|
Outer Space Treaty
The Outer Space Treaty, formally the Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space, including the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies, is a Multilateralism, multilateral treaty that forms the basis of international space law. Negotiated and drafted under the auspices of the United Nations Security Council, United Nations, it was opened for signature in the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union on 27 January 1967, entering into force on 10 October 1967. , 116 countries are parties to the treaty—including all major space-faring nations, spacefaring nations—and another 22 are signatories. The Outer Space Treaty was spurred by the development of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) in the 1950s, which could reach targets through outer space. The Soviet Union's launch of Sputnik 1, Sputnik, the first artificial satellite, in October 1957, followed by a subsequent arms race with the United States, hastened p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Western Europe, with a population of 14.9 million. London stands on the River Thames in southeast England, at the head of a tidal estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for nearly 2,000 years. Its ancient core and financial centre, the City of London, was founded by the Roman Empire, Romans as Londinium and has retained its medieval boundaries. The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has been the centuries-long host of Government of the United Kingdom, the national government and Parliament of the United Kingdom, parliament. London grew rapidly 19th-century London, in the 19th century, becoming the world's List of largest cities throughout history, largest city at the time. Since the 19th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercontinental Ballistic Missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range (aeronautics), range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more Thermonuclear weapon, thermonuclear warheads). Conventional weapon, Conventional, Chemical weapon, chemical, and Biological agent, biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. The Nuclear weapons of the United States, United States, Russia and weapons of mass destruction, Russia, China and weapons of mass destruction, China, France and weapons of mass destruction, France, India and weapons of mass destruction, India, the United Kingdom and weapons of mass destruction, United Kingdom, Nuclear weapons and Israel, Israel, and North Korea and weapons of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
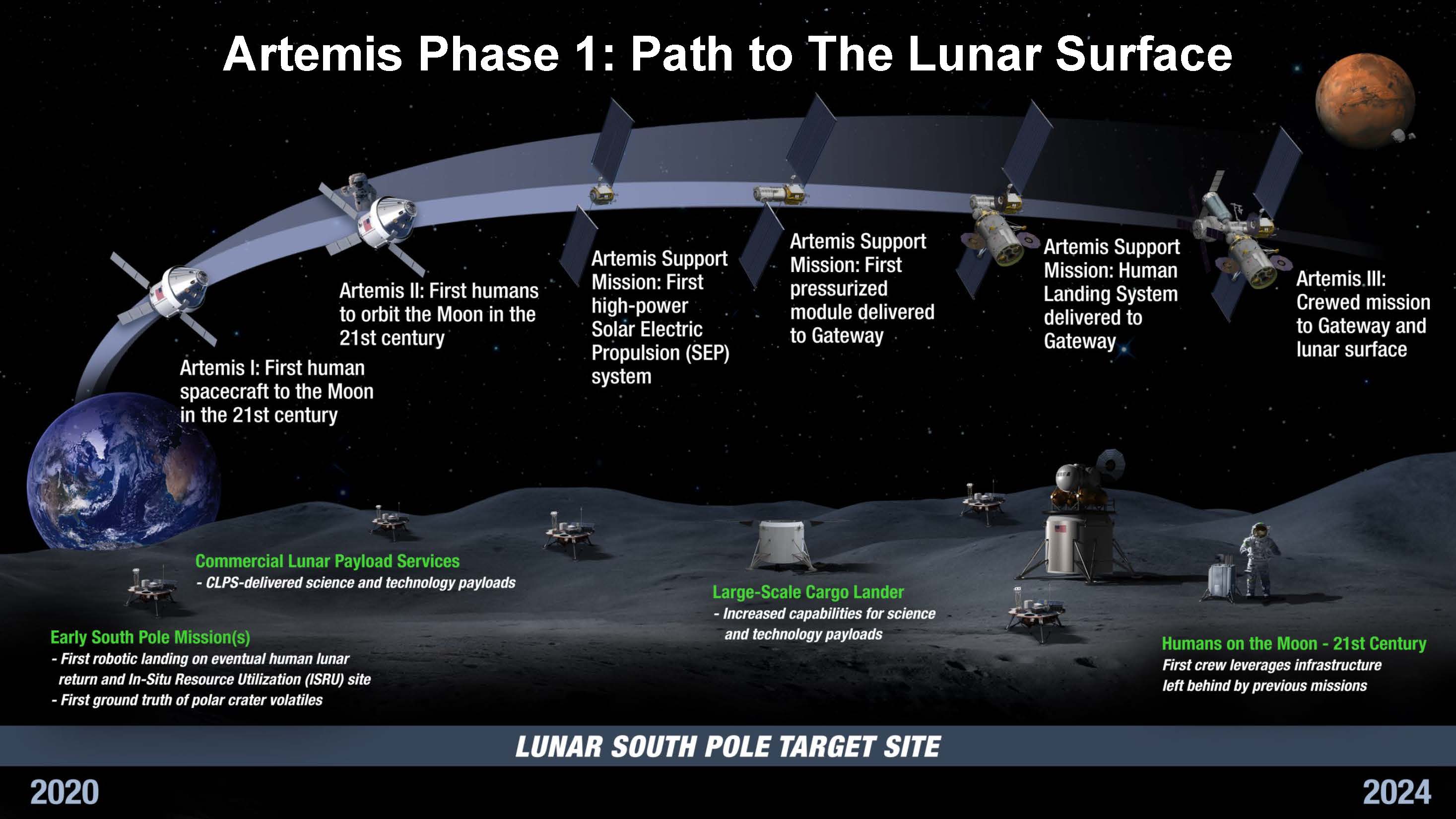
Artemis Program
The Artemis program is a Exploration of the Moon, Moon exploration program led by the United States' National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), formally established in 2017 via Space Policy Directive 1. The program's stated long-term goal is to establish a Moonbase, permanent base on the Moon to facilitate Human mission to Mars, human missions to Mars. It is intended to reestablish a human presence on the Moon for the first time since the Apollo 17 mission in 1972 and continue the direct exploration of Mars begun with data from the Mariner 9 probe in the same year. Two principal elements of the Artemis program are derived from the now-cancelled Constellation program: the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft (with the European Service Module, ESM instead of a US-built service module) and the Space Launch System's Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster#Five-segment booster, solid rocket boosters (originally developed for the Ares V). Other elements of the program, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), European Space Agency, ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan), and Canadian Space Agency, CSA (Canada). As the largest space station ever constructed, it primarily serves as a platform for conducting scientific experiments in microgravity and studying the space environment. The station is divided into two main sections: the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), developed by Roscosmos, and the US Orbital Segment (USOS), built by NASA, ESA, JAXA, and CSA. A striking feature of the ISS is the Integrated Truss Structure, which connect the station’s vast system of solar panels and Spacecraft thermal control, radiators to its pressurized modules. These modules support diverse functions, including scientific research, crew habitation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid Mining
Asteroid mining is the hypothetical extractivism, extraction of materials from asteroids and other minor planets, including near-Earth objects. Notable asteroid mining challenges include the high cost of spaceflight, unreliable identification of asteroids which are suitable for mining, and the challenges of extracting usable material in a space environment. Asteroid Sample-return mission, sample return research missions, such as ''Hayabusa'', ''Hayabusa2'', ''OSIRIS-REx'', and ''Tianwen-2'' illustrate the challenges of collecting ore from space using current technology. As of 2024, around 127 grams of asteroid material has been successfully brought to Earth from space. Asteroid research missions are complex endeavors and yield a tiny amount of material (less than 100 milligrams ''Hayabusa'', 5.4 grams ''Hayabusa2'', ~121.6 grams ''OSIRIS-REx'', Tianwen-2 (in progress)) relative to the size and expense of these projects ($300 million ''Hayabusa'', $800 million ''Hayabusa2'', $1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Resources
An artificially colored mosaic constructed from a series of 53 images taken through three spectral filters by ''Galileo's'' imaging system as the spacecraft flew over the northern regions of the Moon on 7 December 1992. The colors indicate different materials. A lunar anorthosite rock collected by the Apollo 16 crew from near the crater Descartes The Moon bears substantial natural resources which could be exploited in the future. Potential lunar resources may encompass processable materials such as volatiles and minerals, along with geologic structures such as lava tubes that, together, might enable lunar habitation. The use of resources on the Moon may provide a means of reducing the cost and risk of lunar exploration and beyond.M. Anand, I. A. Crawford, M. Balat-Pichelin, S. Abanades, W. van Westrenen, G. Péraudeau, R. Jaumann, W. Seboldt. "Moon and likely initial in situ resource utilization (ISRU) applications." ''Planetary and Space Science''; volume 74; issue 1; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Treaty System
The Antarctic Treaty and related agreements, collectively known as the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS), regulate international relations with respect to Antarctica, Earth's only continent without a native human population. It was the first arms control agreement established during the Cold War, designating the continent as a scientific preserve, establishing freedom of scientific investigation, and banning Military activity in the Antarctic, military activity; for the purposes of the treaty system, Antarctica is defined as all the land and ice shelf, ice shelves south of 60th parallel south, 60°S latitude. Since September 2004, the Antarctic Treaty Secretariat, which implements the treaty system, is headquartered in Buenos Aires, Argentina. The main treaty was opened for signature on 1 December 1959, and officially coming into force, entered into force on 23 June 1961. The original signatories were the 12 countries active in Antarctica during the International Geophysical Year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. Nuclear bombs have had yields between 10 tons (the W54) and 50 megatons for the Tsar Bomba (see TNT equivalent). Yields in the low kilotons can devastate cities. A thermonuclear weapon weighing as little as can release energy equal to more than 1.2 megatons of TNT (5.0 PJ). Apart from the blast, effects of nuclear weapons include firestorms, extreme heat and ionizing radiation, radioactive nuclear fallout, an electromagnetic pulse, and a radar blackout. The first nuclear weapons were developed by the Allied Manhattan Project during World War II. Their production continues to require a large scientific and industrial complex, pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Vehicle
A space vehicle is the combination of a spacecraft and its launch vehicle which carries it into space. The earliest space vehicles were expendable launch systems, using a single or multistage rocket to carry a relatively small spacecraft in proportion to the total vehicle size and mass. An early exception to this, the Space Shuttle, consisted of a reusable orbital vehicle carrying crew and payload, supported by an expendable external propellant tank and two reusable solid-fuel booster rockets. Reusable launch systems are currently being developed by private industry. Early spacecraft or space vehicles were sometimes known as " spaceships", a term which comes from science fiction to designate a hypothetical vehicle which travels beyond low Earth orbit and is 100% reusable, needing only to be refueled like an airplane. History In the 1865 Jules Verne novel ''From the Earth to the Moon'', successful attempts are made to launch three people in a projectile with the goal of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Force
A space force is a military branch of a nation's armed forces that conducts military operations in outer space and space warfare. The world's first space force was the Russian Space Forces, established in 1992 as an independent military service. However, it lost its independence twice, first being absorbed into the Strategic Rocket Forces from 1997–2001 and 2001–2011, then it merged with the Russian Air Force to form the Russian Aerospace Forces in 2015, where it now exists as a sub-branch. , there are two independent space forces: the United States Space Force and China's People's Liberation Army Aerospace Force. Countries with smaller or developing space forces may combine their Aerospace force (other), air and space forces under a single military branch, such as the Russian Aerospace Forces, Spanish Air and Space Force, French Air and Space Force, or Iranian Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps Aerospace Force, or put them in an independent defense agency, such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Object
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists within the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often used interchangeably. However, an astronomical body or celestial body is a single, tightly bound, contiguous entity, while an astronomical or celestial ''object'' is a complex, less cohesively bound structure, which may consist of multiple bodies or even other objects with substructures. Examples of astronomical objects include planetary systems, star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies, while asteroids, moons, planets, and stars are astronomical bodies. A comet may be identified as both a body and an object: It is a ''body'' when referring to the frozen nucleus of ice and dust, and an ''object'' when describing the entire comet with its diffuse coma and tail. History Astronomical objects such as stars, planets, nebulae, aster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weapon Of Mass Destruction
A weapon of mass destruction (WMD) is a biological, chemical, radiological, nuclear, or any other weapon that can kill or significantly harm many people or cause great damage to artificial structures (e.g., buildings), natural structures (e.g., mountains), or the biosphere. The scope and usage of the term has evolved and been disputed, often signifying more politically than technically. Originally coined in reference to aerial bombing with chemical explosives during World War II, it has later come to refer to large-scale weaponry of warfare-related technologies, such as biological, chemical, radiological, or nuclear warfare. Early usage The first use of the term "weapon of mass destruction" on record is by Cosmo Gordon Lang, Archbishop of Canterbury, in 1937 in reference to the bombing of Guernica, Spain: At the time, nuclear weapons had not been developed fully. Japan conducted research on biological weapons, and chemical weapons had seen wide battlefield use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |