|
Opisthorchiasis
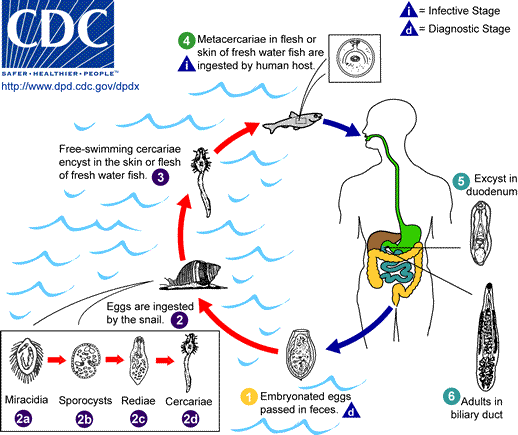
Opisthorchiasis is a parasitic disease caused by certain species of genus '' Opisthorchis'' (specifically, '' Opisthorchis viverrini'' and '' Opisthorchis felineus''). Chronic infection may lead to cholangiocarcinoma, a cancer of the bile ducts. Medical care and loss of wages caused by ''Opisthorchis viverrini'' in Laos and in Thailand costs about $120 million annually.Muller R. & Wakelin D. (2002). ''Worms and human disease''. CABIpage 4344. In Asia, infection by ''Opisthorchis viverrini'' and other liver flukes affects the poorest people. Along with other foodborne trematode infections such as clonorchiasis, fascioliasis and paragonimiasis, opisthorchiasis is listed among the World Health Organization's list of neglected tropical diseases.. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of opisthorchiasis are indistinguishable from clonorchiasis. About 80% of infected people have no symptoms, though they can have eosinophilia. Asymptomatic infection can occur when there are less than 1000 eggs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthorchis Viverrini
''Opisthorchis viverrini'', common name Southeast Asian liver fluke, is a food-borne trematode parasite from the family Opisthorchiidae that infects the bile duct. People are infected after eating raw or undercooked fish. Infection with the parasite is called opisthorchiasis. ''O. viverrini'' infection also increases the risk of cholangiocarcinoma, a cancer of the bile ducts. A small, leaf-like fluke, ''O. viverrini'' completes its lifecycle in three different animals. Snails of the species ''Bithynia'' are the first intermediate hosts, fish belonging to the family Cyprinidae are the second intermediate host, and the definitive hosts are humans and other mammals such as dogs, cats, rats, and pigs. It was first discovered in the Indian fishing cat (''Prionailurus viverrus'') by M.J. Poirier in 1886. The first human case was discovered by Robert Thomson Leiper in 1915. ''O. viverrini'' (together with ''Clonorchis sinensis'' and '' Opisthorchis felineus'') is one of the three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthorchis Felineus
''Opisthorchis felineus'', the Siberian liver fluke or cat liver fluke, is a trematode parasite that infects the liver in mammals. It was first discovered in 1884 in a cat's liver by of Italy. In 1891, Russian parasitologist, (1847–1906) found it in a human, and named the parasite a "Siberian liver fluke". In the 1930s, helminthologist Hans Vogel of Hamburg published an article describing the life cycle of ''Opisthorchis felineus''. Bernhard Nocht Institute for Tropical Medicine Felineus infections may also involve the pancreatic ducts. Diagnosis of Opisthorchis infection is based on microscopic identification of parasite eggs in stool specimens. Safe and effective medication is available to treat Opisthorchis infections. Adequately freezing or cooking fish will kill the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trematoda
Trematoda is a class of flatworms known as trematodes, and commonly as flukes. They are obligate internal parasites with a complex life cycle requiring at least two hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is a mollusk, usually a snail. The definitive host, where the flukes sexually reproduce, is a vertebrate. Infection by trematodes can cause disease in all five vertebrate classes: mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and fish. Etymology Trematodes are commonly referred to as flukes. This term can be traced back to the Old English name for flounder, and refers to the flattened, rhomboidal shape of the organisms. The etymology of trematode stems from the Greek word ''trēmatṓdēs'', which means "pierced with holes", and refers to the worm's sucker, which pierces a hole in the host while the worm is attached and feeding. Taxonomy There are 18,000 to 24,000 known species of trematodes, divided into two subclasses — the Aspidogastrea and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clonorchiasis
Clonorchiasis is an infectious disease caused by the Chinese liver fluke (''Clonorchis sinensis'') and two related species. Clonorchiasis is a known risk factor for the development of cholangiocarcinoma, a neoplasm of the biliary system. Symptoms of opisthorchiasis caused by ''Opisthorchis viverrini'' and by '' O. felineus'' are indistinguishable from clonorchiasis caused by '' Clonorchis sinensis'', leading some to argue that the disease by these three parasites should be referred to collectively as clonorchiasis.. Signs and symptoms Cause ''Clonorchis sinensis'' is a trematode (fluke) which is part of the phylum Platyhelminthes. The parasitic worm is as long as 10 to 25 mm and lives in the bile ducts of the liver. It is a hermaphroditic fluke that requires two intermediate hosts. The eggs of the worms are passed in fecal matter into a body of water and are then ingested by mollusks. The water snail is the first intermediate host, in which a miracidium (an embryonat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neglected Tropical Diseases
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of tropical infections that are common in low-income populations in developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety of pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa, and parasitic worms (helminths). These diseases are contrasted with the "big three" infectious diseases (HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria), which generally receive greater treatment and research funding. In sub-Saharan Africa, disease burden, the effect of neglected tropical diseases as a group is comparable to that of malaria and tuberculosis. NTD co-infection can also make HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis more deadly. Some treatments for NTDs are relatively inexpensive. For example, praziquantel for schistosomiasis costs about US $0.20 per child per year. Nevertheless, in 2010 it was estimated that control of neglected diseases would require funding of between US$2 billion and $3 billion over the subsequent five to sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholangiocarcinoma
Cholangiocarcinoma, also known as bile duct cancer, is a type of cancer that forms in the bile ducts. Symptoms of cholangiocarcinoma may include abdominal pain, yellowish skin, weight loss, generalized itching, and fever. Light colored stool or dark urine may also occur. Other biliary tract cancers include gallbladder cancer and cancer of the ampulla of Vater. Risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma include primary sclerosing cholangitis (an inflammatory disease of the bile ducts), ulcerative colitis, cirrhosis, hepatitis C, hepatitis B, infection with certain liver flukes, and some congenital liver malformations. Most people have no identifiable risk factors. The diagnosis is suspected based on a combination of blood tests, medical imaging, endoscopy, and sometimes surgical exploration. The disease is confirmed by examination of cells from the tumor under a microscope. It is typically an adenocarcinoma (a cancer that forms glands or secretes mucin). Cholangiocarcinoma is ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver Fluke
Liver fluke is a collective name of a polyphyletic group of parasitic trematodes under the phylum Platyhelminthes. They are principally parasites of the liver of various mammals, including humans. Capable of moving along the blood circulation, they can occur also in bile ducts, gallbladder, and liver parenchyma. In these organs, they produce pathological lesions leading to parasitic diseases. They have complex life cycles requiring two or three different hosts, with free-living larval stages in water. Biology The body of liver flukes is leaf-like and flattened. The body is covered with a tegument. They are hermaphrodites having complete sets of both male and female reproductive systems. They have simple digestive systems and primarily feed on blood. The anterior end has the oral sucker opening into the mouth. Inside, the mouth leads to a small pharynx which is followed by an extended intestine that runs the entire length of the body. The intestine is heavily branched and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edema
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, swelling, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin that feels tight, the area feeling heavy, and joint stiffness. Other symptoms depend on the underlying cause. Causes may include Chronic venous insufficiency, venous insufficiency, heart failure, kidney problems, hypoalbuminemia, low protein levels, liver problems, deep vein thrombosis, infections, kwashiorkor, angioedema, certain medications, and lymphedema. It may also occur in immobile patients (stroke, spinal cord injury, aging), or with temporary immobility such as prolonged sitting or standing, and during menstruation or pregnancy. The condition is more concerning if it starts suddenly, or pain or shortness of breath is present. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. If the underlying mechanism involve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peritoneal Cavity
The peritoneal cavity is a potential space located between the two layers of the peritoneum—the parietal peritoneum, the serous membrane that lines the abdominal wall, and visceral peritoneum, which surrounds the internal organs. While situated within the abdominal cavity, the term ''peritoneal cavity'' specifically refers to the potential space enclosed by these peritoneal membranes. The cavity contains a thin layer of lubricating serous fluid that enables the organs to move smoothly against each other, facilitating the movement and expansion of internal organs during digestion. The parietal and visceral peritonea are named according to their location and function. The peritoneal cavity, derived from the coelomic cavity in the embryo, is one of several body cavities, including the pleural cavities surrounding the lungs and the pericardial cavity around the heart. The peritoneal cavity is the largest serosal sac and fluid-filled cavity in the body, it secretes approximately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascites
Ascites (; , meaning "bag" or "sac") is the abnormal build-up of fluid in the abdomen. Technically, it is more than 25 ml of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, although volumes greater than one liter may occur. Symptoms may include increased abdominal size, increased weight, abdominal discomfort, and shortness of breath. Complications can include spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. In the developed world, the most common cause is liver cirrhosis. Other causes include cancer, heart failure, tuberculosis, pancreatitis, and blockage of the hepatic vein. In cirrhosis, the underlying mechanism involves high blood pressure in the portal system and dysfunction of blood vessels. Diagnosis is typically based on an examination together with ultrasound or a CT scan. Testing the fluid can help in determining the underlying cause. Treatment often involves a low-salt diet, medication such as diuretics, and draining the fluid. A transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and stores it. The bile is then released via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of hemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Disease
A parasitic disease, also known as parasitosis, is an infectious disease caused by parasites. Parasites are organisms which derive sustenance from its host while causing it harm. The study of parasites and parasitic diseases is known as parasitology. Medical parasitology is concerned with three major groups of parasites: parasitic protozoa, helminths, and parasitic arthropods. Parasitic diseases are thus considered those diseases that are caused by pathogens belonging taxonomically to either the animal kingdom, or the protozoan kingdom. Terminology Although organisms such as bacteria function as parasites, the usage of the term "parasitic disease" is usually more restricted. The three main types of organisms causing these conditions are protozoa (causing protozoan infection), helminths ( helminthiasis), and ectoparasites. Protozoa and helminths are usually endoparasites (usually living inside the body of the host), while ectoparasites usually live on the surface of the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |