|
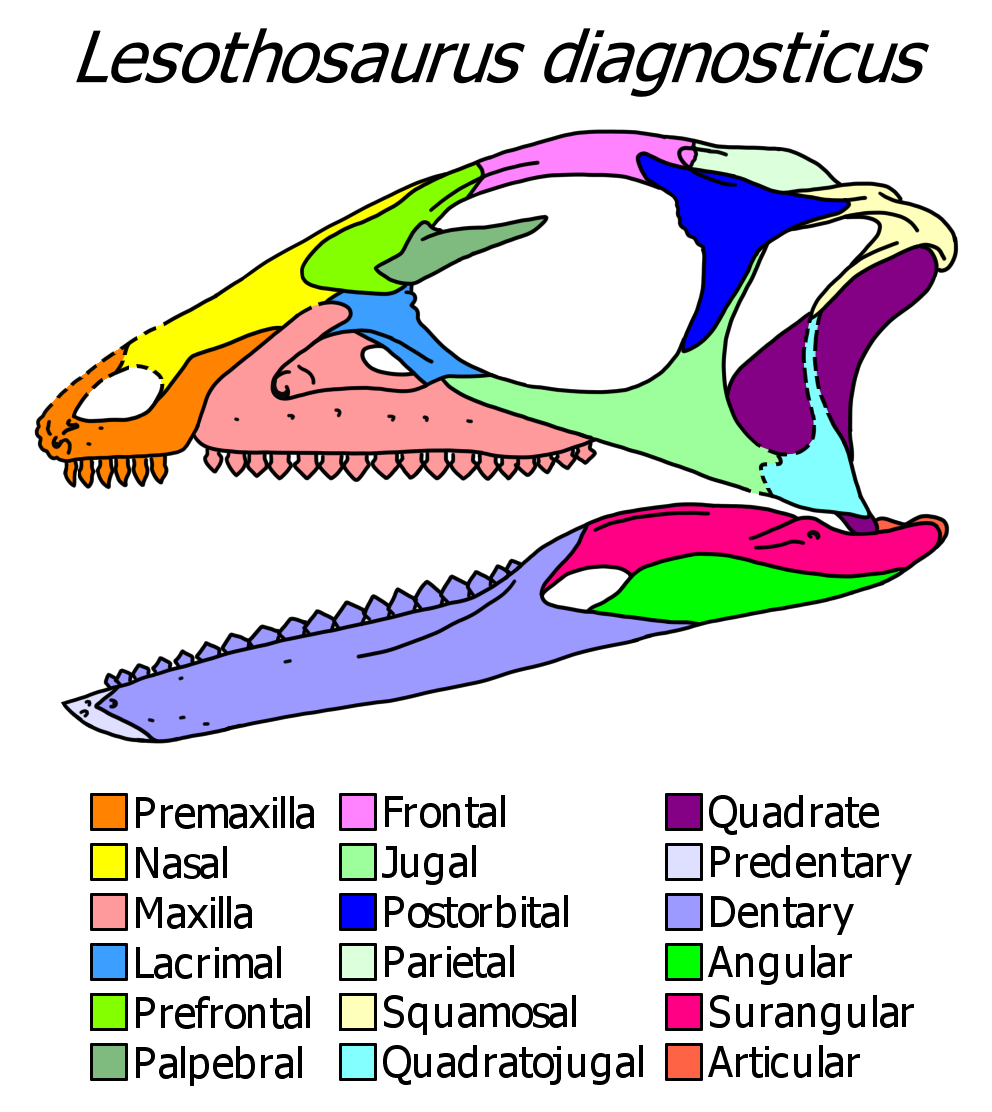
Ornithischia
Ornithischia () is an extinct clade of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek stem ' (), meaning "bird", and ' (), meaning "hip". However, as theropod dinosaurs, birds are only distantly related to this group. Ornithischians with well known anatomical adaptations include the ceratopsians or "horn-faced" dinosaurs (e.g. ''Triceratops''), the pachycephalosaurs or "thick-headed" dinosaurs, the armored dinosaurs ( Thyreophora) such as stegosaurs and ankylosaurs, and the ornithopods. There is strong evidence that certain groups of ornithischians lived in herds, often segregated by age group, with juveniles forming their own flocks separate from adults. Some were at least partially covered in filamentous (hair- or feather- like) pelts, and there is much debate over whether these filaments found in specimens of '' Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stegoceras
''Stegoceras'' is a genus of Pachycephalosauria, pachycephalosaurid (dome-headed) dinosaur that lived in what is now North America during the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), period, about 77.5 to 74 million years ago (mya). The first specimens from Alberta, Canada, were described in 1902, and the type species ''Stegoceras validum'' was based on these remains. The generic name means "horn roof", and the specific name means "strong". Several other species have been placed in the genus over the years, but these have since been moved to other genera or deemed junior synonyms. Currently only ''S. validum'' and ''S. novomexicanum'', named in 2011 from fossils found in New Mexico, remain. The validity of the latter species has also been debated, and it may not even belong to the genus ''Stegoceras.'' ''Stegoceras'' was a small, bipedal dinosaur about long, and weighed around . The skull was roughly triangular with a short snout, and had a thick, broad, and relatively smooth dome o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachycephalosauria
Pachycephalosauria (; from Greek παχυκεφαλόσαυρος for 'thick headed lizards') is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs. Along with Ceratopsia, it makes up the clade Marginocephalia. With the exception of two species, most pachycephalosaurs lived during the Late Cretaceous Period, dating between about 85.8 and 66 million years ago. They are exclusive to the Northern Hemisphere, all of them being found in North America and Asia. They were all bipedal, herbivorous/omnivorous animals with thick skulls. Skulls can be domed, flat, or wedge-shaped depending on the species, and are all heavily ossified. The domes were often surrounded by nodes and/or spikes. Partial skeletons have been found of several pachycephalosaur species, but to date no complete skeletons have been discovered. Often isolated skull fragments are the only bones that are found. Candidates for the earliest-known pachycephalosaur include ''Ferganocephale adenticulatum'' from Middle Jurassic Period strata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterodontosauridae
Heterodontosauridae is a family (biology), family of ornithischian dinosaurs that were likely among the most Basal (phylogenetics), basal (primitive) members of the group. Their phylogenetic placement is uncertain but they are most commonly found outside of the group Genasauria. Although their fossils are relatively rare and their group small in numbers, they have been found on all continents except Australia (continent), Australia and Antarctica, with a range spanning the Early Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous. Heterodontosaurids were fox-sized dinosaurs less than in length, including a long tail. They are known mainly for their characteristic teeth, including enlarged canine (tooth), canine-like tusks and cheek teeth adapted for chewing, Analogy (biology), analogous to those of Cretaceous hadrosaurids. Their diet was herbivore, herbivorous or possibly omnivore, omnivorous. Description Among heterodontosaurids, only ''Heterodontosaurus'' itself is known from a complete ske ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stegosauria
Stegosauria is a group of Herbivore, herbivorous ornithischian dinosaurs that lived during the Jurassic and early Cretaceous Period (geology), periods. Stegosaurian fossils have been found mostly in the Northern Hemisphere (North America, Europe and Asia), Africa and South America. Their geographical origins are unclear; the earliest unequivocal stegosaurian, ''Bashanosaurus primitivus'', was found in the Bathonian Shaximiao Formation of China. Stegosaurians were armored dinosaurs (thyreophorans). Originally, they did not differ much from more primitive members of that group, being small, low-slung, running animals protected by armored scutes. An early evolutionary innovation was the development of spikes as defensive weapons. Later species, belonging to a subgroup called the Stegosauridae, became larger, and developed long hindlimbs that no longer allowed them to run. This increased the importance of active defence by the thagomizer, which could ward off even large predators becau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisanosaurus
''Pisanosaurus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of early dinosauriform, likely an ornithischian or silesaurid, from the Late Triassic of Argentina. It was a small, lightly built, ground-dwelling herbivore, that could grow up to an estimated long. Only one species, the type, ''Pisanosaurus mertii'', is known, based on a single partial skeleton discovered in the Ischigualasto Formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina. This part of the formation has been dated to the late Carnian, approximately 229 million years ago. Discovery and naming ''Pisanosaurus'' is known from a single fragmented skeleton discovered in 1962 by Galileo Juan Scaglia at the Hoyada del Cerro Las Lajas locality (also known as Agua de Las Catas) in the Ischigualasto Formation of La Rioja Province, Argentina. The genus is based on a specimen given the designation PVL 2577, which consists of a partial skull including a fragmentary right maxilla with teeth, and incomplete right ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diodorus Scytobrachion
''Diodorus'' is a genus of Silesauridae, silesaurid dinosauromorph (member of a clade that includes the dinosaurs) that lived during the Late Triassic in what is now Morocco. Fossils were discovered in the Timezgadiouine Formation of the Argana Basin, and were used to name the new genus and species ''Diodorus scytobrachion''. The genus name honors the mythological king Diodorus (king), Diodorus and the ancient historian Diodorus Siculus; the Specific name (zoology), specific name is ancient Greek for and also honors the mythographer Dionysius Scytobrachion. The holotype specimen is a partial dentary bone , and assigned specimens include isolated teeth, two humeri , a metatarsal , and femur . ''Diodorus'' is estimated to have been up to long, and features thought to be shared by most silesaurs include a beak-like front of the lower jaw, leaf-shaped teeth, long limbs, and a quadrupedal posture. ''Diodorus'' differs from other silesaurids in having forward-tilted teeth that decre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterodontosaurus
''Heterodontosaurus'' is a genus of heterodontosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Early Jurassic, 200–190 million years ago. Its only known member species, ''Heterodontosaurus tucki'', was named in 1962 based on a skull discovered in South Africa. The genus name means "different toothed lizard", in reference to its unusual, heterodont dentition; the specific name honours G. C. Tuck, who supported the discoverers. Further specimens have since been found, including an almost complete skeleton in 1966. Though it was a small dinosaur, ''Heterodontosaurus'' was one of the largest members of its family, reaching between and possibly in length, and weighing between . The skull was elongated, narrow, and triangular when viewed from the side. The front of the jaws were covered in a horny beak. It had three types of teeth; in the upper jaw, small, incisor-like teeth were followed by long, canine-like tusks. A gap divided the tusks from the chisel-like cheek-teeth. The body was s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentrosaurus
''Kentrosaurus'' ( ; ) is a genus of stegosaurid dinosaur from the Late Jurassic in Lindi Region of Tanzania. The type species is ''K. aethiopicus'', named and described by German people, German Palaeontology, palaeontologist Edwin Hennig in 1915. Often thought to be a "Primitive (phylogenetics), primitive" member of the Stegosauria, several recent cladistic analyses find it as more derived than many other stegosaurs, and a close relative of ''Stegosaurus'' from the North American Morrison Formation within the Stegosauridae. Fossils of ''K. aethiopicus'' have been found only in the Tendaguru Formation, dated to the late Kimmeridgian and early Tithonian ages, about 152 annum, million years ago. Hundreds of bones were unearthed by German expeditions to German East Africa between 1909 and 1912. Although no complete skeletons are known, the remains provided a nearly complete picture of the build of the animal. In the Tendaguru Formation, it coexisted with a variety of dinosaurs such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimucrodon
''Trimucrodon'' is a genus of ornithischian dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Lourinhã Formation of Portugal. The type, and currently only, species is ''T. cuneatus''. Discovery and naming Three isolated teeth found at the Porto Dinheiro (or Pinhiero) locality in the Lisboa District of Portugal were given the name in 1973 by Richard A. Thulborn, derived from the Latin words for "three" and a dagger point, and , and the Ancient Greek word for "tooth". The only species in the taxon is ''Trimucrodon cuneatus'', taken from the wedge shape of the teeth. Though the unit the specimens came from was originally unnamed, it was referred to the Alcobaça, and then Lourinhã Formations, specifically the late Kimmeridgian Amoreira–Porto Novo Member. The type specimen, uncovered between 1962 and 1967 by German zoologist and paleontologist Georg Krusat, is distinguished by prominent denticles at the front and rear ends of the crown, and comes from an individual under long.G. Krusat, 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alocodon
''Alocodon'' is a genus of ornithischian dinosaur known from multiple teeth from the Middle or Late Jurassic Cabaços Formation of Portugal, and also the Forest Marble and Chipping Norton Formations of England. A single species is known, ''A. kuehnei''. Discovery and naming The taxon was first described in 1973 by Richard A. Thulborn for an assemblage of teeth from the Pedrógão locality of Portugal, distinguished by an enlarged central denticle on the teeth, with the name taken from the Greek ''alox'' and ''odon'' meaning 'furrow tooth'. The type specimen, a single tooth, is stored in the Museu Geológico do Instituto Geológico e Mineiro in Lisbon, Portugal, formerly having been kept in the collections of the Free University of Berlin as IPFUB P X 1, and comes from an individual under in length. Though it was originally described as having been found in an unnamed deposit in the Portuguese Leiria District of upper Callovian age, it was identified as having come from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
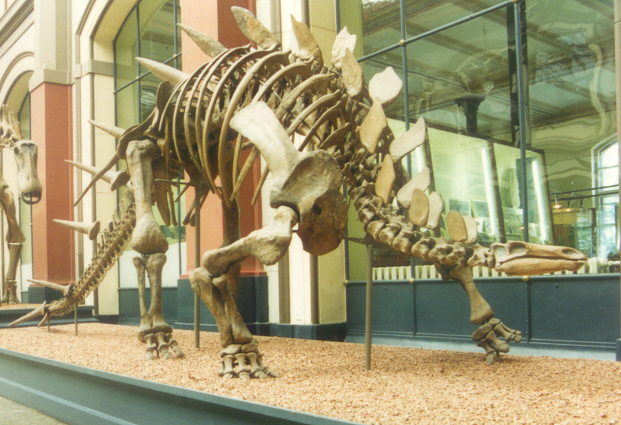
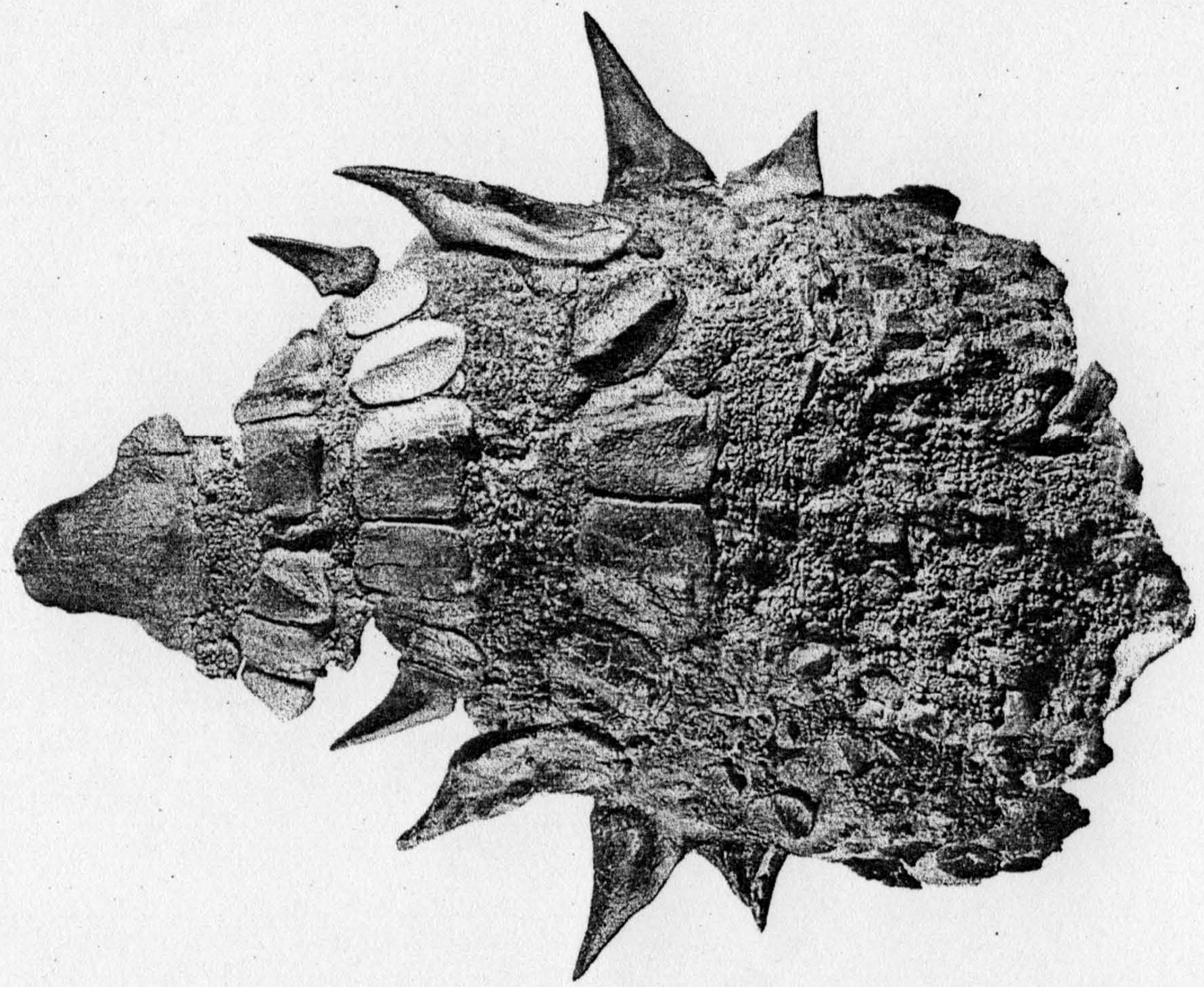
Ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the clade Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs. They are known to have first appeared in North Africa during the Middle Jurassic, and persisted until the end of the Late Cretaceous. The two main families of ankylosaurians, Nodosauridae and Ankylosauridae primarily originated from the Northern Hemisphere (North America, Europe and Asia), but the more basal Parankylosauria originated from southern Gondwana (South America, Australia and Antarctica) during the Cretaceous. Ankylosauria was first named by Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1923.Osborn, H. F. (1923). "Two Lower Cretaceous dinosaurs of Mongolia." ''American Museum Novitates'', 95: 1–1/ref> In the Linnaean classification system, the group is usually considered either a suborder or an infraorder. It is contained within the group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypacrosaurus
''Hypacrosaurus'' (meaning "near the highest lizard" [Greek υπο-, ''hypo-'' = less + ακρος, ''akros'', high], because it was almost but not quite as large as ''Tyrannosaurus'') is an extinct genus of hadrosaurid, duckbill dinosaur similar in appearance to ''Corythosaurus''. Like ''Corythosaurus'', it had a tall, hollow rounded crest, although not as large and straight. It is known from the remains of two species that spanned 75 to 67 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous of Alberta, Canada, and Montana, United States, and is the latest hollow-crested duckbill known from good remains in North America. It was an obscure genus until the discovery in the 1990s of nests, egg (biology), eggs, and hatchlings belonging to ''H. stebingeri''. Discovery and history The holotype, type remains of ''Hypacrosaurus'' were collected in 1910 by Barnum Brown for the American Museum of Natural History. The remains, a partial postcranial skeleton consisting of several vertebrae and a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |