|
Organic Organisation
A term created by Tom Burns and G.M. Stalker in the late 1950s, organic organizations (Organic system theory), unlike mechanistic organizations (also coined by Burns and Stalker), are flexible and value external knowledge. The theories of Burns and Stalker impacted the field of organization theory, with their study of management and structure of Scottish electronics firms. In their writing contrasting mechanistic and organismic structures, they outlined the differences between the two types. Also called organismic organization, this form of organizational structure was widely sought and proposed, but difficult to prove it exists. As opposed to the mechanistic organization, it has the least hierarchy and specialization of functions. For an organization to be organic, the participants or workers should have equal levels, with no job descriptions or classifications, and communication should have a hub-network-like form. Organic organisation thrives on the power of personalities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tom Burns (sociologist)
Tom Burns FBA (1913–2001) was an English sociologist, author and founder of the Sociology department at Edinburgh University. Early life Burns was born on 16 January 1913 in Bethnal Green, East London. He attended Hague Street LCC elementary school and Parmiter's foundation school before reading English Literature at Bristol University. Career A Fellow of the British Academy, Tom Burns was Professor of Sociology at Edinburgh University from 1965 to 1981, and also taught at Harvard and Columbia. He is best known for his studies of the organization of the BBC, local government, the electronics industry and the National Health Service. He also wrote on his experiences as a non-combatant prisoner of war in Germany during the Second World War. His early interests were in urban sociology, and he worked with the West Midland Group on Post-War Reconstruction and Planning. While he was at Edinburgh his particular concern was with studies of different types of organization and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
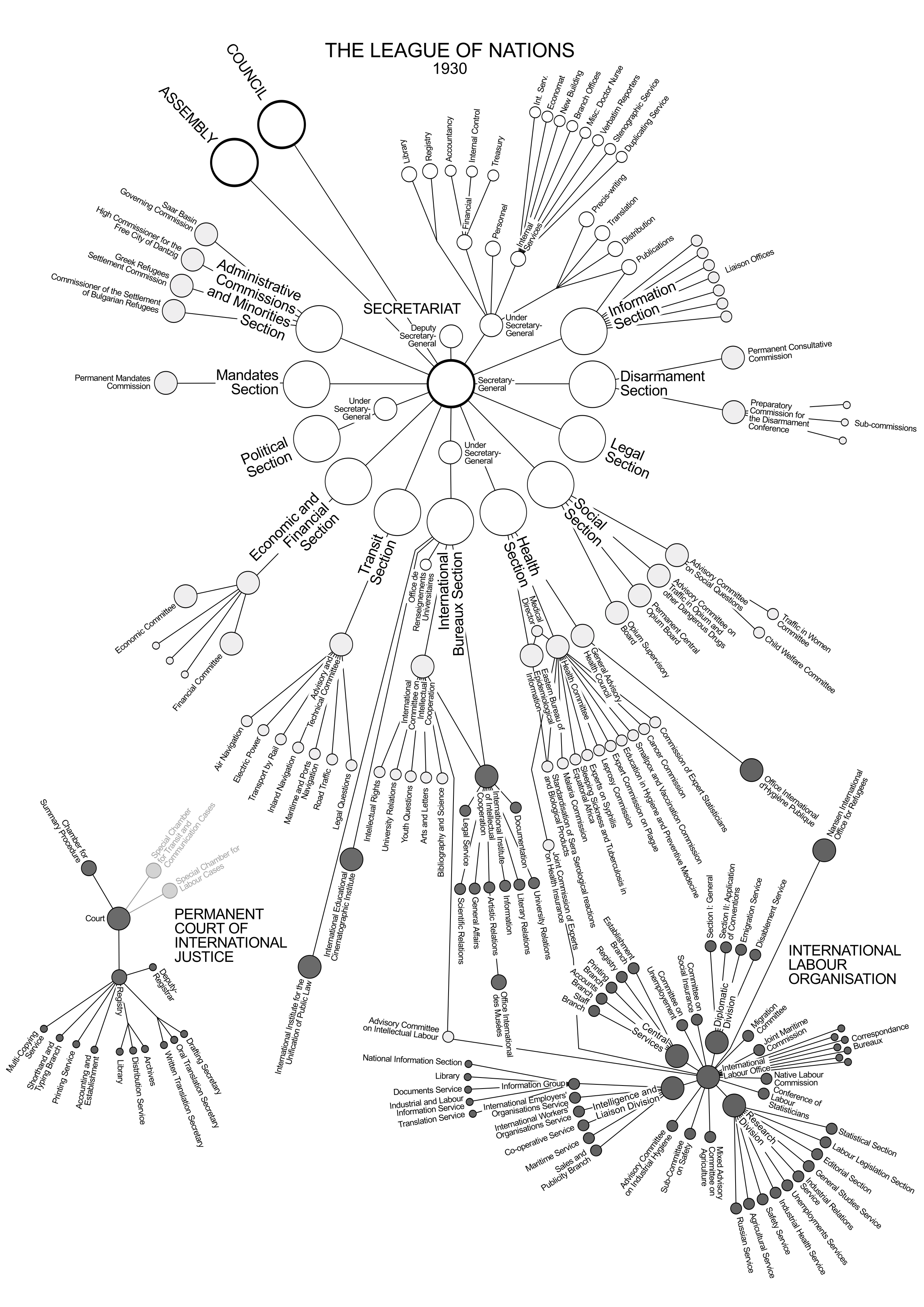
Organizational Structure
An organizational structure defines how activities such as task allocation, coordination, and supervision are directed toward the achievement of organizational aims. Organizational structure affects organizational action and provides the foundation on which standard operating procedures and routines rest. It determines which individuals get to participate in which decision-making processes, and thus to what extent their views shape the organization's actions.Jacobides., M. G. (2007). The inherent limits of organizational structure and the unfulfilled role of hierarchy: Lessons from a near-war. Organization Science, 18, 3, 455–477. Organizational structure can also be considered as the viewing glass or perspective through which individuals see their organization and its environment. Organizations are a variant of clustered entities. An organization can be structured in many different ways, depending on its objectives. The structure of an organization will determine the mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierarchy
A hierarchy (from Ancient Greek, Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important concept in a wide variety of fields, such as architecture, philosophy, design, mathematics, computer science, organizational theory, systems theory, systematic biology, and the social sciences (especially political science). A hierarchy can link entities either directly or indirectly, and either vertically or diagonally. The only direct links in a hierarchy, insofar as they are hierarchical, are to one's immediate superior or to one of one's subordinates, although a system that is largely hierarchical can also incorporate alternative hierarchies. Hierarchical links can extend "vertically" upwards or downwards via multiple links in the same direction, following a path (graph theory), path. All parts of the hierarchy that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organization
An organization or organisation (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), see spelling differences) is an legal entity, entity—such as a company, or corporation or an institution (formal organization), or an Voluntary association, association—comprising one or more person, people and having a particular purpose. Organizations may also operate secretly or illegally in the case of secret society , secret societies, criminal organizations, and resistance movements. And in some cases may have obstacles from other organizations (e.g.: Southern Christian Leadership Conference, MLK's organization). What makes an organization recognized by the government is either filling out Incorporation (business), incorporation or recognition in the form of either societal pressure (e.g.: Advocacy group), causing concerns (e.g.: Resistance movement) or being considered the spokesperson o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic (model)
Organic describes forms, methods and patterns found in living systems such as the organisation of cells, to populations, communities, and ecosystems. Typically organic models stress the interdependence of the component parts, as well as their differentiation. Other properties of organic models include: *the growth, life or development cycle *the ability to adapt, learn, and evolve * emergent behaviour or emergent properties *steady change or growth, as opposed to instant change *regulatory feedback *composed of heterogeneous (diverse) parts Organic models are used especially in the design of artificial systems, and the description of social systems and constructs. Uses In the social sciences, the organic model has been drawn upon for ideas such as mechanical and organic solidarity and organic unity. Carl Ritter advanced the idea of Lebensraum using the metaphor of an organic, growing state. In computer science, organic networks grow in an ad hoc manner, while organic comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Church
A house church or home church is a label used to describe a group of Christians who regularly gather for worship in private homes. The group may be part of a larger Christian body, such as a parish, but some have been independent groups that see the house church as the primary form of Christian community. Sometimes these groups meet because the membership is small, and a home is the most appropriate place to assemble until such time as the group has sufficient funds to rent a regular place to meet (as in the beginning phase of the British New Church Movement). Sometimes this meeting style is advantageous because the group is a member of a Christian congregation which is otherwise banned from meeting as is the case in House church (China), China and Iran. Some recent Christian writers like Francis Chan have supported the view that the Christian Church should meet in houses, and have based the operation of their communities around multiple small home meetings. Other Christian gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Viola (author)
Frank Viola (born October 12, 1964) is an American author, speaker, and blogger on Christian topics. His work focuses on Jesus studies and biblical narrative, with a strong emphasis on helping the poor and the oppressed. He is most noted for his emphasis on the gospel of the kingdom, the centrality and supremacy of Jesus Christ, and the idea that Jesus indwells all Christians and they can learn to live by his life. Viola's early work was focused on organic church and missional church themes. His older books advocated church life based on the spiritual principles of the New Testament, the headship of Christ, face-to-face community, and the priesthood of all believers. Since 2009, Viola's work has been focused on Jesus studies, living by the indwelling life of Christ, God's eternal purpose, the present-day ministry of Christ, and biblical narrative. Viola has authored over 20 books, over 1,000 blog articles, and over 300 podcast episodes. His podcast, Christ is All, has bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Barna
George Barna (born 1954) is the founder of The Barna Group, a market research firm specializing in studying the religious beliefs and behavior of Americans, and the intersection of faith and culture. From 2013–2018 he served as the executive director of the American Culture & Faith Institute, the research division of United in Purpose. In 2019 he became a professor at Arizona Christian University in Phoenix, Arizona, where he also started the Cultural Research Center at Arizona Christian University. He is also the senior research fellow for Christian ethics and Biblical worldview at Family Research Council. Background George Barna grew up a Catholic in New York City and Princeton, New Jersey but he has since engaged with evangelical Christianity.George Barna, quoted in Barna has filled executive roles in politics, marketing, advertising, media development, research and ministry. He founded the Barna Research Group in 1984 (now The Barna Group), a marketing researc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outline Of Organizational Theory
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to organizational theory: Organizational theory – the interdisciplinary study of social organizations. Organizational theory also concerns understanding how groups of individuals behave, which may differ from the behavior of individuals. The theories of organizations include bureaucracy, rationalization (scientific management), and the division of labor. Each theory provides distinct advantages and disadvantages when applied. The classical perspective emerges from the Industrial Revolution in the private sector and the need for improved public administration in the public sector. Forms * Conglomerate * Community organization * Formal organization ** Articles of organization ** Corporate structure ** Self-regulatory organization * Functional organization * Informal organization ** Cooperative ** Non-governmental organization * International organization ** Intellectual property organization * Membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |