|
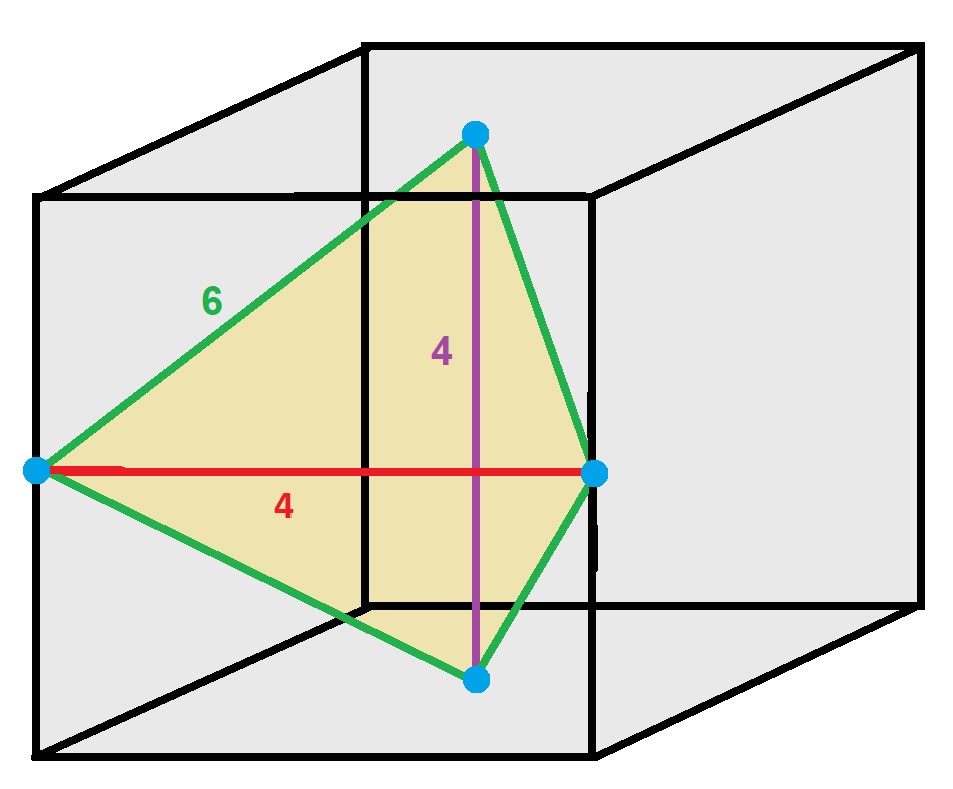
Orthocentric Tetrahedron
In geometry, an orthocentric tetrahedron is a tetrahedron where all three pairs of opposite edges are perpendicular. It is also known as an orthogonal tetrahedron since orthogonal means perpendicular. It was first studied by Simon Lhuilier in 1782, and got the name orthocentric tetrahedron by G. de Longchamps in 1890.. In an orthocentric tetrahedron the four altitudes are concurrent. This common point is called the tetrahedron orthocenter (a generalization of the orthocenter of a triangle). It has the property that it is the symmetric point of the center of the circumscribed sphere with respect to the centroid. Hence the orthocenter coincides with the Monge point of the tetrahedron. Characterizations All tetrahedra can be inscribed in a parallelepiped. A tetrahedron is orthocentric if and only if its circumscribed parallelepiped is a rhombohedron. Indeed, in any tetrahedron, a pair of opposite edges is perpendicular if and only if the corresponding faces of the circumscrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumscribed Sphere
In geometry, a circumscribed sphere of a polyhedron is a sphere that contains the polyhedron and touches each of the polyhedron's Vertex (geometry), vertices. The word circumsphere is sometimes used to mean the same thing, by analogy with the term ''circumcircle''. As in the case of two-dimensional circumscribed circles (circumcircles), the radius of a sphere circumscribed around a polyhedron is called the circumradius of , and the center point of this sphere is called the circumcenter of . Existence and optimality When it exists, a circumscribed sphere need not be the Smallest-circle problem, smallest sphere containing the polyhedron; for instance, the tetrahedron formed by a vertex of a cube and its three neighbors has the same circumsphere as the cube itself, but can be contained within a smaller sphere having the three neighboring vertices on its equator. However, the smallest sphere containing a given polyhedron is always the circumsphere of the convex hull of a subset of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disphenoid
In geometry, a disphenoid () is a tetrahedron whose four faces are congruent acute-angled triangles. It can also be described as a tetrahedron in which every two edges that are opposite each other have equal lengths. Other names for the same shape are isotetrahedron,. sphenoid,. bisphenoid, isosceles tetrahedron,. equifacial tetrahedron, almost regular tetrahedron, and tetramonohedron. All the solid angles and vertex figures of a disphenoid are the same, and the sum of the face angles at each vertex is equal to two right angles. However, a disphenoid is not a regular polyhedron, because, in general, its faces are not regular polygons, and its edges have three different lengths. Special cases and generalizations If the faces of a disphenoid are equilateral triangles, it is a regular tetrahedron with Td tetrahedral symmetry, although this is not normally called a disphenoid. When the faces of a disphenoid are isosceles triangles, it is called a tetragonal disphenoid. In this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volume
Volume is a measure of regions in three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). The definition of length and height (cubed) is interrelated with volume. The volume of a container is generally understood to be the capacity of the container; i.e., the amount of fluid (gas or liquid) that the container could hold, rather than the amount of space the container itself displaces. By metonymy, the term "volume" sometimes is used to refer to the corresponding region (e.g., bounding volume). In ancient times, volume was measured using similar-shaped natural containers. Later on, standardized containers were used. Some simple three-dimensional shapes can have their volume easily calculated using arithmetic formulas. Volumes of more complicated shapes can be calculated with integral calculus if a formula exists for the shape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazewinkel, Michiel
Michiel Hazewinkel (born 22 June 1943) is a Dutch mathematician, and Emeritus Professor of Mathematics at the Centre for Mathematics and Computer Science and the University of Amsterdam, particularly known for his 1978 book ''Formal groups and applications'' and as editor of the ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics''. Biography Born in Amsterdam to Jan Hazewinkel and Geertrude Hendrika Werner, Hazewinkel studied at the University of Amsterdam. He received his BA in mathematics and physics in 1963, his MA in mathematics with a minor in philosophy in 1965 and his PhD in 1969 under supervision of Frans Oort and Albert Menalda for the thesis "Maximal Abelian Extensions of Local Fields".Michiel Hazewinkel, Curriculum vitae at michhaz.home.xs4all.nl. Accessed September 10, 2013 After graduation Hazewinkel started h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necessary And Sufficient Condition
In logic and mathematics, necessity and sufficiency are terms used to describe a conditional or implicational relationship between two statements. For example, in the conditional statement: "If then ", is necessary for , because the truth of is guaranteed by the truth of . (Equivalently, it is impossible to have without , or the falsity of ensures the falsity of .) Similarly, is sufficient for , because being true always implies that is true, but not being true does not always imply that is not true. In general, a necessary condition is one (possibly one of several conditions) that must be present in order for another condition to occur, while a sufficient condition is one that produces the said condition. The assertion that a statement is a "necessary ''and'' sufficient" condition of another means that the former statement is true if and only if the latter is true. That is, the two statements must be either simultaneously true, or simultaneously false. In ordinary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhombohedron
In geometry, a rhombohedron (also called a rhombic hexahedron or, inaccurately, a rhomboid) is a special case of a parallelepiped in which all six faces are congruent rhombi. It can be used to define the rhombohedral lattice system, a honeycomb with rhombohedral cells. A rhombohedron has two opposite apices at which all face angles are equal; a prolate rhombohedron has this common angle acute, and an oblate rhombohedron has an obtuse angle at these vertices. A cube is a special case of a rhombohedron with all sides square. Special cases The common angle at the two apices is here given as \theta. There are two general forms of the rhombohedron: oblate (flattened) and prolate (stretched). In the oblate case \theta > 90^\circ and in the prolate case \theta < 90^\circ. For the figure is a cube. Certain proportions of the rhombs give rise to some well-known special cases. These typically occur in both prolate and oblate forms. ...
|
If And Only If
In logic and related fields such as mathematics and philosophy, "if and only if" (often shortened as "iff") is paraphrased by the biconditional, a logical connective between statements. The biconditional is true in two cases, where either both statements are true or both are false. The connective is biconditional (a statement of material equivalence), and can be likened to the standard material conditional ("only if", equal to "if ... then") combined with its reverse ("if"); hence the name. The result is that the truth of either one of the connected statements requires the truth of the other (i.e. either both statements are true, or both are false), though it is controversial whether the connective thus defined is properly rendered by the English "if and only if"—with its pre-existing meaning. For example, ''P if and only if Q'' means that ''P'' is true whenever ''Q'' is true, and the only case in which ''P'' is true is if ''Q'' is also true, whereas in the case of ''P if Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallelepiped
In geometry, a parallelepiped is a three-dimensional figure formed by six parallelograms (the term ''rhomboid'' is also sometimes used with this meaning). By analogy, it relates to a parallelogram just as a cube relates to a square. Three equivalent definitions of ''parallelepiped'' are *a hexahedron with three pairs of parallel faces, *a polyhedron with six faces (hexahedron), each of which is a parallelogram, and *a prism (geometry), prism of which the base is a parallelogram. The rectangular cuboid (six rectangular faces), cube (six square faces), and the rhombohedron (six rhombus faces) are all special cases of parallelepiped. "Parallelepiped" is now usually pronounced or ; traditionally it was because of its etymology in Ancient Greek, Greek παραλληλεπίπεδον ''parallelepipedon'' (with short -i-), a body "having parallel planes". Parallelepipeds are a subclass of the prismatoids. Properties Any of the three pairs of parallel faces can be viewed as the bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron
In geometry, a tetrahedron (: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular Face (geometry), faces, six straight Edge (geometry), edges, and four vertex (geometry), vertices. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polytope, convex polyhedra. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean geometry, Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid (geometry), pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron, the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such net (polyhedron), nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centroid
In mathematics and physics, the centroid, also known as geometric center or center of figure, of a plane figure or solid figure is the arithmetic mean position of all the points in the figure. The same definition extends to any object in n-dimensional Euclidean space. In geometry, one often assumes uniform mass density, in which case the '' barycenter'' or ''center of mass'' coincides with the centroid. Informally, it can be understood as the point at which a cutout of the shape (with uniformly distributed mass) could be perfectly balanced on the tip of a pin. In physics, if variations in gravity are considered, then a '' center of gravity'' can be defined as the weighted mean of all points weighted by their specific weight. In geography, the centroid of a radial projection of a region of the Earth's surface to sea level is the region's geographical center. History The term "centroid" was coined in 1814. It is used as a substitute for the older terms "center of grav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthocenter
The orthocenter of a triangle, usually denoted by , is the point (geometry), point where the three (possibly extended) altitude (triangle), altitudes intersect. The orthocenter lies inside the triangle if and only if the triangle is acute triangle, acute. For a right triangle, the orthocenter coincides with the vertex (geometry), vertex at the right angle. For an equilateral triangle, all triangle center, triangle centers (including the orthocenter) coincide at its centroid. Formulation Let denote the vertices and also the angles of the triangle, and let a = \left, \overline\, b = \left, \overline\, c = \left, \overline\ be the side lengths. The orthocenter has trilinear coordinatesClark Kimberling's Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers \begin & \sec A:\sec B:\sec C \\ &= \cos A-\sin B \sin C:\cos B-\sin C \sin A:\cos C-\sin A\sin B, \end and Barycentric coordinates (mathematics), barycentric coordinates \begin & (a^2+b^2-c^2)(a^2-b^2+c^2) : (a^2+b^2-c^2)(-a^2+b^2+c^2) : (a^2- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |