|
Online Content Analysis
Online content analysis or online textual analysis refers to a collection of research techniques used to describe and make inferences about online material through systematic coding and interpretation. Online content analysis is a form of content analysis for analysis of Internet-based communication. History and definition Content analysis as a systematic examination and interpretation of communication dates back to at least the 17th century. However, it was not until the rise of the newspaper in the early 20th century that the mass production of printed material created a demand for quantitative analysis of printed words. Berelson’s (1952) definition provides an underlying basis for textual analysis as a "research technique for the objective, systematic and quantitative description of the manifest content of communication." Content analysis consists of categorizing units of texts (i.e. sentences, quasi-sentences, paragraphs, documents, web pages, etc.) according to their subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Content Analysis
Content analysis is the study of documents and communication artifacts, known as texts e.g. photos, speeches or essays. Social scientists use content analysis to examine patterns in communication in a replicable and systematic manner. One of the key advantages of using content analysis to analyse social phenomena is their non-invasive nature, in contrast to simulating social experiences or collecting survey answers. Practices and philosophies of content analysis vary between academic disciplines. They all involve systematic reading or observation of texts or artifacts which are assigned labels (sometimes called codes) to indicate the presence of interesting, meaningful pieces of content. By systematically labeling the content of a set of texts, researchers can analyse patterns of content quantitatively using statistical methods, or use qualitative methods to analyse meanings of content within texts. Computers are increasingly used in content analysis to automate the labeling ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
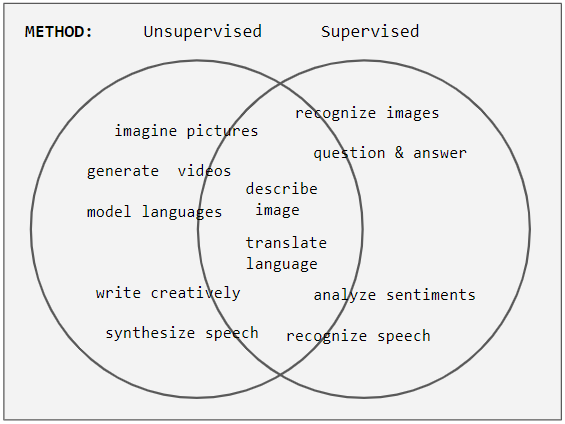
Supervised Learning
In machine learning, supervised learning (SL) is a paradigm where a Statistical model, model is trained using input objects (e.g. a vector of predictor variables) and desired output values (also known as a ''supervisory signal''), which are often human-made labels. The training process builds a function that maps new data to expected output values. An optimal scenario will allow for the algorithm to accurately determine output values for unseen instances. This requires the learning algorithm to Generalization (learning), generalize from the training data to unseen situations in a reasonable way (see inductive bias). This statistical quality of an algorithm is measured via a ''generalization error''. Steps to follow To solve a given problem of supervised learning, the following steps must be performed: # Determine the type of training samples. Before doing anything else, the user should decide what kind of data is to be used as a Training, validation, and test data sets, trainin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leah Findlater
Leah K. Findlater is a Canadian-American computer scientist specializing in human-computer interaction, mobile computing, and computer accessibility. She is an associate professor of computer science at the University of Washington. Education Findlater studied computer science at the University of Regina, graduating with high honors in 2001. She went to the University of British Columbia (UBC) for graduate study, becoming a participant there in Maria Klawe's project on aphasia. She earned a master's degree at UBC in 2004, with the thesis ''Comparing Static, Adaptable, and Adaptive Menus'', and completed her Ph.D. in 2009 with the dissertation ''Supporting Feature Awareness and Improving Performance with Personalized Graphical User Interfaces'', both under the supervision of Joanna McGrenere. Career After postdoctoral research at the University of Washington with Professor Jacob O. Wobbrock, Findlater joined the College of Information Studies faculty, UMIACS, and University of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precision And Recall
In pattern recognition, information retrieval, object detection and classification (machine learning), precision and recall are performance metrics that apply to data retrieved from a collection, corpus or sample space. Precision (also called positive predictive value) is the fraction of relevant instances among the retrieved instances. Written as a formula: \text = \frac Recall (also known as sensitivity) is the fraction of relevant instances that were retrieved. Written as a formula: \text = \frac Both precision and recall are therefore based on relevance. Consider a computer program for recognizing dogs (the relevant element) in a digital photograph. Upon processing a picture which contains ten cats and twelve dogs, the program identifies eight dogs. Of the eight elements identified as dogs, only five actually are dogs ( true positives), while the other three are cats ( false positives). Seven dogs were missed ( false negatives), and seven cats were correctly ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ad-hoc
''Ad hoc'' is a Latin phrase meaning literally for this. In English, it typically signifies a solution designed for a specific purpose, problem, or task rather than a generalized solution adaptable to collateral instances (compare with ''a priori''). Common examples include ad hoc committees and commissions created at the national or international level for a specific task, and the term is often used to describe arbitration (ad hoc arbitration). In other fields, the term could refer to a military unit created under special circumstances (see ''task force''), a handcrafted network protocol (e.g., ad hoc network), a temporary collaboration among geographically-linked franchise locations (of a given national brand) to issue advertising coupons, or a purpose-specific equation in mathematics or science. Ad hoc can also function as an adjective describing temporary, provisional, or improvised methods to deal with a particular problem, the tendency of which has given rise to the no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ex-ante
The term (sometimes written or ) is a New Latin phrase meaning "before the event". In economics, ''ex-ante'' or notional demand refers to the desire for goods and services that is not backed by the ability to pay for those goods and services. This is also termed as 'wants of people'. ''Ex-ante'' is used most commonly in the commercial world, where results of a particular action, or series of actions, are forecast (or intended). The opposite of ''ex-ante'' is '' ex-post'' (actual) (or ''ex post''). Buying a lottery ticket loses you money ''ex ante'' (in expectation), but if you win, it was the right decision ''ex post''. Examples Finance * In the financial world, the ''ex-ante return'' is the expected return of an investment portfolio. * In the recruitment industry, ''ex-ante'' is often used when forecasting resource requirements on large future projects. The ''ex-ante'' (and ''ex-post'') reasoning in economic topics was introduced mainly by Swedish economist Gunna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Validity
External validity is the validity of applying the conclusions of a scientific study outside the context of that study. In other words, it is the extent to which the results of a study can generalize or transport to other situations, people, stimuli, and times.Aronson, E., Wilson, T. D., Akert, R. M., & Fehr, B. (2007). Social psychology. (4 ed.). Toronto, ON: Pearson Education. Generalizability refers to the applicability of a predefined sample to a broader population while transportability refers to the applicability of one sample to another target population. In contrast, internal validity is the validity of conclusions drawn ''within'' the context of a particular study. Mathematical analysis of external validity concerns a determination of whether generalization across heterogeneous populations is feasible, and devising statistical and computational methods that produce valid generalizations. In establishing external validity, scholars tend to identify the "scope" of the study ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Validity
Internal validity is the extent to which a piece of evidence supports a claim about cause and effect, within the context of a particular study. It is one of the most important properties of scientific studies and is an important concept in reasoning about evidence more generally. Internal validity is determined by how well a study can rule out alternative explanations for its findings (usually, sources of systematic error or 'bias'). It contrasts with external validity, the extent to which results can justify conclusions about other contexts (that is, the extent to which results can be generalized). Both internal and external validity can be described using qualitative or quantitative forms of causal notation. Details Inferences are said to possess internal validity if a causal relationship between two variables is properly demonstrated.Shadish, W., Cook, T., and Campbell, D. (2002). Experimental and Quasi-Experimental Designs for Generilized Causal Inference Boston:Houghton M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
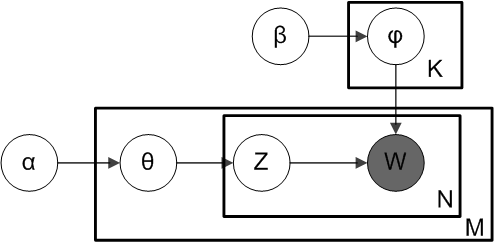
Latent Dirichlet Allocation
In natural language processing, latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) is a Bayesian network (and, therefore, a generative statistical model) for modeling automatically extracted topics in textual corpora. The LDA is an example of a Bayesian topic model. In this, observations (e.g., words) are collected into documents, and each word's presence is attributable to one of the document's topics. Each document will contain a small number of topics. History In the context of population genetics, LDA was proposed by J. K. Pritchard, M. Stephens and P. Donnelly in 2000. LDA was applied in machine learning by David Blei, Andrew Ng and Michael I. Jordan in 2003. Overview Population genetics In population genetics, the model is used to detect the presence of structured genetic variation in a group of individuals. The model assumes that alleles carried by individuals under study have origin in various extant or past populations. The model and various inference algorithms allow sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topic Model
In statistics and natural language processing, a topic model is a type of statistical model for discovering the abstract "topics" that occur in a collection of documents. Topic modeling is a frequently used text-mining tool for discovery of hidden semantic structures in a text body. Intuitively, given that a document is about a particular topic, one would expect particular words to appear in the document more or less frequently: "dog" and "bone" will appear more often in documents about dogs, "cat" and "meow" will appear in documents about cats, and "the" and "is" will appear approximately equally in both. A document typically concerns multiple topics in different proportions; thus, in a document that is 10% about cats and 90% about dogs, there would probably be about 9 times more dog words than cat words. The "topics" produced by topic modeling techniques are clusters of similar words. A topic model captures this intuition in a mathematical framework, which allows examining a set o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning is a framework in machine learning where, in contrast to supervised learning, algorithms learn patterns exclusively from unlabeled data. Other frameworks in the spectrum of supervisions include weak- or semi-supervision, where a small portion of the data is tagged, and self-supervision. Some researchers consider self-supervised learning a form of unsupervised learning. Conceptually, unsupervised learning divides into the aspects of data, training, algorithm, and downstream applications. Typically, the dataset is harvested cheaply "in the wild", such as massive text corpus obtained by web crawling, with only minor filtering (such as Common Crawl). This compares favorably to supervised learning, where the dataset (such as the ImageNet1000) is typically constructed manually, which is much more expensive. There were algorithms designed specifically for unsupervised learning, such as clustering algorithms like k-means, dimensionality reduction techniques l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Support Vector Machine
In machine learning, support vector machines (SVMs, also support vector networks) are supervised max-margin models with associated learning algorithms that analyze data for classification and regression analysis. Developed at AT&T Bell Laboratories, SVMs are one of the most studied models, being based on statistical learning frameworks of VC theory proposed by Vapnik (1982, 1995) and Chervonenkis (1974). In addition to performing linear classification, SVMs can efficiently perform non-linear classification using the ''kernel trick'', representing the data only through a set of pairwise similarity comparisons between the original data points using a kernel function, which transforms them into coordinates in a higher-dimensional feature space. Thus, SVMs use the kernel trick to implicitly map their inputs into high-dimensional feature spaces, where linear classification can be performed. Being max-margin models, SVMs are resilient to noisy data (e.g., misclassified examples). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |