|
Orthomyxoviridae
''Orthomyxoviridae'' () is a family of negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus, negative-sense RNA viruses. It includes nine genus, genera: ''Influenza A virus, Alphainfluenzavirus'', ''Influenza B virus, Betainfluenzavirus'', ''Influenza C virus, Gammainfluenzavirus'', ''Influenza D virus, Deltainfluenzavirus'', ''Isavirus'', ''Mykissvirus'', ''Quaranjavirus'', ''Sardinovirus'', and ''Thogotovirus''. The first four genera contain viruses that cause influenza in birds (see also avian influenza) and mammals, including humans. Isaviruses infect salmon; the thogotoviruses are arboviruses, infecting vertebrates and invertebrates (such as ticks and mosquitoes). The Quaranjaviruses are also arboviruses, infecting vertebrates (birds) and invertebrates (arthropods). The four genera of Influenza virus that infect vertebrates, which are identified by antigenic differences in their nucleoprotein and matrix protein, are as follows: * ''Influenza A virus, Alphainfluenzavirus'' infects huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thogotovirus
''Thogotovirus'' is a genus of viral envelope, enveloped RNA viruses in the virus family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. Their single-stranded, sense (molecular biology), negative-sense RNA genome has six or seven segments. Thogotoviruses are distinguished from most other orthomyxoviruses by being arboviruses – viruses that are transmitted by arthropods, in this case usually ticks. Thogotoviruses can replicate in both tick cells and vertebrate cells; one subtype has also been isolated from mosquitoes. A consequence of being transmitted by blood-sucking vector (epidemiology), vectors is that the virus must spread systemically in the vertebrate host – unlike influenza viruses, which are transmitted by respiratory droplets and are usually confined to the respiratory system. The genus contains eight species. A wide range of mammals are infected by members of the genus; some types also infect birds. THOV causes disease in livestock. THOV, DHOV and Bourbon virus can infect humans, and have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaranjavirus
''Quaranjavirus'' is a genus of enveloped RNA viruses, one of seven genera in the virus family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. The genome is single-stranded, negative-sense segmented RNA, generally with six segments. The genus contains six species. Quaranjaviruses predominantly infect arthropods and birds; ''Quaranfil quaranjavirus'' is the only member of the genus to have been shown to infect humans. The Quaranfil and Johnston Atoll viruses are transmitted between vertebrates by ticks, resembling members of ''Thogotovirus'', another genus of ''Orthomyxoviridae''. History Quaranfil virus was first isolated from humans in Egypt in 1953. Johnston Atoll virus and Lake Chad virus were first isolated from birds in 1964 and 1969, respectively. In 1989, based on the appearance of the virus particles under the electron microscope, H.G. Zeller and colleagues suggested that they should be classified as arenaviruses, but this was not accepted by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza B Virus
''Influenza B virus'' is the Monotypic taxon, only species in the genus ''Betainfluenzavirus'' in the virus family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. Influenza B virus is a Negative-strand RNA virus, negative-sense single-strand RNA virus known only to infect certain mammal species, including humans, ferrets, pigs, and Pinniped, seals. This limited host range is apparently responsible for the lack of influenza pandemics associated with influenza B virus, in contrast with those caused by the morphologically similar influenza A virus, as both mutate by both antigenic drift and reassortment. Nevertheless, it is accepted that influenza B virus could cause significant morbidity and mortality worldwide, and significantly impacts adolescents and schoolchildren. Until 2020, two distinct lineages of influenza B virus co-circulated in humans. Known as B/Yamagata and B/Victoria, these lineages are distinguished by differences in the antigenic structure of the surface glycoprotein hemagglutinin_(influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza C Virus
Influenza C virus is the only species in the genus ''Gammainfluenzavirus'', in the virus family '' Orthomyxoviridae'', which like other influenza viruses, causes influenza. Influenza C viruses are known to infect humans and pigs. Flu due to the Type C species is rare compared with Types B or A, but can be severe and can cause local epidemics. Type C has 7 RNA segments and encodes 9 proteins, while Types A and B have 8 RNA segments and encode at least 10 proteins. Influenza C virus Influenza viruses are members of the family '' Orthomyxoviridae''. Influenza viruses A, B, C, and D represent the four antigenic types of influenza viruses. Of the four antigenic types, influenza A virus is the most severe, influenza B virus is less severe but can still cause outbreaks, and influenza C virus is usually only associated with minor symptoms. Influenza D virus is 50% similar in amino acid composition to influenza C virus, similar to the level of divergence between types A and B, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flu Pandemic
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms begin one to four (typically two) days after exposure to the virus and last for about two to eight days. Diarrhea and vomiting can occur, particularly in children. Influenza may progress to pneumonia from the virus or a subsequent bacterial infection. Other complications include acute respiratory distress syndrome, meningitis, encephalitis, and worsening of pre-existing health problems such as asthma and cardiovascular disease. There are four types of influenza virus: types A, B, C, and D. Aquatic birds are the primary source of influenza A virus (IAV), which is also widespread in various mammals, including humans and pigs. Influenza B virus (IBV) and influenza C virus (ICV) primarily infect humans, and influenza D virus (ID ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza D Virus
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, Rhinorrhea, runny nose, sore throat, Myalgia, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms begin one to four (typically two) days after exposure to the virus and last for about two to eight days. Diarrhea and vomiting can occur, particularly in children. Influenza may progress to pneumonia from the virus or a subsequent bacterial infection. Other complications include acute respiratory distress syndrome, meningitis, encephalitis, and worsening of pre-existing health problems such as asthma and cardiovascular disease. There are four types of influenza virus: types A, B, C, and D. Aquatic birds are the primary source of influenza A virus (IAV), which is also widespread in various mammals, including humans and pigs. Influenza B virus (IBV) and influenza C virus (ICV) primarily infect humans, and influenza D vir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
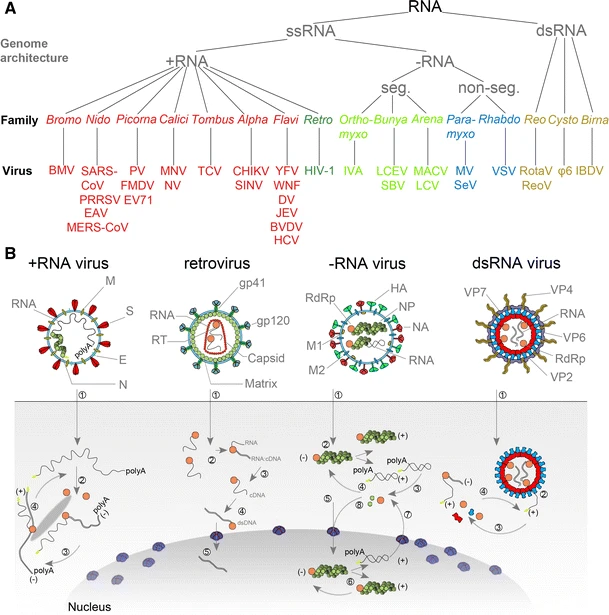
RNA Virus
An RNA virus is a virus characterized by a ribonucleic acid (RNA) based genome. The genome can be single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) or double-stranded (Double-stranded RNA, dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include influenza, SARS, MERS, COVID-19, Dengue virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles. All known RNA viruses, that is viruses that use a homologous RNA-dependent polymerase for replication, are categorized by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) into the realm ''Riboviria''. This includes RNA viruses belonging to ''Group III'', ''Group IV'' or ''Group V'' of the Virus classification#Baltimore classification, Baltimore classification system as well as ''Group VI. Group VI'' viruses are retroviruses, viruses with RNA genetic material that use DNA intermediates in their Viral life cycle, life cycle including HIV-1 and HIV-2 which cause AIDS. The majority of such RNA viruses fall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isavirus
Infectious salmon anemia (ISA) is a viral disease of Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') caused by Infectious salmon anemia virus. It affects fish farms in Canada, Norway, Scotland and Chile, causing severe losses to infected farms. ISA has been a World Organisation for Animal Health notifiable disease since 1990. In the EU, it is classified as a non-exotic disease, and is monitored by the European Community Reference Laboratory for Fish Diseases. Virology ISA is caused by the infectious salmon anemia virus (ISAV). ISAV, a segmented RNA virus that is the only species in the genus ''Isavirus'', which is in the family '' Orthomyxoviridae'', and therefore related to the influenza viruses. The genome encodes at least 10 proteins. There are several distinct strains of the virus. The most common are a European strain and a North American strain. Pathology ISA virus causes severe anemia in infected fish. Unlike the mature red blood cells of mammals, the mature red blood cells of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
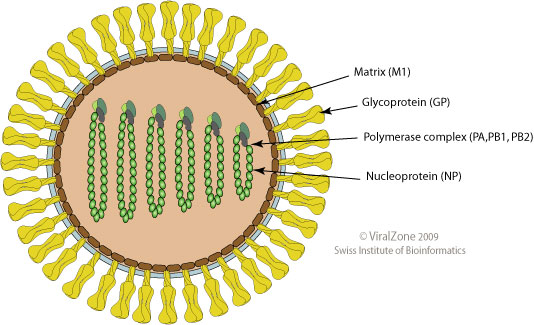
Matrix Protein
Viral matrix proteins are structural proteins linking the viral envelope with the virus core. They play a crucial role in virus assembly, and interact with the RNP complex as well as with the viral membrane. They are found in many enveloped viruses including paramyxoviruses, orthomyxoviruses, herpesviruses, retroviruses, filoviruses and other groups. An example is the M1 protein of the influenza virus, showing affinity to the glycoproteins inserted in the host cell membrane on one side and affinity for the RNP complex molecules on the other side, which allows formation at the membrane of a complex made of the viral ribonucleoprotein at the inner side indirectly connected to the viral glycoproteins protruding from the membrane. This assembly complex will now bud In botany, a bud is an undeveloped or Plant embryogenesis, embryonic Shoot (botany), shoot and normally occurs in the axil of a leaf or at the tip of a Plant stem, stem. Once formed, a bud may remain for some ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza A Virus
''Influenza A virus'' (''Alphainfluenzavirus influenzae'') or IAV is the only species of the genus ''Alphainfluenzavirus'' of the virus family '' Orthomyxoviridae''. It is a pathogen with strains that infect birds and some mammals, as well as causing seasonal flu in humans. Mammals in which different strains of IAV circulate with sustained transmission are bats, pigs, horses and dogs; other mammals can occasionally become infected. IAV is an enveloped negative-sense RNA virus, with a segmented genome. Through a combination of mutation and genetic reassortment the virus can evolve to acquire new characteristics, enabling it to evade host immunity and occasionally to jump from one species of host to another. Subtypes of IAV are defined by the combination of the antigenic H and N proteins in the viral envelope; for example, "H1N1" designates an IAV subtype that has a type-1 hemagglutinin (H) protein and a type-1 neuraminidase (N) protein. Almost all possible combinations of H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tick
Ticks are parasitic arachnids of the order Ixodida. They are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, and species, but can become larger when engorged. Ticks are external parasites, living by feeding on the blood of mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles and amphibians. The timing of the origin of ticks is uncertain, though the oldest known tick fossils are around 100 million years old, and come from the Cretaceous period. Ticks are widely distributed around the world, especially in warm, humid climates. Ticks belong to two major families: the Ixodidae, or hard ticks, and the Argasidae, or soft ticks. '' Nuttalliella'', a genus of tick from southern Africa, is the only member of the family Nuttalliellidae, and represents the most primitive living lineage of ticks. Adults have ovoid/pear-shaped bodies (idiosomas) which become engorged with blood when they feed, and eight legs. Their cephalotho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |