudal: it originated as Roman ''comes'', which was a non-hereditary court title of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
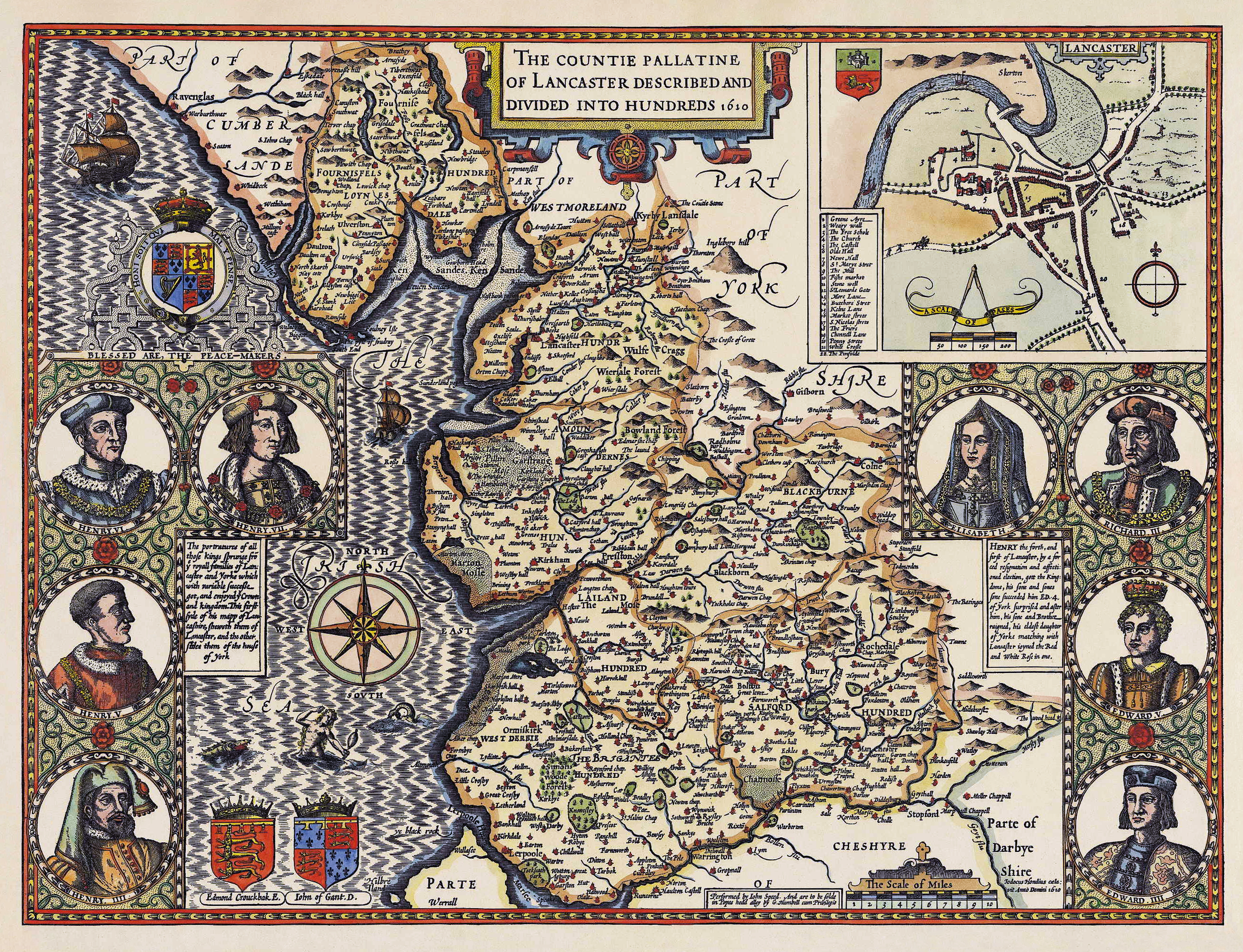
County Palatine
In England, Wales and Ireland a county palatine or palatinate was an area ruled by a hereditary nobleman enjoying special authority and autonomy from the rest of a kingdom. The name derives from the Latin adjective ''palātīnus'', "relating to the palace", from the noun ''palātium'', "palace". It thus implies the exercise of a ''quasi''-royal prerogative within a county, that is to say, a jurisdiction ruled by an earl, the English equivalent of a count. A duchy palatine is similar but is ruled over by a duke, a nobleman of higher precedence than an earl or count. The nobleman swore allegiance to the monarch yet had the power to rule the county largely independently of the king. It should therefore be distinguished from the feudal barony, held from the king, which possessed no such independent authority. Rulers of counties palatine created their own feudal baronies, to be held directly from them '' in capite'', such as the Barony of Halton. County palatine jurisdictions wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Paladin
The Paladins, also called the Twelve Peers (), are twelve legendary knights, the foremost members of Charlemagne's court in the 8th century. They first appear in the medieval (12th century) ''chanson de geste'' cycle of the Matter of France, where they play a similar role to the Knights of the Round Table in Arthurian romance.-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ..., deriving from the Latin ''comes palatinus'' (count palatine), a title given to close Affinity (medieval), retainers. The paladins remained a popular subject throughout medieval French literature. Literature of the Italian Renaissance (15th and 16th centuries) introduced more fantasy elements into the legend, which later became a popular subject for operas in the Baroque music of the 16th and 17th centuries. During the 19th and early 20th centuries the term was reused outside fiction for small numbers of close military confida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Palatine Hill
The Palatine Hill (; Classical Latin: ''Palatium''; Neo-Latin: ''Collis/Mons Palatinus''; ), which relative to the seven hills of Rome is the centremost, is one of the most ancient parts of the city; it has been called "the first nucleus of the Roman Empire". The site is now mainly a large open-air museum whilst the Palatine Museum houses many finds from the excavations here and from other ancient Italian sites. Imperial palaces were built there, starting with Augustus. Before imperial times the hill was mostly occupied by the houses of the rich. The hill originally had two summits separated by a depression: the higher summit was called ''Palatium''; the lower ''Germalus'' (or ''Cermalus''). Using the Forma Urbis Romae, Forma Urbis its perimeter enclosed ; while the Regionary Catalogues of the 4th century enclose . Etymology According to Livy (59 BC – AD 17) the Palatine hill got its name from the Arcadia (ancient region), Arcadian settlers from Pallantium, named fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Judices Palatini
Palatinus (plural: Palatini), Latin for "palatial", were designations for various ecclesiastical offices in the Catholic Church, primarily of certain high officials in the papal court. Medieval Palatine judges In the Middle Ages, the judices palatini (''papal palace judges'') were the highest administrative officers of the pope's household; with the growth of the temporal power of the popes they acquired great importance. These judices palatini were * chief were the primicerius notariorum and secundarius notariorum, the two superintendents of the papal ''notarii'' (notaries), who superintended the preparation of official documents, conducted judicial investigations and exercised jurisdiction in legal matters voluntarily submitted by the interested parties to the papal court; they were the highest officers of the papal Chancery and of the archives of the Lateran Palace. * the nomenculator or adminiculator (originally perhaps two distinct officials), who took charge of, and deci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
County Of Burgundy
The Free County of Burgundy (; ) was a medieval and early modern feudal polity ruled by a count from 982 to 1678. It became known as Franche-Comté (the ''Free County''), and was located in the modern region of Franche-Comté. It belonged to the wider historical region of Upper Burgundy, and bordered the Duchy of Burgundy to the west. Its territory had initially been part of the Kingdom of Upper Burgundy (888–933), and then the united Kingdom of Burgundy, later known as the Kingdom of Arles. The county was formed in 982 by count Otto-William, encompassing his domains in northern parts of the Burgundian realm. In 1032, the Kingdom of Arles was inherited by Conrad II, Holy Roman Emperor, who incorporated the Kingdom, including the County of Burgundy, into the Holy Roman Empire (HRE). As a state of the HRE, the county was granted a high degree of autonomy. The largest city, Besançon, was granted the status of free imperial city. The rest of the county was given imperial i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It shares Anglo-Scottish border, a land border with Scotland to the north and England–Wales border, another land border with Wales to the west, and is otherwise surrounded by the North Sea to the east, the English Channel to the south, the Celtic Sea to the south-west, and the Irish Sea to the west. Continental Europe lies to the south-east, and Ireland to the west. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the population was 56,490,048. London is both List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, the largest city and the Capital city, capital. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic. It takes its name from the Angles (tribe), Angles, a Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe who settled du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelanda sovereign state covering five-sixths of the island) and Northern Ireland (part of the United Kingdomcovering the remaining sixth). It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest in the world. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islands by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lenition
In linguistics, lenition is a sound change that alters consonants, making them "weaker" in some way. The word ''lenition'' itself means "softening" or "weakening" (from Latin 'weak'). Lenition can happen both synchronically (within a language at a particular point in time) and diachronically (as a language changes over time). Lenition can involve such changes as voicing a voiceless consonant, causing a consonant to relax occlusion, to lose its place of articulation (a phenomenon called '' debuccalization'', which turns a consonant into a glottal consonant like or ), or even causing a consonant to disappear entirely. An example of synchronic lenition is found in most varieties of American English, in the form of tapping: the of a word like ''wait'' is pronounced as the more sonorous in the related form ''waiting'' . Some varieties of Spanish show debuccalization of to at the end of a syllable, so that a word like "we are" is pronounced . An example of diachronic l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, Virginia, and more substantially with the founding of the Thirteen Colonies along the Atlantic coast of North America. The British Empire's colonial territories in North America were greatly expanded by the Treaty of Paris (1763), which formally concluded the Seven Years' War, referred to by the English colonies in North America as the French and Indian War, and by the French colonies as . With the ultimate acquisition of most of New France (), British territory in North America was more than doubled in size, and the exclusion of France also dramatically altered the political landscape of the continent. The term ''British America'' was used to refer to the British Empire's colonial territories in North America prior to the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |