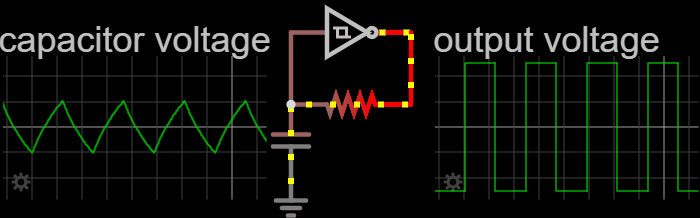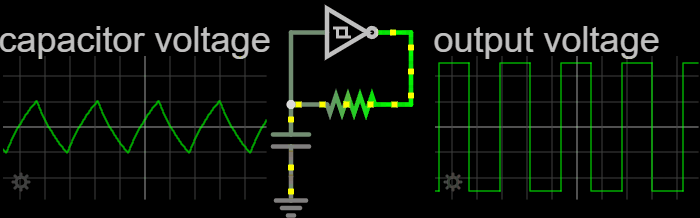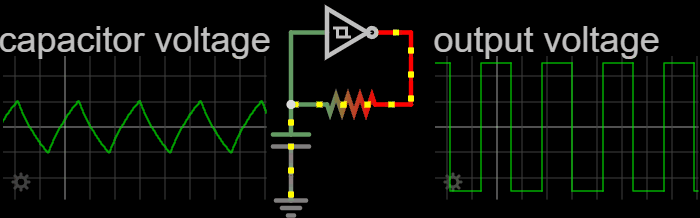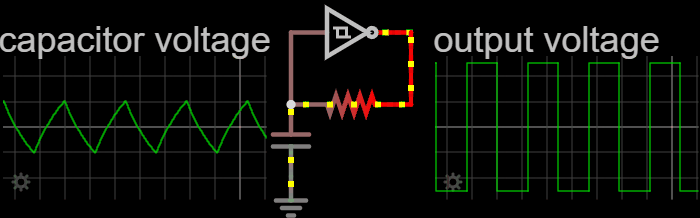
|
Optical Feedback
Optical feedback (OF) refers to the phenomenon in a laser, where a part of the coherent emission light returns to the laser cavity. The effect is typical for any laser, although the cause of the feedback light varies: reflection from optical components, fiber edges, spectroscopy cell windows. Operation of the semiconductor laser is very sensitive to OF due to its very high intrinsic gain and chirping effect, as well as the relaxation oscillation. Upon return, the feedback light will be delayed with respect to the light in the cavity, and will have different phase, thus either amplifying or suppressing the laser output. While the recombination of the feedback light and light already in the cavity is usually linear, the delay, high gain, chirping, and relaxation oscillation create complex dynamic effects at the output. In the case of the optical resonator, this is accomplished by parallel mirrors which cause light to be reflected within the lasing cavity, allowing for a single p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles H. Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow and the optical amplifier patented by Gordon Gould. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light that is coherence (physics), ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling uses such as optical communication, laser cutting, and Photolithography#Light sources, lithography. It also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimated light, collimation), used in laser pointers, lidar, and free-space optical communication. Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which permits them to emit light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherent Emission
In physics, superradiance, or superradiation, is the radiation enhancement effects in several contexts including quantum mechanics, astrophysics and relativity. Quantum optics In quantum optics, superradiance is a phenomenon that occurs when a group of ''N'' emitters, such as excited atoms, interact with a common light field. If the wavelength of the light is much greater than the separation of the emitters, then the emitters interact with the light in a collective and coherent fashion. This causes the group to emit light as a high-intensity pulse (with rate proportional to ''N''2). This is a surprising result, drastically different from the expected exponential decay (with rate proportional to ''N'') of a group of independent atoms (see spontaneous emission). Superradiance has since been demonstrated in a wide variety of physical and chemical systems, such as quantum dot arrays and J-aggregates. This effect has been used to produce a superradiant laser. Rotational superradia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopy Cell
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Spectroscopy, primarily in the electromagnetic spectrum, is a fundamental exploratory tool in the fields of astronomy, chemistry, materials science, and physics, allowing the composition, physical structure and electronic structure of matter to be investigated at the atomic, molecular and macro scale, and over astronomical distances. Historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism. Current applications of spectroscopy include biomedical spectroscopy in the areas of tissue analysis and medical imaging. Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associated with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
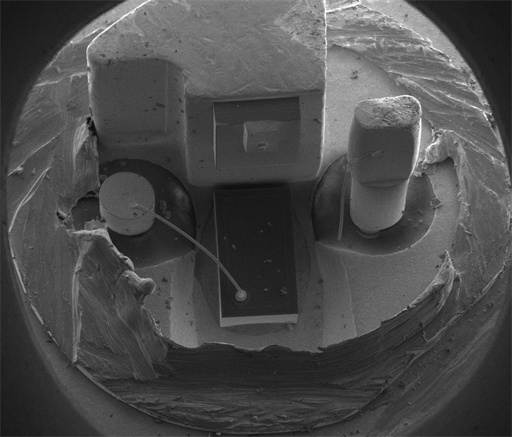
Semiconductor Laser
The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD or semiconductor laser or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emitting diode in which a diode pumped directly with electrical current can create lasing conditions at the diode's junction. Driven by voltage, the doped p–n-transition allows for recombination of an electron with a hole. Due to the drop of the electron from a higher energy level to a lower one, radiation is generated in the form of an emitted photon. This is spontaneous emission. Stimulated emission can be produced when the process is continued and further generates light with the same phase, coherence, and wavelength. The choice of the semiconductor material determines the wavelength of the emitted beam, which in today's laser diodes range from the infrared (IR) to the ultraviolet (UV) spectra. Laser diodes are the most common type of lasers produced, with a wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrinsic Gain
In science and engineering, an intrinsic property is a property of a specified subject that exists itself or within the subject. An extrinsic property is not essential or inherent to the subject that is being characterized. For example, mass is an intrinsic property of any physical object, whereas weight is an extrinsic property that depends on the strength of the gravitational field in which the object is placed. Applications in science and engineering In materials science, an intrinsic property is independent of how much of a material is present and is independent of the form of the material, e.g., one large piece or a collection of small particles. Intrinsic properties are dependent mainly on the fundamental chemical composition and structure of the material. Extrinsic properties are differentiated as being dependent on the presence of avoidable chemical contaminants or structural defects. In biology, intrinsic effects originate from inside an organism or cell, such as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirping Effect
*
{{disambiguation ...
Chirping may refer to: * Bird vocalization * Chirping, the act of signaling with chirps, signals in which the frequency increases / decreases with time ** Chirping, pulse compression by linear frequency modulation * Trash-talk in ice hockey See also * Chirp (other) * Chirplet transform In signal processing, the chirplet transform is an inner product of an input signal with a family of analysis primitives called chirplets.S. Mann and S. Haykin,The Chirplet transform: A generalization of Gabor's logon transform, ''Proc. Vision In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relaxation Oscillation (laser)
In electronics, a relaxation oscillator is a nonlinear electronic oscillator circuit that produces a nonsinusoidal repetitive output signal, such as a triangle wave or square wave. on Peter Millet'Tubebookswebsite The circuit consists of a feedback loop containing a switching device such as a transistor, comparator, relay, op amp, or a negative resistance device like a tunnel diode, that repetitively charges a capacitor or inductor through a resistance until it reaches a threshold level, then discharges it again. The period of the oscillator depends on the time constant of the capacitor or inductor circuit. The active device switches abruptly between charging and discharging modes, and thus produces a discontinuously changing repetitive waveform. This contrasts with the other type of electronic oscillator, the harmonic or linear oscillator, which uses an amplifier with feedback to excite resonant oscillations in a resonator, producing a sine wave. Relaxation oscillators may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Resonator
An optical cavity, resonating cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors or other optical elements that confines light waves similarly to how a cavity resonator confines microwaves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, surrounding the gain medium and providing feedback of the laser light. They are also used in optical parametric oscillators and some interferometers. Light confined in the cavity reflects multiple times, producing Mode (electromagnetism), modes with certain resonance, resonance frequencies. Modes can be decomposed into longitudinal modes that differ only in frequency and transverse modes that have different intensity patterns across the cross section of the beam. Many types of optical cavities produce standing wave modes. Different resonator types are distinguished by the focal lengths of the two mirrors and the distance between them. Flat mirrors are not often used because of the difficulty of aligning them to the needed precision. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Laser
A random laser (RL) is a laser in which optical feedback is provided by scattering particles. As in conventional lasers, a gain medium is required for optical amplification. However, in contrast to Fabry–Pérot interferometer, Fabry–Pérot cavities and distributed feedback laser, distributed feedback lasers, neither reflective surfaces nor distributed periodic structures are used in RLs, as light is confined in an active region by diffusive elements that either may or may not be spatially distributed inside the gain medium. The main principle behind a random laser is to increase the light path with disordered media; this can be done by diffusive disordered media or by using strong localization in a disordered media, with laser active background. Random lasing has been reported from a large variety of materials, e.g. colloidal solutions of dye and scattering particles, semiconductor powders, Semiconductor polycrystalline thin films, optical fibers and polymers. Due to the ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Lasers
The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD or semiconductor laser or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emitting diode in which a diode pumped directly with electrical current can create lasing conditions at the diode's junction. Driven by voltage, the doped p–n-transition allows for recombination of an electron with a hole. Due to the drop of the electron from a higher energy level to a lower one, radiation is generated in the form of an emitted photon. This is spontaneous emission. Stimulated emission can be produced when the process is continued and further generates light with the same phase, coherence, and wavelength. The choice of the semiconductor material determines the wavelength of the emitted beam, which in today's laser diodes range from the infrared (IR) to the ultraviolet (UV) spectra. Laser diodes are the most common type of lasers produced, with a wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |