|
Organizational Routines
In organisational theory, organisational routines are "repetitive, recognizable patterns of interdependent actions carried out by multiple actors". In evolution and evolutionary economics routines serve as social replicators – mechanisms that help to maintain organisational behaviors and knowledge. In the theory of organisational learning, routines serve as a sort of memory, especially of uncodified, tacit knowledge. In strategic management, especially in the resource-based view of firms, organisational routines form the microfoundations of organisational capabilities and dynamic capabilities. Despite the extensive usage of the routines concept in the research literature, there is still much debate about organisational routines. For example, scholars see them both as a source of stability and as a driver of organisational change. In an attempt to better understand the "inside" of organisational routines, Pentland and Feldman offered the distinction between the ostensive an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organizational Theory
Organizational theory refers to the set of interrelated concepts that involve the sociological study of the structures and operations of formal social organizations. Organizational theory also attempts to explain how interrelated units of organization do or do not connect with each other. Organizational theory also concerns understanding how groups of individuals behave, which may differ from the behavior of an individual. The behavior organizational theory often focuses on is goal-directed. Organizational theory can cover intra-organizational as well as inter-organizational fields of study. In the early 20th century, theories of organizations initially took a rational perspective but have since become more diverse. In a rational organization system, there are two significant parts: Specificity of Goals and Formalization. The ''division of labor'' is the specialization of individual labor roles, associated with increasing output and trade. Modernization theorist Frank Dobbin wrot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habit
A habit (or wont as a humorous and formal term) is a routine of behavior that is repeated regularly and tends to occur subconsciously.Definition of ''Habituation'' ''Merriam Webster Dictionary''. Retrieved on August 29, 2008 The '' American Journal of Psychology'' (1903) defined a "habit, from the standpoint of , sa more or less fixed way of thinking, willing, or feeling acquired through previous repetition of a mental |
Black Box
In science, computing, and engineering, a black box is a system which can be viewed in terms of its inputs and outputs (or transfer characteristics), without any knowledge of its internal workings. Its implementation is "opaque" (black). The term can be used to refer to many inner workings, such as those of a transistor, an engine, an algorithm, the human brain, or an institution or government. To analyse an open system with a typical "black box approach", only the behavior of the stimulus/response will be accounted for, to infer the (unknown) ''box''. The usual representation of this ''black box system'' is a data flow diagram centered in the box. The opposite of a black box is a system where the inner components or logic are available for inspection, which is most commonly referred to as a white box (sometimes also known as a "clear box" or a "glass box"). History The modern meaning of the term "black box" seems to have entered the English language around 1945. In elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outcome-Driven Innovation
Outcome-Driven Innovation (ODI) is a strategy and innovation process developed by Anthony W. Ulwick. It is built around the theory that people buy products and services to get jobs done.Anthony Ulwick, ''What Customers Want: Using Outcome-Driven Innovation to Create Breakthrough Products and Services'', 2005 As people complete these jobs, they have certain measurable outcomes that they are attempting to achieve.Rebbeck, Tom"Outcome-Driven Innovation: A New Approach to Tackling Over-the-Top Services?"Analysys Mason. June 22, 2012 It links a company's value creation activities to customer-defined metrics. Ulwick found that previous innovation practices were ineffective because they were incomplete, overlapping, or unnecessary. ODI attempts to identify jobs and outcomes that are either important but poorly served or unimportant but over-served. ODI focuses on customer-desired outcome rather than demographic profile in order to segment markets and offer well-targeted products. By knowi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consensus Decision-making
Consensus decision-making or consensus process (often abbreviated to ''consensus'') are group decision-making processes in which participants develop and decide on proposals with the aim, or requirement, of acceptance by all. The focus on establishing agreement of at least the majority or the supermajority and avoiding unproductive opinion differentiates consensus from unanimity, which requires all participants to support a decision. Origin and meaning of terms The word ''consensus'' is Latin meaning "agreement, accord", derived from ''consentire'' meaning "feel together". Broadly, ''consensus'' relates to a generally accepted opinion, but in the context of this article refers to the process ''and'' the outcome of consensus decision-making (e.g. "to decide ''by'' consensus" and "''a'' consensus was reached"). History Consensus decision-making, as a self-described practice, originates from several nonviolent, direct action groups that were active in the Civil rights, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collective Mind
''Geist'' () is a German noun with a significant degree of importance in German philosophy. Its semantic field corresponds to English ghost, spirit, mind, intellect. Some English translators resort to using "spirit/mind" or "spirit (mind)" to help convey the meaning of the term. ''Geist'' is also a central concept in Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel's 1807 '' The Phenomenology of Spirit'' (''Phänomenologie des Geistes''). Notable compounds, all associated with Hegel's view of world history of the late 18th century, include ''Weltgeist'' "world-spirit", ''Volksgeist'' "national spirit" and ''Zeitgeist'' "spirit of the age". Etymology and translation German ''Geist'' (masculine gender: ''der Geist'') continues Old High German ''geist'', attested as the translation of Latin ''spiritus''. It is the direct cognate of English ''ghost'', from a West Germanic ''gaistaz''. Its derivation from a PIE root ''g̑heis-'' "to be agitated, frightened" suggests that the Germanic word o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabotage
Sabotage is a deliberate action aimed at weakening a polity, effort, or organization through subversion, obstruction, disruption, or destruction. One who engages in sabotage is a ''saboteur''. Saboteurs typically try to conceal their identities because of the consequences of their actions and to avoid invoking legal and organizational requirements for addressing sabotage. Etymology The English word derives from the French word , meaning to "bungle, botch, wreck or sabotage"; it was originally used to refer to labour disputes, in which workers wearing wooden shoes called interrupted production through different means. A popular but incorrect account of the origin of the term's present meaning is the story that poor workers in the Belgian city of Liège would throw a wooden into the machines to disrupt production. One of the first appearances of and in French literature is in the of d'Hautel, edited in 1808. In it the literal definition is to 'make noise with sabots' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endogenous
Endogenous substances and processes are those that originate from within a living system such as an organism, tissue, or cell. In contrast, exogenous substances and processes are those that originate from outside of an organism. For example, estradiol is an endogenous estrogen hormone produced within the body, whereas ethinylestradiol is an exogenous synthetic estrogen, commonly used in birth control pills Oral contraceptives, abbreviated OCPs, also known as birth control pills, are medications taken by mouth for the purpose of birth control. Female Two types of female oral contraceptive pill, taken once per day, are widely available: * The combin .... References External links *{{Wiktionary-inline, endogeny Biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complexity
Complexity characterises the behaviour of a system or model whose components interact in multiple ways and follow local rules, leading to nonlinearity, randomness, collective dynamics, hierarchy, and emergence. The term is generally used to characterize something with many parts where those parts interact with each other in multiple ways, culminating in a higher order of emergence greater than the sum of its parts. The study of these complex linkages at various scales is the main goal of complex systems theory. The intuitive criterion of complexity can be formulated as follows: a system would be more complex if more parts could be distinguished, and if more connections between them existed. Science takes a number of approaches to characterizing complexity; Zayed ''et al.'' reflect many of these. Neil Johnson states that "even among scientists, there is no unique definition of complexity – and the scientific notion has traditionally been conveyed using particular examples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
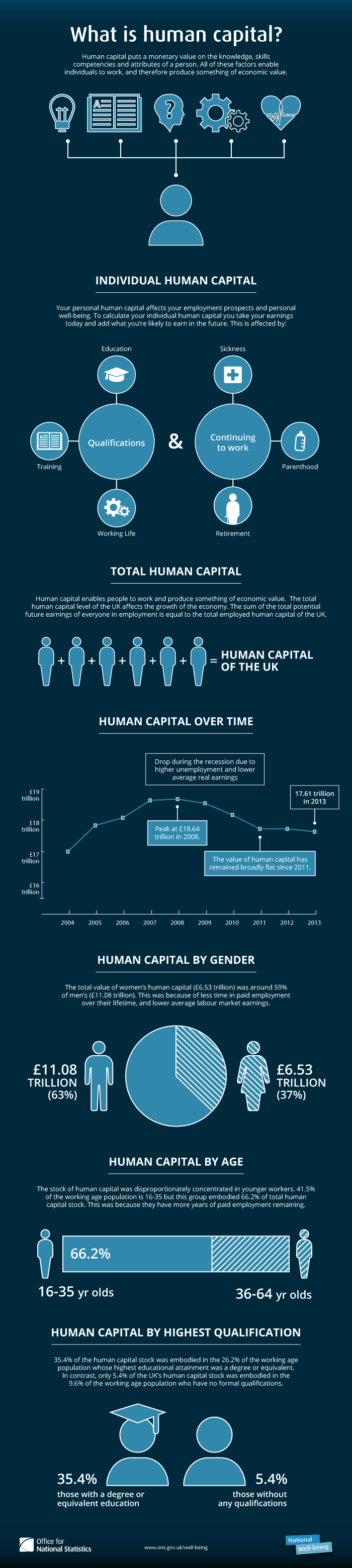
Human Capital
Human capital is a concept used by social scientists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a substantial impact on individual earnings. Research indicates that human capital investments have high economic returns throughout childhood and young adulthood. Companies can invest in human capital, for example, through education and training, enabling improved levels of quality and production. As a result of his conceptualization and modeling work using Human Capital as a key factor, the 2018 Nobel Prize for Economics was jointly awarded to Paul Romer, who founded the modern innovation-driven approach to understanding economic growth. In the recent literature, the new concept of task-specific human capital was coined in 2004 by Robert Gibbons, an economist at MIT, and Michael Waldman, an economist at Cornell University. The concept emphasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus is a detectable change in the physical or chemical structure of an organism's internal or external Environment (systems), environment. The ability of an organism or Organ (anatomy), organ to detect external stimuli, so that an appropriate reaction can be made, is called sensitivity (excitability). Sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanoreceptors. When a stimulus is detected by a sensory receptor, it can elicit a Reflex action, reflex via Transduction (physiology), stimulus transduction. An Internal stimuli, internal stimulus is often the first component of a Homeostasis, homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level of strengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skill
A skill is the learned ability to act with determined results with good execution often within a given amount of time, energy, or both. Skills can often be divided into domain-general and domain-specific skills. For example, in the domain of work, some general skills would include time management, teamwork and leadership, self-motivation and others, whereas domain-specific skills would be used only for a certain job. Skill usually requires certain environmental stimuli and situations to assess the level of skill being shown and used. A skill may be called an art when it represents a body of knowledge or branch of learning, as in ''the art of medicine'' or ''the art of war''. Although the arts are also skills, there are many skills that form an art but have no connection to the fine arts. People need a broad range of skills to contribute to the modern economy. A joint ASTD and U.S. Department of Labor study showed that through technology, the workplace is changing, and id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |