|
Ostomy
In anatomy, a stoma (: stomata or stomas) is any opening in the body. For example, a mouth, a nose, and an anus are natural stomata. Any hollow organ can be manipulated into an artificial stoma as necessary. This includes the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, ileum, colon, pleural cavity, ureters, urinary bladder, and renal pelvis. Such a stoma may be permanent or temporary. Surgical procedures that involve the creation of an artificial stoma have names that typically end with the suffix "-ostomy", and the same names are also often used to refer to the stoma thus created. For example, the word " colostomy" often refers either to an artificial anus or the procedure that creates one. Accordingly, it is not unusual for a stoma to be called an ostomy (plural ostomies), as is the norm in wound, ostomy, and continence nursing. Gastrointestinal stomata Stomata are created in particular in surgical procedures involving the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) or gastrointestinal system (GIS). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ileostomy
Ileostomy is a stoma (medicine), stoma (surgical opening) constructed by bringing the end or loop of small intestine (the ileum) out onto the surface of the skin, or the surgical procedure which creates this opening. Intestinal waste passes out of the ileostomy and is collected in an external Ostomy pouching system, ostomy system which is placed next to the opening. Ileostomies are usually sited above the groin on the right hand side of the abdomen. Uses Ileostomies are necessary where injury or a surgical response to disease has meant the large intestine cannot safely process waste, typically because the colon (anatomy), colon and rectum have been partially or wholly removed. Diseases of the large intestine which may require surgical removal include Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, familial adenomatous polyposis, and total colonic Hirschsprung's disease. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
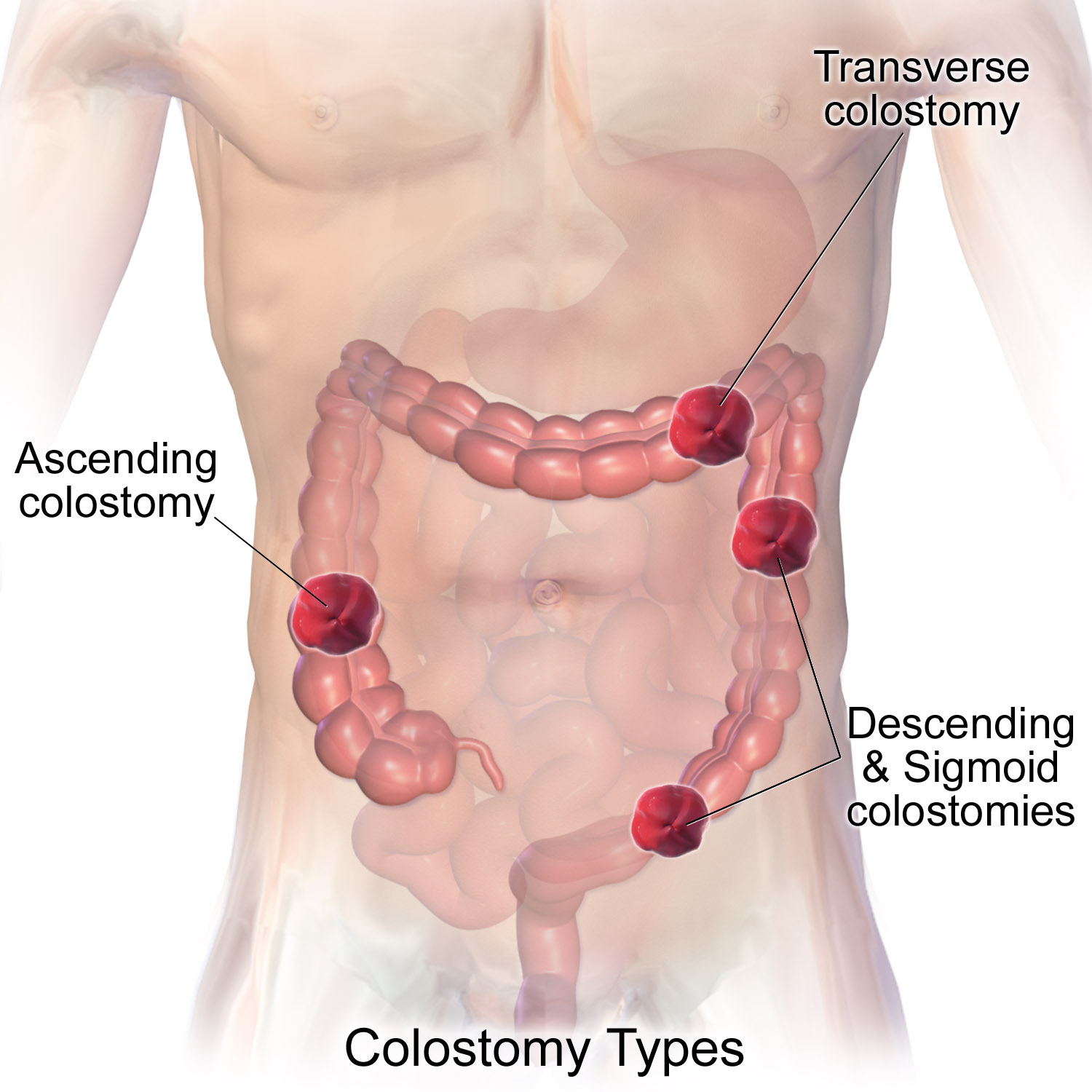
Colostomy And Parastomal Hernia - CT
A colostomy is an opening (stoma) in the large intestine (colon), or the surgical procedure that creates one. The opening is formed by drawing the healthy end of the colon through an incision in the anterior abdominal wall and suturing it into place. This opening, often in conjunction with an attached ostomy system, provides an alternative channel for feces to leave the body. Thus if the natural anus is unavailable for that function (for example, in cases where it has been removed as part of treatment for colorectal cancer or ulcerative colitis), an artificial anus takes over. It may be reversible or irreversible, depending on the circumstances. Uses There are many reasons for this procedure. Some common reasons are: * A part of the colon has been removed, e.g. due to colon cancer requiring a total mesorectal excision, diverticulitis, injury, etc., so that it is no longer possible for feces to exit via the anus. * A part of the colon has been operated upon and needs to be 'r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colostomy
A colostomy is an opening (stoma) in the large intestine (colon), or the surgical procedure that creates one. The opening is formed by drawing the healthy end of the colon through an incision in the anterior abdominal wall and suturing it into place. This opening, often in conjunction with an attached ostomy system, provides an alternative channel for feces to leave the body. Thus if the natural anus is unavailable for that function (for example, in cases where it has been removed as part of treatment for colorectal cancer or ulcerative colitis), an artificial anus takes over. It may be reversible or irreversible, depending on the circumstances. Uses There are many reasons for this procedure. Some common reasons are: * A part of the colon has been removed, e.g. due to colon cancer requiring a total mesorectal excision, diverticulitis, injury, etc., so that it is no longer possible for feces to exit via the anus. * A part of the colon has been operated upon and needs t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrostomy
A gastrostomy is the creation of an artificial external opening into the stomach for nutritional support or gastric decompression. Typically this would include an incision in the patient's epigastrium as part of a formal operation. When originally devised over a century ago the procedure was completed through open surgery using the Stamm technique. It can be performed through surgical approach, percutaneous approach by interventional radiology, percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) or percutaneous ultrasound gastrostomy (PUG). A gastrostomy may be required due to illness, trauma or disability impacting upon the ability to eat or swallow safely, or conditions causing increased nutritional requirement and once formed (or for some techniques, during formation), a gastrostomy tube is inserted. Techniques The Stamm gastrostomy is an open technique, requiring an upper midline laparotomy and gastrotomy, with the catheter brought out in the left hypochondrium. It was first devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) is an endoscopic medical procedure in which a tube (PEG tube) is passed into a patient's stomach through the abdominal wall, most commonly to provide a means of feeding when oral intake is not adequate (for example, because of dysphagia or sedation). This provides enteral nutrition (making use of the natural digestion process of the gastrointestinal tract) despite bypassing the mouth; enteral nutrition is generally preferable to parenteral nutrition (which is only used when the GI tract must be avoided). The PEG procedure is an alternative to open surgical gastrostomy insertion, and does not require a general anesthetic; mild sedation is typically used. PEG tubes may also be extended into the small intestine by passing a jejunal extension tube (PEG-J tube) through the PEG tube and into the jejunum via the pylorus. PEG administration of enteral feeds is the most commonly used method of nutritional support for patients in the commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholecystostomy
Cholecystostomy or (cholecystotomy) is a medical procedure used to drain the gallbladder through either a percutaneous or endoscopic approach. The procedure involves creating a stoma in the gallbladder, which can facilitate placement of a tube or stent for drainage, first performed by American surgeon, Dr. John Stough Bobbs, in 1867. It is sometimes used in cases of cholecystitis or other gallbladder disease where the person is ill, and there is a need to delay or defer cholecystectomy. The first endoscopic cholecystostomy was performed by Drs. Todd Baron and Mark Topazian in 2007 using ultrasound guidance to puncture the stomach wall and place a plastic biliary catheter for gallbladder drainage. Indications Cholecystostomy finds its application when the patient has cholecystitis and is not a good candidate for surgery. Some indications include: * Critically ill patients that are clinically unstable to tolerate surgical cholecystectomy * Patients unable to tolerate anesthesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malone Antegrade Continence Enema
A Malone antegrade continence enema (MACE), also known as an appendicostomy or Malone procedure, is a surgical procedure used to create a continent pathway proximal to the anus that facilitates fecal evacuation using enemas. Description The operation involves connecting the appendix to the abdominal wall and fashioning a valve mechanism that allows catheterization of the appendix, but avoids leakage of stool through it. By using the patient’s own appendix for the procedure, doctors can avoid using artificial devices which can be seen and can cause the patient irritation. If the appendix was previously removed or is unusable, a neoappendix can be created with a cecal flap. Indications It is done to treat fecal incontinence unresponsive to treatment with medications. It is frequently done with a procedure ( Mitrofanoff procedure) to treat urinary incontinence as the two often co-exist, such as in spina bifida. Cecostomy tube alternative A percutaneous cecostomy tube (C-tube) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jejunostomy
Jejunostomy is the surgical creation of an opening (stoma) through the skin at the front of the abdomen and the wall of the jejunum (part of the small intestine). It can be performed either endoscopically, or with open surgery. A jejunostomy may be formed following bowel resection in cases where there is a need to bypass the distal small bowel and/or colon due to a bowel leak or perforation. Depending on the length of jejunum resected or bypassed the patient may have resultant short bowel syndrome and require parenteral nutrition. A jejunostomy is different from a jejunal feeding tube. A jejunal feeding tube is an alternative to a gastrostomy feeding tube and is commonly used when gastric enteral feeding is contraindicated or carries significant risks. The advantage over a gastrostomy is its low risk of aspiration due to its distal placement. Disadvantages include small bowel obstruction, ischemia Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |