|
Openness To Experience
Openness to experience is one of the domains which are used to describe personality psychology, human personality in the Big Five personality traits, Five Factor Model. Openness involves six Facet (psychology), facets, or dimensions: active imagination (fantasy), aesthetic sensitivity, attentiveness to inner feelings, preference for variety (adventurousness), intellectual curiosity, and challenging authority (psychological liberalism). A great deal of psychometric research has demonstrated that these facets or qualities are significantly correlated. Thus, openness can be viewed as a global personality trait consisting of a set of specific traits, habits, and tendencies that cluster together. Openness tends to be Normal distribution, normally distributed, with a small number of people scoring extremely high or low on the trait and most people scoring moderately. People who score low on openness are considered to be ''closed to experience''. They tend to be conventional and traditiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Personality Psychology
Personality psychology is a branch of psychology that examines personality and its variation among individuals. It aims to show how people are individually different due to psychological forces. Its areas of focus include: * Describing what personality is * Documenting how personalities develop * Explaining the mental processes of personality and how they affect functioning * Providing a framework for understanding Individual, individuals "Personality" is a dynamic and organized set of characteristics possessed by an individual that uniquely influences their environment, cognition, emotions, motivations, and Behavioural sciences, behaviors in various situations. The word ''personality'' originates from the Latin ''persona'', which means "mask". Personality also pertains to the pattern of thoughts, feelings, Adjustment (psychology), social adjustments, and behaviors persistently exhibited over time that strongly influences one's expectations, Self-concept, self-perceptions, Valu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
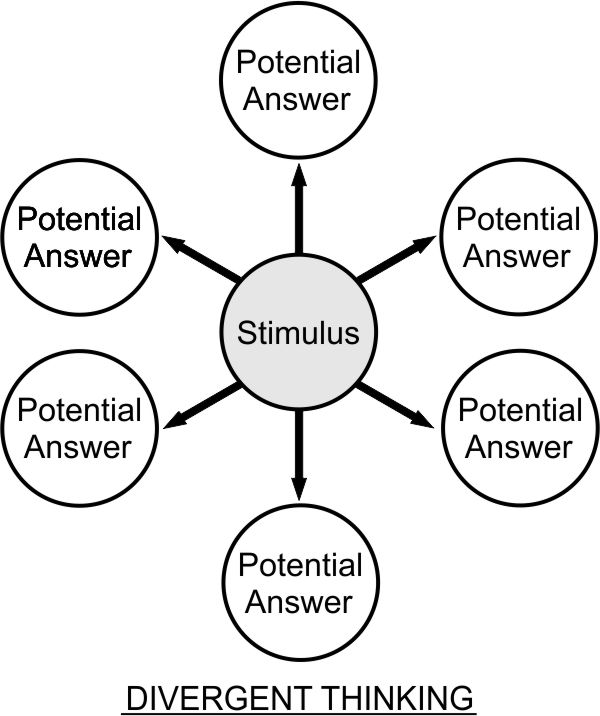 |
Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking is a thought process used to generate creative ideas by exploring many possible solutions. It typically occurs in a spontaneous, free-flowing, "non-linear" manner, such that many ideas are generated in an emergent cognitive fashion. Many possible solutions are explored in a short amount of time, and unexpected connections are drawn. Divergent thinking is often contrasted with convergent thinking. Convergent thinking is the opposite of divergent thinking as it organizes and structures ideas and information, which follows a particular set of logical steps to arrive at one solution, which in some cases is a "correct" solution. The psychologist J. P. Guilford first coined the terms ''convergent thinking'' and ''divergent thinking'' in 1956. Activities Activities which promote divergent thinking include creating lists of questions, setting aside time for thinking and meditation, brainstorming, subject mapping, bubble mapping, keeping a journal, playing table ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Neuroticism
Neuroticism is a personality trait associated with negative emotions. It is one of the Big Five traits. Individuals with high scores on neuroticism are more likely than average to experience such feelings as anxiety, worry, fear, anger, shame, frustration, envy, jealousy, pessimism, guilt, depressed mood, and loneliness. Such people are thought to respond worse to stressors and are more likely to interpret ordinary situations, such as minor frustrations, as appearing hopelessly difficult. Their behavioral responses may include procrastination, substance use, and other maladaptive behaviors, which may temporarily aid in relieving negative emotions and in generating positive ones. People with high scores on the neuroticism index are thought to be at risk of developing common mental disorders ( mood disorders, anxiety disorders, and substance use disorders have been studied), and the sorts of symptoms once referred to as " neuroses". Individuals who score low in neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Extraversion
Extraversion and introversion are a central trait dimension in human personality theory. The terms were introduced into psychology by Carl Jung, though both the popular understanding and current psychological usage are not the same as Jung's original concept. Extraversion (also spelled ''extroversion'') is typically associated with sociability, talkativeness, and high energy, while introversion is linked to introspection, reserve, and a preference for solitary activities. Jung defined introversion as an "attitude-type characterised by orientation in life through subjective psychic contents", and extraversion as "an attitude-type characterised by concentration of interest on the external object". While often presented as opposite ends of a single continuum, many personality theorists, such as Carl Jung, have suggested that most individuals possesses elements of both traits, with one being more dominant. Jung provides a different perspective and suggests that everyone has bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Revised NEO Personality Inventory
The Revised NEO Personality Inventory (NEO PI-R) is a personality inventory that assesses an individual on five dimensions of personality. These are the same dimensions found in the Big Five personality traits. These traits are openness to experience, conscientiousness, extraversion (-introversion), agreeableness, and neuroticism. In addition, the NEO PI-R also reports on six subcategories of each Big Five personality trait (called facets). Historically, development of the Revised NEO PI-R began in 1978 when Paul Costa and Robert McCrae published a personality inventory. The researchers later published three updated versions of their personality inventory in 1985, 1992, and 2005. These were called the NEO PI (Neuroticism, Extraversion, Openness Personality Inventory), NEO PI-R (or Revised NEO PI), and NEO PI-3, respectively. The revised inventories feature updated vocabulary that could be understood by adults of any education level, as well as children. The inventories hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Paul Costa Jr
Paul Costa Jr. (born September 16, 1942) is an American psychologist associated with the Five Factor Model. He earned his Ph.D. from the University of Chicago in 1970. Author of over 300 academic articles, several books, he is perhaps best known for the Revised NEO Personality Inventory, or NEO PI-R, a psychological personality inventory; a 240-item measure of the Five Factor Model: Extraversion, Agreeableness, Conscientiousness, Neuroticism, and Openness to Experience Openness to experience is one of the domains which are used to describe personality psychology, human personality in the Big Five personality traits, Five Factor Model. Openness involves six Facet (psychology), facets, or dimensions: active imagina .... Additionally, the test measures six subordinate dimensions (known as 'facets') of each of the "FFM" personality factors, developed together with Robert McCrae. Work on this model has made Costa one of the most cited living psychologists,Thomson Reuters Researc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Hypnotic Susceptibility
Hypnotic susceptibility measures how easily a person can be hypnotized. Several types of scales are used; the most common are the Harvard Group Scale of Hypnotic Susceptibility (administered predominantly to large groups of people) and the Stanford Hypnotic Susceptibility Scales (administered to individuals). No scale can be seen as completely reliable due to the nature of hypnosis. It has been argued that no person can be hypnotized if they do not want to be; therefore, a person who scores very low may not want to be hypnotized, making the actual test score averages lower than they otherwise would be. Hypnotic depth scales Hypnotic susceptibility scales, which mainly developed in experimental settings, were preceded by more primitive scales, developed within clinical practice, which were intended to infer the "depth" or "level" of "hypnotic trance" on the basis of various subjective, behavioural or physiological changes. The Scottish surgeon James Braid (who introduced the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Typical Intellectual Engagement
Typical intellectual engagement (TIE) is a personality construct referring to a person's enjoyment (or dislike) of intellectually demanding activities. TIE was developed to identify aspects of personality most closely related to intelligence and knowledge and measures a person's ''typical performance'' in intellectual domains rather than their ''maximal performance'' (intellectual capacity measured by IQ tests). TIE is moderately positively associated with crystallized intelligence, and with general knowledge, and predicts academic performance. TIE is hard to distinguish from the earlier construct need for cognition and is positively correlated with openness to experience. Typical performance vs. maximal performance Goff and Ackerman proposed a distinction between ''typical'' and ''maximal'' performance on intellectual tasks. Traditional approaches to intelligence testing attempt to assess capacity or maximal performance and aim to minimise the impact of situational or envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Need For Cognition
The need for cognition (NFC), in psychology, is a personality variable reflecting the extent to which individuals are inclined towards effortful cognitive activities. Need for cognition has been variously defined as "a need to structure relevant situations in meaningful, integrated ways" and "a need to understand and make reasonable the experiential world". Higher NFC is associated with increased appreciation of debate, idea evaluation, and problem solving. Those with a high need for cognition may be inclined towards high elaboration. Those with a lower need for cognition may display the opposite tendencies, and may process information more heuristically, often through low elaboration. Need for cognition is closely related to the five factor model domain openness to experience, typical intellectual engagement, and epistemic curiosity (see below). History Cohen, Stotland and Wolfe (1955), in their work on individual differences in cognitive motivation, identified a "''need ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
General Knowledge
General knowledge is information that has been accumulated over time through various media and sources. It excludes specialized learning that can only be obtained with extensive training and information confined to a single medium. General knowledge is an essential component of crystallized intelligence. It is strongly associated with G factor (psychometrics), general intelligence and with openness to experience. Studies have found that people who are highly knowledgeable in a particular domain of knowledge, domain tend to be knowledgeable in many. General knowledge is thought to be supported by long-term semantic memory ability. General knowledge also supports Schema (psychology), schemata for textual understanding. Individual differences Intelligence High scorers on tests of general knowledge tend to also score highly on intelligence tests. IQ has been found to robustly predict general knowledge scores even after accounting for differences in age, and five factor model, five- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
American Psychological Association
The American Psychological Association (APA) is the main professional organization of psychologists in the United States, and the largest psychological association in the world. It has over 170,000 members, including scientists, educators, clinicians, consultants, and students. It has 54 divisions, which function as interest groups for different subspecialties of psychology or topical areas. The APA has an annual budget of nearly $135 million. Profile The APA has task forces that issue policy statements on various matters of social importance, including abortion, human rights, the welfare of detainees, human trafficking, the rights of the Mental disorder, mentally ill, IQ testing, sexual orientation change efforts, and gender equality. Governance APA is a corporation chartered in Washington, D.C. APA's bylaws describe structural components that serve as a system of checks and balances to ensure democratic process. The organizational entities include: * APA President. The APA pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Fluid Intelligence
The concepts of fluid intelligence (''g''f) and crystallized intelligence (''g''c) were introduced in 1943 by the psychologist Raymond Cattell. According to Cattell's psychometrically-based theory, general intelligence (''g'') is subdivided into ''g''f and ''g''c. Fluid intelligence is the ability to solve novel reasoning problems and is correlated with a number of important skills such as comprehension, problem-solving, and learning. Crystallized intelligence, on the other hand, involves the ability to deduce secondary relational abstractions by applying previously learned primary relational abstractions. History Fluid and crystallized intelligence are constructs originally conceptualized by Raymond Cattell. The concepts of fluid and crystallized intelligence were further developed by Cattell and his former student John L. Horn. Most of the intelligence testing had mainly been focused on children, and young adults. Cattell and Horn wanted to see how intelligence changed and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |