|
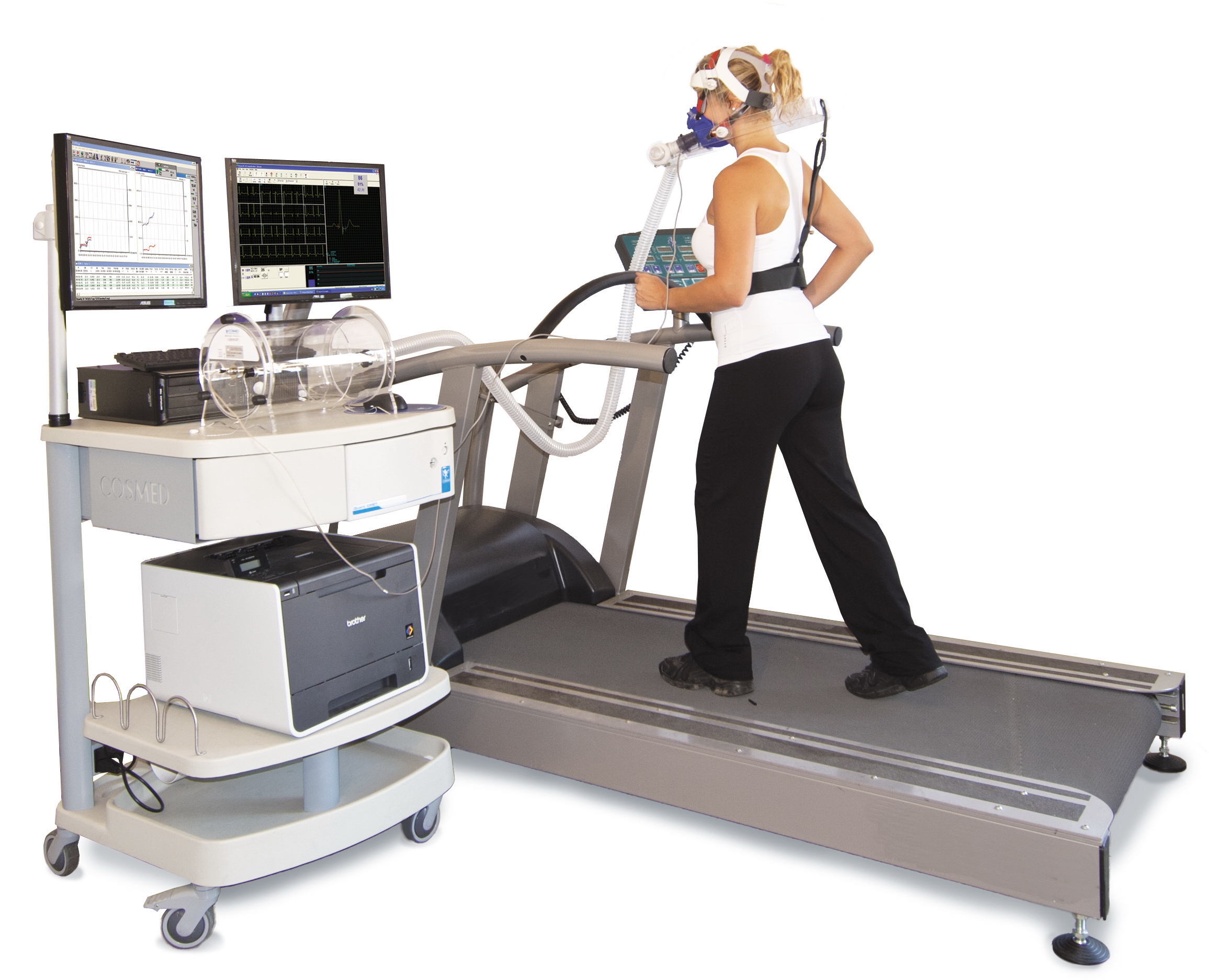
Oxygen Debt
Excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC, informally called afterburn) is a measurably increased rate of oxygen intake following strenuous activity. In historical contexts the term "oxygen debt" was popularized to explain or perhaps attempt to quantify anaerobic energy expenditure, particularly as regards lactic acid/ lactate metabolism; in fact, the term "oxygen debt" is still widely used to this day. However, direct and indirect calorimeter experiments have definitively disproven any association of lactate metabolism as causal to an elevated oxygen uptake. In recovery, oxygen (EPOC) is used in the processes that restore the body to a resting state and adapt it to the exercise just performed. These include: hormone balancing, replenishment of fuel stores, cellular repair, innervation, and anabolism. Post-exercise oxygen consumption replenishes the phosphagen system. New ATP is synthesized and some of this ATP donates phosphate groups to creatine until ATP and creatine le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excess Post-oxygen Consumption (2)
Excess may refer to: * Angle excess, in spherical trigonometry * Insurance excess, similar to a deductible * Excess, in chemistry, a reagent that is not the limiting reagent * "Excess", a song by Tricky from the album '' Blowback'' * ''Excess'' (album), an album by Coma See also * Excess-K Offset binary, also referred to as excess-K, excess-''N'', excess-e, excess code or biased representation, is a method for signed number representation where a signed number n is represented by the bit pattern corresponding to the unsigned numbe ..., or offset binary, in computing * XS (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yo-yo Effect
Weight cycling, also known as yo-yo dieting, is the repeated loss and gain of weight, resembling the up-down motion of a yo-yo. The temporary weight loss of yo-yo dieting is often caused by quick yet unsustainable success of strict diets. The dieter often gives up due to hunger or discomfort, and gains the weight back. The dieter then seeks to lose the regained weight, and the cycle begins again. Other individuals cycle weight deliberately in service of bodybuilding or athletic goals. Weight cycling contributes to increased risk of later obesity, due to repeated signals being sent to the body signalling that it's in starvation mode; therefore it learns to be better and better at storing fat, and increases the strain on vital organs, likely promoting cardiometabolic disease. Causes Dieting The reasons for yo-yo dieting are varied but often include embarking upon a hypocaloric diet too extreme to maintain. At first the dieter may experience elation at the thought of weight loss and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exercise Physiology
Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise. It is one of the allied health professions, and involves the study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to exercise. Exercise physiologists are the highest qualified exercise professionals and utilise education, lifestyle intervention and specific forms of exercise to rehabilitate and manage acute and chronic injuries and conditions. Understanding the effect of exercise involves studying specific changes in muscular, cardiovascular, and Neuro-hormonal, neurohormonal Biological system, systems that lead to changes in functional capacity and Physical strength, strength due to endurance training or strength training. The effect of training on the body has been defined as the reaction to the adaptive responses of the body arising from exercise or as "an elevation of metabolism produced by exercise". Exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-intensity Interval Training
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is a training protocol alternating short periods of intense or explosive anaerobic exercise with brief recovery periods until the point of exhaustion. HIIT involves exercises performed in repeated quick bursts at maximum or near maximal effort with periods of rest or low activity between bouts. The very high level of intensity, the interval duration, and number of bouts distinguish it from aerobic (cardiovascular) activity, because the body significantly recruits anaerobic energy systems (although not completely to the exclusion of aerobic pathways). The method thereby relies on "the anaerobic energy releasing system almost maximally". Although there are varying forms of HIIT-style workouts which may involve exercises associated with both cardiovascular activity and also resistance training, HIIT's crucial features of maximal effort, duration, and short rest periods (thereby triggering the anaerobic pathways of energy production) materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipose Tissue
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of White blood cell, immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages. Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions and Thermal insulation, insulates the body. Previously treated as being hormonally inert, in recent years adipose tissue has been recognized as a major endocrine organ, as it produces hormones such as leptin, estrogen, resistin, and cytokines (especially TNF-alpha, TNFα). In obesity, adipose tissue is implicated in the chronic release of pro-inflammatory markers known as adipokines, which are responsible for the development of metabolic syndromea constellation of diseases including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. Adipose tissue is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-intensity Interval Training
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is a training protocol alternating short periods of intense or explosive anaerobic exercise with brief recovery periods until the point of exhaustion. HIIT involves exercises performed in repeated quick bursts at maximum or near maximal effort with periods of rest or low activity between bouts. The very high level of intensity, the interval duration, and number of bouts distinguish it from aerobic (cardiovascular) activity, because the body significantly recruits anaerobic energy systems (although not completely to the exclusion of aerobic pathways). The method thereby relies on "the anaerobic energy releasing system almost maximally". Although there are varying forms of HIIT-style workouts which may involve exercises associated with both cardiovascular activity and also resistance training, HIIT's crucial features of maximal effort, duration, and short rest periods (thereby triggering the anaerobic pathways of energy production) materia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calorie
The calorie is a unit of energy that originated from the caloric theory of heat. The large calorie, food calorie, dietary calorie, kilocalorie, or kilogram calorie is defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one liter of water by one degree Celsius (or one kelvin). The small calorie or gram calorie is defined as the amount of heat needed to cause the same increase in one milliliter of water. Thus, 1 large calorie is equal to 1,000 small calories. In nutrition and food science, the term ''calorie'' and the symbol ''cal'' may refer to the large unit or to the small unit in different regions of the world. It is generally used in publications and package labels to express the energy value of foods in per serving or per weight, recommended dietary caloric intake, metabolic rates, etc. Some authors recommend the spelling ''Calorie'' and the symbol ''Cal'' (both with a capital C) if the large calorie is meant, to avoid confusion; however, this convention ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Exercise
Anaerobic exercise is a type of exercise that breaks down glucose in the body without using oxygen; ''anaerobic'' means "without oxygen". This type of exercise leads to a buildup of lactic acid. In practical terms, this means that anaerobic exercise is more intense, but shorter in duration than aerobic exercise. The biochemistry of anaerobic exercise involves a process called glycolysis, in which glucose is converted to adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary source of energy for cellular reactions. Anaerobic exercise may be used to help build endurance, muscle strength, and power. Metabolism Anaerobic metabolism is a natural part of metabolic energy expenditure. Fast twitch muscles (as compared to slow twitch muscles) operate using anaerobic metabolic systems, such that any use of fast twitch muscle fibers leads to increased anaerobic energy expenditure. Intense exercise lasting upwards of four minutes (e.g. a mile race) may still have considerable anaerobic energy e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerobic Exercise
Aerobic exercise, also known as cardio, is physical exercise of low to high intensity that depends primarily on the aerobic energy-generating process. "Aerobic" is defined as "relating to, involving, or requiring oxygen", and refers to the use of oxygen to meet energy demands during exercise via aerobic metabolism adequately. Aerobic exercise is performed by repeating sequences of light-to-moderate intensity activities for extended periods of time. According to the World Health Organization, over 31% of adults and 80% of adolescents fail to maintain the recommended levels of physical activity. Examples of cardiovascular or aerobic exercise are medium- to long-distance running or jogging, swimming, cycling, stair climbing and walking. For reducing the risk of health issues, 2.5 hours of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week is recommended. At the same time, even doing an hour and a quarter (11 minutes/day) of exercise can reduce the risk of early death, cardiovascular di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their Structures#Biological, structures, and respond to their environments. The word ''metabolism'' can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic''—the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an Branched chain fatty acids, unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important diet (nutrition), dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cell (biology), cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |