|
Osadnictwo
Osadniks (, "settler/settlers, colonist/colonists") were veterans of the Polish Army and civilians who were given or sold state land in the ''Kresy'' (current Western Belarus and Western Ukraine) territory ceded to Poland by Polish-Soviet Riga Peace Treaty of 1921 (and occupied by the Soviet Union in 1939 and ceded to it after World War II). The Polish word was also a loanword that was used in the Soviet Union. Settlement process Shortly before the Battle of Warsaw on August 7, 1920, Polish Prime Minister Wincenty Witos announced that after the war, volunteers and soldiers who served on the front would have priority in purchase of state-owned land, while the soldiers to receive medals for bravery would receive land free of charge. The announcement was partly to repair the Polish morale, shaken after the retreat from the east. On December 17 the Sejm (Polish parliament) passed the ''Act on Nationalization of North-Eastern Powiats of the Republic'' and ''Act on Granting the Sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sejm Of The Republic Of Poland
The Sejm (), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland (), is the lower house of the bicameralism, bicameral parliament of Poland. The Sejm has been the highest governing body of the Third Polish Republic since the Polish People's Republic, transition of government in 1989. Along with the upper house of parliament, the Senate of Poland, Senate, it forms the national legislature in Poland known as Parliament of Poland#National Assembly, National Assembly (). The Sejm comprises 460 Member of parliament, deputies (singular or ) elected every four years by Universal suffrage, universal ballot. The Sejm is presided over by a Speaker of parliament, speaker, the "Marshal of the Sejm" (). In the Kingdom of Poland (1385–1569), Kingdom of Poland, the term ''Sejm'' referred to an entire two-Chambers of parliament, chamber parliament, comprising the Chamber of Deputies (), the Senate and the King. It was thus a three-estate parliament. The 1573 Henrician Articles strengthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hectare
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), that is, square metres (), and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is about and one hectare contains about . In 1795, when the metric system was introduced, the ''are'' was defined as 100 square metres, or one square decametre, and the hectare (" hecto-" + "are") was thus 100 ''ares'' or km2 ( square metres). When the metric system was further rationalised in 1960, resulting in the International System of Units (), the ''are'' was not included as a recognised unit. The hectare, however, remains as a non-SI unit accepted for use with the SI and whose use is "expected to continue indefinitely". Though the dekare/decare daa () and are (100 m2) are not officially "accepted for use", they are still used in some contexts. Description The hectare (), although not a unit of SI, is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dvoryanstvo
The Russian nobility or ''dvoryanstvo'' () arose in the Middle Ages. In 1914, it consisted of approximately 1,900,000 members, out of a total population of 138,200,000. Up until the February Revolution of 1917, the Russian noble estates staffed most of the Russian government and possessed a self-governing body, the Assembly of the Nobility. The Russian word for nobility, ''dvoryanstvo'' derives from Slavonic ''dvor'' (двор), meaning the court of a prince or duke (''knyaz''), and later, of the tsar or emperor. Here, ''dvor'' originally referred to servants at the estate of an aristocrat. In the late 16th and early 17th centuries, the system of hierarchy was a system of seniority known as ''mestnichestvo''. The word ''dvoryane'' described the highest rank of gentry, who performed duties at the royal court, lived in it (''Moskovskie zhiltsy'', "Moscow dwellers"), or were candidates to it, as for many boyar scions (''dvorovye deti boyarskie'', ''vybornye deti boyarskie''). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of Monasticism, monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in Cenobitic monasticism, communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which may be a chapel, Church (building), church, or temple, and may also serve as an Oratory (worship), oratory, or in the case of Cenobium, communities anything from a single building housing only one senior and two or three junior monks or nuns, to vast complexes and estates housing tens or hundreds. A monastery complex typically comprises a number of buildings which include a church, dormitory, cloister, refectory, library, Wiktionary:balneary, balneary and Hospital, infirmary and outlying Monastic grange, granges. Depending on the location, the monastic order and the occupation of its inhabitants, the complex may also include a wide range of buildings that facilitate self-sufficiency and service to the commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsar
Tsar (; also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar''; ; ; sr-Cyrl-Latn, цар, car) is a title historically used by Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word '' caesar'', which was intended to mean ''emperor'' in the European medieval sense of the term—a ruler with the same rank as a Roman emperor, holding it by the approval of another emperor or a supreme ecclesiastical official—but was usually considered by Western Europeans to be equivalent to "king". Tsar and its variants were the official titles in the First Bulgarian Empire (681–1018), Second Bulgarian Empire (1185–1396), the Kingdom of Bulgaria (1908–1946), the Serbian Empire (1346–1371), and the Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721). The first ruler to adopt the title ''tsar'' was Simeon I of Bulgaria. Simeon II, the last tsar of Bulgaria, is the last person to have held this title. Meaning in Slavic languages The title tsar is derived from the Latin title for the Roman emperors, ''c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Russia
The Russian Government () or fully titled the Government of the Russian Federation () is the highest federal executive governmental body of the Russian Federation. It is accountable to the president of the Russian Federation and controlled by the State Duma. The status and procedure of its activities are determined by chapter 6 of the Constitution of the Russian Federation and the provisions of the federal constitutional law "On the Government of the Russian Federation". The Government's terms of reference include the development and enforcement of the federal budget and the implementation of socially oriented government policies in various cultural areas of Russian society. Although the Government of the Russian Federation does not adopt laws, its responsibilities include issuing federal by-laws (resolutions) based on federal laws passed by the Federal Assembly. According to the 1991 amendment to the 1978 constitution, the president of Russia was the head of the executi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
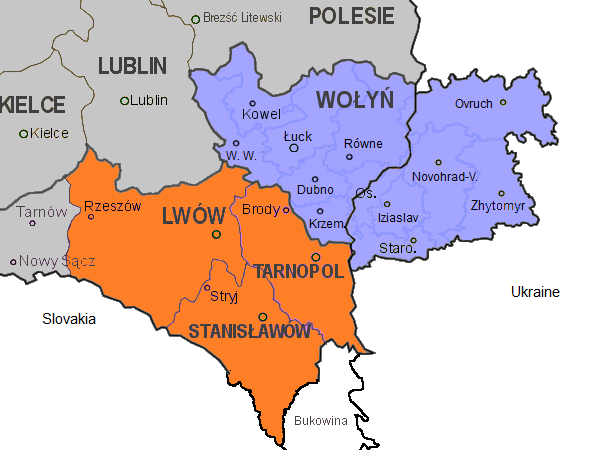
Wołyń
Volhynia or Volynia ( ; see below) is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between southeastern Poland, southwestern Belarus, and northwestern Ukraine. The borders of the region are not clearly defined, but in Ukraine it is roughly equivalent to Volyn and Rivne Oblasts; the territory that still carries the name is Volyn Oblast. Volhynia has changed hands numerous times throughout history and been divided among competing powers. For centuries it was part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. After the Russian annexation during the Partitions of Poland, all of Volhynia was made part of the Pale of Settlement on the southwestern border of the Russian Empire. Important cities include Rivne, Lutsk, Zviahel, and Volodymyr. Names and etymology *, ; * ; *, ; * or ; *; * ; *; *; * or (both ); Volhynian German: , , or (all ); *, or . The alternative name for the region is Lodomeria after the city of Volodymyr, which was once a political capital of the medieval Vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Academy Of Sciences
The Polish Academy of Sciences (, PAN) is a Polish state-sponsored institution of higher learning. Headquartered in Warsaw, it is responsible for spearheading the development of science across the country by a society of distinguished scholars and a network of research institutes. It was established in 1951, during the early period of the Polish People's Republic following World War II. History The Polish Academy of Sciences is a Polish state-sponsored institution of higher learning, headquartered in Warsaw, that was established by the merger of earlier science societies, including the Polish Academy of Learning (''Polska Akademia Umiejętności'', abbreviated ''PAU''), with its seat in Kraków, and the Warsaw Society of Friends of Learning (Science), which had been founded in the late 18th century. The Polish Academy of Sciences functions as a learned society acting through an elected assembly of leading scholars and research institutions. The Academy has also, operating throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Białystok Voivodeship (1919–1939)
Białystok Voivodeship () was an administrative unit of Second Polish Republic, interwar Poland (1918–1939). The province's capital and its biggest city was Białystok with a population of over 91,000 people. The voivodeship reached an area of 32,518 km2 and became the second largest voivodeship of the Second Polish Republic, after Polesie. Following the Invasion of Poland, Nazi German and the Soviet invasion of Poland, the Voivodeship was occupied by both invading armies and divided according to German–Soviet Frontier Treaty, Nazi-Soviet boundary treaty. History The voivodeship was established in 1919 on the territory of Bialystok-Grodno District a German-occupied territory during and after the First World War from 1917 to 1921, and which prior to that was part of the Russian Empire, as Grodno Governorate. On February 4, 1921 the voivodeship was expanded by three more counties: Grodno County, Grodno, Wołkowysk County, Wołkowysk and Białowieża County, Białowieża. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wołożyn
Valozhyn or Volozhin (, ; ; ; ; ) is a town in Minsk Region, Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Valozhyn District. It is located northwest of the capital Minsk, on the Valozhynka River in the Neman River basin, and the beginning of the Naliboki forest. In 1995, its population was approximately 11,500. As of 2025, it has a population of 9,923. Before World War II, about half the town's population were Jewish but they were murdered during the Holocaust. History Overview The town was built on the main road leading from Vilnius to Minsk. It is divided into two sections: the "lower neighborhood" along the river and the "upper neighborhood" toward the hills. Half of the town square is framed by the remains of 12th century buildings, including a bell tower, a palace, and a monastery. Most of the other remaining impressive buildings in the town are from the 19th century. Valozhyn was established as a "privately owned city" by Count Tyszkiewicz in the 14th century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |